Abstract
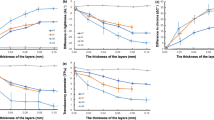
The objectives of this study were to evaluate the color difference depending on the surface topography of roughness and glazing, and to determine the effects of color measuring geometry and the standard illuminant on the color of a dental porcelain. Disk specimens of A3 shade were fired with commercial dental porcelain for PFM. Specimens were divided into non-polished (ST 1), polished with 200, 400, 1000, 1500-grit SiC papers (ST 2, 3, 4, 5) and glazed (ST 6) groups. After measuring the average surface roughness (Ra), color was determined under the illuminant A and D65 on a spectrophotometer with the specular component excluded (SCE) and included (SCI) geometry. Ra values were significantly influenced by the surface topography. With the SCE, the CIE L* value after glazing was significantly lower than that after polishing. Color differences (ΔE*) measured with the SCE were higher than those with the SCI (2.61–4.66 vs. 0.93–1.57). Therefore the SCE geometry seemed to more accurate protocol for the color measurement of dental porcelain.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
ASTM, in “ASTM E805-81, Standard Practice for Identification of Instrumental Methods of Color or Color-Difference Measurement of Materials” (ASTM, Philadelphia, 1981, reapproved in 1987).
CIE, in “CIE 15.2, Colorimetry-Technical Report”, 2nd edn. (CIE Central Bureau, Vienna, 1986, corrected reprint 1996).
A. Obregon, R. J. Goodkind, W. B. Schwabacher and B. Chem, J. Prosthet. Dent. 46 (1981) 330.
Y. K. Lee, B. S. Lim, C. W. Kim and J. M. Powers, J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 58 (2001) 613.
ISO/CIE, in “ISO/CIE 10527 (E), CIE Standard Colorimetric Observers” (ISO/CIE, Geneve, 1991).
W. J. O'Brien, Dent. Clin. North. Am. 29 (1985) 667.
R. R. Seghi, E. R. Hewlett and J. Kim, J. Dent. Res. 68 (1989) 1760.
B. K. Davis, W. M. Johnston and R. F. Saba, Int. J. Prosthodont. 7 (1994) 227.
G. R. Norman and D. L. Streiner, in “Biostatistics” (Mosby, St. Louis, 1994).
R. G. Craig and J. M. Powers, in “Restorative Dental Materials”, 11th edn. (Mosby, St. Louis, 2002) p. 233.
D. B. Judd and G. Wyszecki, in “Color in Business, Science and Industry” (John Wiley & Sons, New York, 1975).
G. Wyszecki and W. S. Stiles, in “Color Science; Concepts and Materials, Quantitative Data and Formulas” (John Wiley & Sons, New York, 1967).
W. M. Johnston and E. C. Kao, J. Dent. Res. 68 (1989) 819.
R. R. Seghi, W. M. Johnston and W. J. O'Brien, ibid. 68 (1989) 1755.
B. K. Davis, S. A. Aqulino, P. S. Lund, A. M. Diaz and G. E. Denehy, Int. J. Prosthodont. 5 (1992) 130.
A. U. Yap, C. W. Sau and K. W. Lye, J. Oral. Rehabil. 25 (1998) 456.
L. H. Klausner, C. B. Cartwright and G. T. Charbeneau, J. Prosthet. Dent. 47 (1982) 157.
W. D. Sulik and E. J. Plekavich, ibid. 46 (1981) 17.
M. S. Scurria and J. M. Powers, ibid. 71 (1994) 174.
C. J. W. Patterson, A. C. Mclundie, D. R. Stirrups and W. G. Taylor, ibid. 65 (1991) 383.
C. J. W. Patterson, A. C. Mclundie, D. R. Stirrups and W. G. Taylor, ibid. 68 (1992) 402.
R. L. Raimondo, J. T. Richardson and B. Wiedner, ibid. 64 (1990) 553.
A. V. Makarenko and I. A. Shaykevich, Color Res. Appl. 25 (2000) 170.
E. N. Dalal and K. M. Natale-Hoffman, ibid. 24 (1999) 369.
T. P. Van Der Burgt, J. J. Ten Bosch, P. C. Borsboom and W. J. Kortsmit, J. Prosthet. Dent. 63 (1990) 155.
P. Lemire and B. Burke, in “Color in Dentistry” (J.M. Ney Co, Bloomfield, 1975).
B. Bruke, in “Dental Porcelain. Color and Esthetics. The State of the Art 1977” (University of Southern California, Los Angels, 1977).
L. P. Balderamos and K. L. O'Keefe, Int. J. Prosthodont. 10 (1992) 111.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, IJ., Lee, YK., Lim, BS. et al. Effect of surface topography on the color of dental porcelain. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Medicine 14, 405–409 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1023206716774
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1023206716774