Abstract
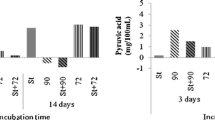
The bacteriocin, lacticin 3147, increased isoleucine transamination by Lactococcus lactis IFPL359 in a cheese model system. The formation of α-keto-β-methyl-n-valeric acid and 2-hydroxy-3-methyl-valeric acid increased by three times in cheese slurries at 12 °C and cheese aroma intensity increased as well, which corresponded with a higher 2-methylbutanal formation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amárita F, Fernández–Esplá D, Requena T, Peláez C (2001) Conversion of methionine to methional by Lactococcus lactis. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 204: 1–7.
Amárita F, Martínez–Cuesta MC, Taborda G, Soto–Yárritu P, Requena T, Peláez C (2002) Formation of methional by Lactococcus lactis IFPL730 under cheese model conditions. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 214: 58–62.
Casla D, Requena T, Gómez R (1996) Antimicrobial activity of lactic acid bacteria isolated from goat's milk and artisanal cheeses: characteristics of a bacteriocin produced by Lactobacillus curvatus IFPL105. J. Appl. Bacteriol. 81: 35–41.
Klein N, Maillard MB, Thierry A, Lortal S (2001) Conversion of amino acids into aroma compounds by cell–free extracts of Lactobacillus helveticus. J. Appl. Microbiol. 91: 404–411.
Kuchroo CN, Fox PF (1982) Soluble nitrogen in Cheddar cheese. Comparison of extraction procedures. Milchwissenschaft 37: 331–335.
Kuntz DA, Chen JL, Pan G (1998) Accumulation of α–ketoacids as essential components in cyanide assimilation by Pseudomonas fluorescens. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 64: 4452–4459.
Martínez–Cuesta MC, Fernández de Palencia P, Requena T, Peláez C (1998) Enhancement of proteolysis by a Lactococcus lactis bacteriocin producer in a cheese model system. J. Agric. Food Chem. 46: 3863–3867.
Martínez–Cuesta MC, Kok J, Herranz E, Peláez C, Requena T, Buist G (2000) Requirement of autolytic activity for bacteriocin induced lysis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 66: 3174–3179.
Martínez–Cuesta MC, Peláez C, Juárez M, Requena T (1997) Autolysis of Lactococcus lactis ssp. lactis and Lactobacillus casei ssp. casei. Cell lysis induced by a crude bacteriocin. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 38: 125–131.
Martínez–Cuesta MC, Requena T, Peláez C (2001) Use of a bacteriocin–producing transconjugant as starter in acceleration of cheese ripening. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 70: 79–88.
Martínez–Cuesta MC, Requena T, Peláez C (2002) Effect of bacteriocin–induced cell damage on the branched–chain amino acid transamination by Lactococcus lactis. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 217: 109–113.
Morgan S, Ross RP, Hill C (1997) Increasing starter cell lysis in Cheddar cheese using a bacteriocin–producing adjunct. J. Dairy Sci. 80: 1–10.
Nierop Groot MN, de Bont JAM (1998) Conversion of phenylalanine to benzaldehyde initiated by an aminotransferase in Lactobacillus plantarum. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 64: 3009–3013.
Oumer A, Garde S, Medina M, Nññez M (1999) Defined starter system including a bacteriocin producer for the enhancement of cheese flavour. Biotechnol. Tech. 13: 267–270.
Schmidt RH, Davidson SM, Lowry SP (1983) Determination of acetaldehyde in Streptococcus lactis cultures as 2,4–dinitrophenylhydrazone by high–performance liquid chromatography. J. Agric. Food Chem. 31: 978–980.
Smit G, Braber AM, van Spronsen W, van den Berg G (1995) Cheasy model: a cheese–based model to study cheese ripening. Bioflavour 95: 185–190.
Yvon N, Rijnen M (2001) Cheese flavour formation by amino acid catabolism. Int. Dairy J. 11: 185–201.
Yvon M, Chambellon M, Bolotin A, Roudot–Algaron (2000) Characterization and role of the branched–chain aminotransferase (BcaT) isolated from Lactococcus lactis subsp. cremoris NCDO 763. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 66: 571–577.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Martínez-Cuesta, C., Peláez, C. & Requena, T. Lacticin 3147 favours isoleucine transamination by Lactococcus lactis IFPL359 in a cheese-model system. Biotechnology Letters 25, 599–602 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1023003306373
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1023003306373