Abstract
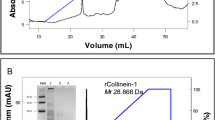
The mature gene of gloshedobin, a snake venom thrombin-like enzyme from the snake, Gloydius shedaoensis, was cloned and expressed in strain E. coli BL21(DE3). Having been induced by IPTG, the recombinant gloshedobin was in both soluble and insoluble forms. To avoid inclusion body formation, expression was optimized at 25 °C. Furthermore, a 50% increase in solubilization of the target protein was obtained by adding 0.1 mM Mg2+ to the medium. The purified recombinant gloshedobin gave a 44 kDa band on SDS-PAGE gel.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Forrer P, Jaussi R (1998) High–level expression of soluble heterogeneous proteins in the cytoplasm of Escherichia coli by fusion to the bacteriophage lambda head protein D. Gene 224: 45–52.
Georgiou G, Valax P (1996) Expression of correctly folded proteins in Escherichia coli. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 7: 190–197.
Koh YS, Chung KH, Kim DS (2001) Biochemical characterization of a thrombin–like enzyme and a fibrinolytic serine protease from snake (Agkistrodon saxatilis) venom. Toxicon 39: 555–560.
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of the bacteriophage T4. Nature 227: 680–685.
Li ZY, Liu CP, Zhu LQ, Jing GZ, Zhou JM (2001) The chaperone activity of trigger factor is distinct from its isomerase activity during co–expression with adenylate kinase in Escherichia coli. FEBS Lett. 506: 108–112.
Matsui T, Fujimura Y, Titani K (2000) Snake venom proteases affecting hemostasis and thrombosis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1477: 146–156.
Pirkle H (1998) Thrombin–like enzymes from snake venoms: an updated inventory. Thromb. Haem. 79: 675–683.
Stewart EJ, Åslund F, Beckwith J (1998) Disulfide bond formation in the Escherichia coli cytoplasm: an in vivo role reversal for the thioredoxins. EMBO J. 17: 5543–5550.
Swartz JR (2001) Advances in Escherichia coli production of therapeutic proteins. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 12: 195–201.
Yang Q, Xu XM, Li M, Yuan XD, Su ZG, Janson JC, An LJ (2002) Cloning and expression of gloshedobin cDNA from the venom of Gloydius shedaoensis. Biotechnol. Lett. 24: 135–138.
Yon JM (1996) The specificity of protein aggregation. Nat. Biotechnol. 14: 1231.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, Q., Xu, J., Li, M. et al. High-level expression of a soluble snake venom enzyme, gloshedobin, in E. coli in the presence of metal ions. Biotechnology Letters 25, 607–610 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1023067626846
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1023067626846