Abstract
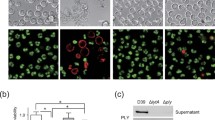
Stachylysin is a proteinaceous hemolytic agent that is produced by Stachybotrys chartarum. Stachylysin was found, using immunohistochemical and immunocytochemical methods, to be localized in S. chartarum spores/mycelia primarily in the inner wall suggesting that it is constitutively produced. Spores instilled in mouse or rat lung tissues resulted in granuloma formation, which showed the highest stachylysin concentration in the inner wall of the spore and near the spore, with less at distance indicating that it had diffused out from the spore. The in vitro high stachylysin producing strain (58-06) was also highest in vivo, based on immunohistochemistical staining. More stachylysin was observed in the mouse lung tissue at 72 h than at 24 h indicating that production/release is a relatively slow process. The localization of stachylysin in macrophage phagolysosomes suggests that these cells may be involved with hemolysin inactivation. This would be consistent with what is known about asp-hemolysin produced by Aspergillus fumigatus.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bhakdi S, Bayley H, Valeva I, Walev A,Walker B, Weller U, Kehoe M, Palmer M. Staphylococcal alpha-toxin, streptolysin-O, and Escherichia coli hemolysin prototypes of pore-forming bacterial cytolysins. Arch. Microbiol. 1996; 165: 73–79.
Bhakdi S, Tranum-Jensen J. Alpha-toxin of Staphylococcus aureus. Microbiol. Rev. 1991; 55: 733–751.
Bozzola JJ, Russell LD. Electron Microscopy. Boston: Jones and Bartlett Publishers, 1992.
Cavalieri SJ, Bohach GA, Snyder IS. Escherichia coli a-hemolysin characteristics and probable role in pathogenicity. Microbiol Rev 1984; 48: 326–343.
CCAC. Guide to the care and use of experimental animals. Volume 1. Ottawa: Bradda Printing Services Inc., Ottawa, 1993.
Davies P. Quantitative morphology of the lung. A practical Manual. Harvard Medical School Publication, 1980.
Dearborn DG, Yike I, Sorenson WG, Miller MJ, Etzel RA. Overview of investigations into pulmonary hemorrhage among infants in Cleveland, Ohio. Environ Health Persp 1999; 107: 495–499.
Deacon JW. Introduction to Modern Mycology. Boston: Blackwell Scientific Publications, 1984.
Ebina K, Yokota K, Sakaguchi O. Studies on the toxin of Aspergillus fumigatus. XIV. Relationship between Asp-hemolysin and experimental infection of mice. Jpn J Med Mycol 1982; 23: 246–252.
Ebina K, Yokota K, Sakaguchi O. Studies on the toxin of Aspergillus fumigatus. XVI. Biological properties of Asp-hemolysin as a parasitic factor. Jpn J Med Mycol 1983; 24: 245–252.
Ebina K, Sakagami H, Yokota K, Kondo H. Cloning and nucleotide sequence of cDNA encoding Asp-hemolysin from Aspergillus fumigatus. Biochimia et Biophysica Acta. 1994; 1219: 148–150.
Elidemir O, Colasurdo GN, Rossmann SN, Fan LL. Isolation of Stachybotrys from the lung of a child with Pulmonary Hemosiderosis. Pediatrics 1999; 102: 964–966.
Etzel RA, Montana E, Sorenson WG, Kullman GJ, Allan TM, Dearborn, DG. Acute pulmonary hemorrhage in infants associated with exposure to Stachybotrys atra and other fungi. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med 1998; 152: 757–762.
Flappan SM, Portnoy J, Jones P, Barnes C. Infant pulmonary hemorrhage in a suburban home with water damage and mold (Stachybotrys atra). Envir Health Persp 1999; 107: 927-930.
Forgacs J. Stachybotryotoxicosis. In Kadis S, Ciegler A, Ajl SJ, eds. Microbial Toxins, Vol. VIII. New York, NY: Academic Press, Inc., 1972; 95–128.
Gibson RL, Nizet V, Rubens CE. Group B streptococcal ?-hemolysin promotes injury of lung microvascular endothelial cells. Ped Res 1999; 45: 626–634.
Happerfield LC. Assessment of oestrogen and progesterone receptor antibodies in formalin-fixed routinely processed paraffin-wax embedded tissue. J Cell Path 1996; 1: 170–178.
Hintikka E.-L. Human stachybotrytoxicosis. In Willie TD, Morehouse LG, eds. Mycotoxic Fungi, Mycotoxins, Mycotoxicoses, An Encyclopedic Handbook. Vol 3, New York: Marcel Dekker, Inc. 1978; 87–89.
Humason GL. Animal Tissue Techniques. San Francisco: W.H. Freeman and Co., 1976.
Jarvis BB, Sorenson WG, Hintikka E.-L, Nikulin M, Zhou Z, Jiang J, Wang S, Hinkley S, Etzel RA, Dearborn DG. Study of toxin production by isolates of Stachybotrys atra and Memnoniella echinata isolated during a study of pulmonary hemosiderosis in infants. Appl Environ Microbiol 1998; 64: 3620–3625.
Johnson P, Lindberg M, Haraldsson I, Waldstrom T. Virulence of Staphylococcus aureus in a mouse mastitis model: studies of alpha hemolysin, coagulase and protein A as possible virulence determinants with protoplast fusion and gene cloning. Infect Immun 1985; 49: 765–769.
MaCrae KC, Rand TG, Shaw RA, Mason C, Oulton MR, Hastings C, Cherlet T, Thliveris JA, Mantsch HH, MacDonald J, Scott JE. Analysis of pulmonary surfactant by Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy following exposure to Stachybotrys chartarum (atra) spores. Chemistry and Physics of Lipids 2001; 110: 1–10.
Manns JM, Mosser DM, Buckley HR. Production of a hemolytic factor by Candida albicans. Infect Immun 1994; 62: 5154–5156.
Mason CD, Rand TG, Oulton M, MacDonald JM, Scott JE. Effects of Stachybotrys chartarum (atra) Conidia and Isolated Toxin on Lung Surfactant Production and Homeostasis. Natural Toxins 1998; 6: 27–33.
Mason CD, Rand TG, Oulton M, MacDonald J. The effect of Stachybotrys chartarum spores and an isolated trichothecene, isosatratoxin F, on convertase activity in mice. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology 2001; 172: 21–28.
McDowell EM, Trump BF. Histological fixatives suitable for diagnostic light and electron microscopy. Arch Pathol Lab Med 1976; 100: 405–414.
Nikulin M, Reijula K, Jarvis BB, Hintikka E.-L. Experimental lung mycotoxicosis in mice induced by Stachybotrys atra. Int J Exp Path 1996; 77: 213–218.
Nikulin M, Reijula K, Jarvis B, Veijalainen P, Hintikka E-L. Effects of intranasal exposure to Stachybotrys atra. Fundam Appl Toxicol 1997; 35: 182–188.
Nizet V, Gibson RL, Chi EY, Framson PE, Hulse M, Rubens CE. Group B streptococcal beta-hemolysin expression is associated with injury of lung epithelial cells. Infect Immun 1996; 64: 3818–3826.
Nomura T, Fujii Y, Okamota K. Secretion of hemolysin of Aeromonas sobria as protoxin and contribution of the propeptide region removed from the protoxin to the proteolytic stability of the toxin. Microbiol Immunol 1999; 43: 29–38.
Ou Said A M, Contrepois MG, Vartanian MD, Girardeau J. Virulence factors and markers in Escherichia coli from calves with bacteremia. Am J Vet Res 1988; 49: 1657–1660.
Rand TG, Mahoney M, White K, Oulton M. Microanatomical changes associated with alveolar type II cells in juvenile mice exposed to Stachybotrys chartarum and isolated toxin. Toxicological Sciences. 2002; in press.
Rao CY, Burge HA, Brain JD. The time course of responses to intratracheally instilled toxic Stachybotrys chartarum spores in rats. Mycopathologia 2000; 149: 27–34.
Sakaguchi O, Yokota K. Studies on the toxin of Aspergillus fumigatus III. Fraction causing dermonecrosis and hemorrhage-like changes. Japan J Bacteriol 1972; 27: 649–655.
Sakaguchi O, Shimada H, Yokota K. Purification and characteristics of hemolytic toxin from Aspergillus fumigatus. Japan J Med Sci Biol 1975; 28: 328–331.
Seeger W, Obernitz R, Thomas M, Walmrath D, Suttorn N, Holland IB, Grimminger F, Eberspacher B, Hugo F, Bhakdi S. Lung vascular injury after administration of viable hemolysin-forming Escherichia coli in isolated rabbit lungs. Am Rev Resp Dis 1991; 143: 797–785.
Sorenson WG, Lewis DM. Organic dust toxic syndrome. In Esser K, Lempke PA, eds. The Mycota, Vol. VII. Animal and Human Relationships. Springer Verlag, Berlin. 1996; 159–172.
Sumarah MW, Rand TG, Mason CD, Oulton M, MacDonald J, Anthes M. Effects of Stachybotrys chartarum spores and toxin on mouse lung surfactant phospholipid vomposition. In: Johanning E, ed. Bioaerosols, Fungi and Mycotoxins: Health Effects, Assessment, Prevention and Control. Eastern New York Occupational and Environmental Health Center, Albany, New York, 1999; 444–452.
Vesper SJ, Dearborn DG, Yike I, Sorenson WG, Haugland RA. Hemolysis, toxicity and randomly amplified polymorphic DNA analysis of Stachybotrys chartarum strains. Applied and Environ. Microbiology 1999; 65(7): 3175–3181.
Vesper SJ, Dearborn DG, Elidemir O, Haugland RA. Quantification of siderophore and hemolysin from Stachybotrys chartarum strains including a strain isolated from the lung of a child with pulmonary hemorrhage and haemosiderosis. Applied and Environ Microbiology. 2000; 66(6): 2678–2681.
Vesper SJ, Magnuson DG, Dearborn G, Yike I, Haugland RA. Initial characterization of the hemolysin stachylysin from Stachybotrys chartarum. Infect. Immun. 2001; 69: 912–916.
Yike I, Allan T, Sorenson WG, Dearborn DG. Highly sensitive protein translation assay for trichothecene toxicity in airborne particulates. Comparison with cytotoxicity assays. Appl Environ Microbiol 1999; 65: 88–94.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gregory, L., Rand, T., Dearborn, D. et al. Immunocytochemical localization of stachylysin in Stachybotrys chartarum . Mycopathologia 156, 109–117 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022968121285
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022968121285