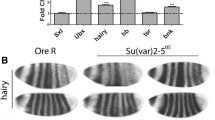
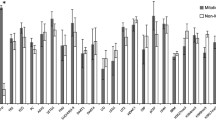
Abstract
We have used the highly conserved heterochromatin component, heterochromatin protein 1 (HP1), as a molecular tag for purifying other protein components of Drosophila heterochromatin. A complex of HP1 associated with the origin recognition complex (ORC) and an HP1/ORC-associated protein (HOAP) was purified from the maternally loaded cytoplasm of early Drosophila embryo. We propose that the DNA-binding activities of ORC and HOAP function to recruit underphosphorylated isoforms of HP1 to sites of heterochromatin nucleation. The roles of highly phosphorylated HP1, other DNA-binding proteins known to interact with HP1, and histone modifying activities in heterochromatin assembly are also addressed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aagaard, L., G. Laible, P. Selenko, M. Schmid, R. Dorn, G. Schotta, S. Kuhfittig, A. Wolf, A. Lebersorger, P.B. Singh, G. Reuter & T. Jenuwein, 1999. Functional mammalian homologues of the Drosophila PEV-modifier Su(var)3-9 encode centromereassociated proteins which complex with the heterochromatin component M31. EMBO J. 18: 1923-1938.
Aasland, R. & A.F. Stewart, 1995. The chromo shadow domain, a second chromo domain in heterochromatin-binding protein 1, HP1. Nucleic Acids Res. 23: 3168-3174.
Abraham, J., J. Feldman, K.A. Nasmyth, J.N. Strathern, A.J. Klar, J.R. Broach & J.B. Hicks, 1983. Sites required for position-effect regulation of mating-type information in yeast. Cold Spring Harbour, Symp. Quant. Biol. 47: 989–998.
Austin, R.J., T.L. Orr-Weaver & S.P. Bell, 1999. Drosophila ORC specifically binds to ACE3, an origin of DNA replication control element. Gene. Dev. 13: 2639-2649.
Bannister, A.J., P. Zegerman, J.F. Partridge, E.A. Miska, J.O. Thomas, R.C. Allshire & T. Kouzarides, 2001. Selective recognition of methylated lysine 9 on histone H3 by the HP1 chromo domain. Nature 410: 120–124.
Bell, S.P., R. Kobayashi & B. Stillman, 1993. Yeast origin recognition complex functions in transcription silencing and DNA replication. Science 262: 1844-1849.
Bell, S.P. & B. Stillman, 1992. ATP-dependent recognition of eucaryotic origins of DNA replication by a multiprotein complex. Nature 357: 128–134.
Brasher, S.V., B.O. Smith, R.H. Rasmus, D. Nietlispach, A. Thiru, P.R. Nielsen, R.W. Broadhurst, L.J. Ball, N.V. Murzina & E.D. Laue, 2000. The structure of mouse HP1 suggests a unique mode of single peptide recognition by the shadow chromo domain dimer. EMBO J. 19: 1587-1597.
Chien, C.T., S. Buck, R. Sternglanz & D. Shore, 1993. Targeting of SIR1 protein establishes transcriptional silencing at HM loci and telomeres in yeast. Cell 75: 531–541.
Eissenberg, J.C., C.J. Tharappel, D.M. Foster-Hartnett, T. Hartnett, V. Ngan & S.C.R. Elgin, 1990. Mutation in a heterochromatinspecific chromosomal protein is associated with suppression of position-effect variegation in Drosophila melanogaster. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 87: 9923-9927.
Eissenberg, J.C., Y.W. Guo & T. Hartnett, 1994. Increased phosphorylation of HP1, a heterochromatin-associated protein of Drosophila, is correlated with heterochromatin assembly. J. Biol. Chem. 269: 21315–21321.
Eissenberg, J.C. & S.C.R. Elgin, 2000. The HP1 protein family: getting a grip on chromatin. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 10: 04–210.
Farkas, G., J. Gausz, M. Galloni, G. Reuter, H. Gyurkovics & F. Karch, 1994. The Trithorax-like gene encodes the Drosophila GAGA factor. Nature 371: 806–808.
Firestein, R., C. Xiangmin, P. Huie & M.L. Cleary, 2000. Set domain-dependent regulation of transcriptional silencing and growth control by SUV39H1, a mammalian ortholog of Drosophila Su(var)3-9. Mol. Cell. Biol. 20: 4900-4909.
Gall, J.G. & D.D. Atherton, 1974. Satellite DNA sequences in Drosophila virilis. J. Mol. Biol. 85: 633–664.
Grigliatti, T., 1991. Position effect variegation - an assay for nonhistone chromosomal proteins and chromatin assembly and modifying factors. Method. Cell Biol. 35: 587–627.
Hecht, A., T. Laroche, S. Strahl-Bolsinger, S.M. Gasser & M. Grunstein, 1995. Histone H3 and H4 N-termini interact with SIR3 and SIR4 proteins: a molecular model for the formation of heterochromatin in yeast. Cell 80: 583–592.
Hecht, A., S. Strahl-Bolsinger & M. Grunstein, 1996. Spreading of transcriptional repressor SIR3 from telomeric heterochromatin. Nature 383: 92–95.
Heitz, E., 1928. Das Heterochromatin der Moose. I Jahrb. Wissensch. Bot. 69: 762–818.
Huang, D.W., L. Fanti, D.T.S. Pak, M.R. Botchan, S. Pimpinelli & R. Kellum, 1998. Distinct cytoplasmic and nuclear fractions of Drosophila heterochromatin protein 1: their phosphorylation levels and associations with origin recognition complex proteins. J. Cell Biol. 142: 307–318.
Ivanova, A.V., M.J. Bonaduce, S.V. Ivanov & A.J.S. Klar, 1998. The chromo and SET domains of the Clr4 protein are essential for silencing in fission yeast. Nat. Genet. 19: 192–195.
Jacobs, S.A., S.D. Taverna, Y. Zhang, S.D. Briggs, J. Li, J.C. Eissenberg, C.D. Allis & S. Khorasanizadeh, 2001. Specificity of the HP1 chromo domain for the methylated N-terminus of histone H3. EMBO J. 20: 5232-5241.
James, T.C. & S.C.R. Elgin, 1986. Identification of a nonhistone chromosomal protein associated with heterochromatin in Drosophila melanogaster and its gene. Mol. Cell. Biol. 6: 3862-3872.
Lachner, M., D. O'Carroll, S. Rea, K. Mechtler & T. Jenuwein, 2001. Methylation of histone H3 lysine 9 creates a binding site for HP1 proteins. Nature 410: 116–120.
Lima de Faria, A. & H. Jaworska, 1968. Late DNA synthesis in heterochromatin. Nature 217: 138–142.
Locke, J., M.A. Kotarski & K.D. Tartof, 1988. Dosage-dependent modifiers of position effect variegation in Drosophila and a mass action model that explains their effect. Genetics 120: 181–198.
Lohe, A.R. & P.A. Roberts, 1988. Evolution of satellite DNA sequences in Drosophila, pp. 148–186 in Heterochromatin: Molecular and Structural Aspects, edited by R.S. Verma. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom.
Lohe, A.R., A.J. Hilliker & P.A. Roberts, 1993. Mapping simple repeated DNA sequences in heterochromatin of Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics 134: 1149-1174.
Miklos, G.L.G. & J.N. Cotsell, 1990. Chromosome structure at interfaces between major chromatin types: alpha-and betaheterochromatin. BioEssays 12: 1–6.
Miller, A.M. & K.A. Nasmyth, 1984. Role of DNA replication in the repression of silent mating type loci in yeast. Nature 312: 247–251.
Moazed, D., 2001. Common themes in mechanisms of gene silencing. Mol. Cell. 8: 489–498.
Moretti, P.K., K. Freeman, L. Coodly & D. Shore, 1994. Evidence that a complex of SIR proteins interacts with the silencer and telomere-binding protein RAP1. Gene. Dev. 8: 2257-2269.
Muller, H.J., 1930. Types of visible variations induced by X-rays in Drosophila. J. Genet. 22: 299–334.
Nakayama, J.-I., J.C. Rice, B.D. Strahl, C.D. Allis & S.I.S. Grewal, 2001. Role of histone H3 lysine 9 methylation in epigenetic control of heterochromatin assembly. Science 292: 110–113.
Nielsen, S.J., R. Schneider, U.-M. Bauer, A.J. Bannister, A. Morrison, D. O'Carroll, R. Firestein, M. Cleary, T. Jenuwein, R.E. Herrera & T. Kouzarides, 2001. Rb targets histone H3 methylation and HP1 to promoters. Nature 412: 561–565.
Pak, D.T.S., M. Pflumm, I. Chesnokov, D.W. Huang, R. Kellum, J. Marr, P. Romanowski & M. Botchan, 1997. Association of the origin recognition complex with heterochromatin and HP1 in higher eukaryotes. Cell 91: 311–323.
Raff, J.W., R. Kellum & B. Alberts, 1994. The Drosophila GAGA transcription factor is associated with specific regions of heterochromatin throughout the cell cycle. EMBO J. 13: 5977-5983.
Schmid, K.J. & D. Tautz, 1997. A screen for fast evolving genes from Drosophila. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95: 9746-9750.
Shareef, M.M., C. King, M. Damaj, R. Badagu, D.W. Huang & R. Kellum, 2001. Drosophila heterochromatin protein 1 (HP1)/origin recognition complex (ORC) protein is associated with HP1 and ORC and functions in heterochromatin-induced silencing. Mol. Biol. Cell 12: 1671-1685.
Smothers, J.F. & S. Henikoff, 2000. The HP1 chromo shadow domain binds a consensus peptide pentamer. Curr. Biol. 10: 27–30.
Stone, E.M. & L. Pillus, 1996. Activation of an MAP kinase cascade leads to Sir3p hyperphosphorylation and strengthens transcriptional silencing. J. Cell Biol. 135: 571–583.
Tsukiyama, T., P.B. Becker & C. Wu, 1994. ATP-dependent nucleosome disruption at a heat-shock promoter mediated by binding of GAGA transcription factor. Nature 367: 525–532.
Turner, B.M. & A.J. Birley, 1992. Histone H4 isoforms acetylated at specific lysine residues define individual chromosomes and chromatin domains in Drosophila polytene nuclei. Cell 69: 375–384.
Wustmann, G., J. Szidonya, H. Taubert & G. Reuter, 1989. The genetics of position-effect variegation modifying loci in Drosophila melanogaster. Mol. Gen. Genet. 217: 520–527.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shareef, M.M., Badugu, R. & Kellum, R. HP1/ORC Complex and Heterochromatin Assembly. Genetica 117, 127–134 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022963223220
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022963223220