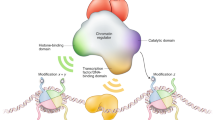
Abstract
The repression of gene activity and the maintenance of the repressed state are fundamental requirements of cell differentiation, ordered embryonic development and tissue integrity. Furthermore, large regions of the genome such as centromeres and telomeres have a structural function and have to be kept transcriptionally inactive to be functional. In both cases the transcriptional silencing is accomplished through a dense packaging of the corresponding DNA into heterochromatin or heterochromatin-like structures. In this minireview we summarise recent findings, which point towards a major function of posttranslational histone modifications in the process of establishment and maintenance of condensed heterochromatin. The physical association of two enzymatic activities, histone methylation and histone deacetylation, which are thought to be involved in transcriptional silencing, provide the framework of a molecular model of how heterochromatin is initiated and maintained during cell division and differentiation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aagaard, L., G. Laible, P. Selenko, M. Schmid, R. Dorn, G. Schotta, S. Kuhfittig, A. Wolf, A. Lebersorger, P.B. Singh, G. Reuter & T. Jenuwein, 1999. Functional mammalian homologues of the Drosophila PEV-modifier Su(var)3-9 encode centromere-associated proteins which complex with the heterochromatin component M31. Embo J. 18: 1923-1938.
Bannister, A.J., P. Zegerman, J.F. Partridge, E.A. Miska, J.O. Thomas, R.C. Allshire & T. Kouzarides, 2001. Selective recognition of methylated lysine 9 on histone H3 by the HP1 chromo domain. Nature 410: 120–124.
Belyaeva, E.S., O.V. Demakova, G.H. Umbetova & I.F. Zhimulev, 1993. Cytogenetic and molecular aspects of position-effect variegation in Drosophila melanogaster. V. Heterochromatinassociated protein HP1 appears in euchromatic chromosomal regions that are inactivated as a result of position-effect variegation. Chromosoma 102: 583–590.
Brehm, A. & T. Kouzarides, 1999. Retinoblastoma protein meets chromatin. Trends Biochem. Sci. 24: 142–145.
Brehm, A., E.A. Miska, D.J. McCance, J.L. Reid, A.J. Bannister & T. Kouzarides, 1998. Retinoblastoma protein recruits histone deacetylase to repress transcription. Nature 391: 597–601.
Chestier, A. & M. Yaniv, 1979. Rapid turnover of acetyl groups in the four core histones of simian virus 40 minichromosomes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 76: 46–50.
Covault, J. & R. Chalkley, 1980. The identification of distinct populations of acetylated histone. J. Biol. Chem. 255: 9110-9116.
Czermin, B., G. Schotta, B.B. Hulsmann, A. Brehm, P.B. Becker, G. Reuter & A. Imhof, 2001. Physical and functional association of SU(VAR)3-9 and HDAC1 in Drosophila. EMBORep. 2: 915–919.
Ekwall, K., T. Olsson, B.M. Turner, G. Cranston & R.C. Allshire, 1997. Transient inhibition of histone deacetylation alters the structural and functional imprint at fission yeast centromeres. Cell 91: 1021-1032.
Festenstein, R., M. Tolaini, P. Corbella, C. Mamalaki, J. Parrington, M. Fox, A. Miliou, M. Jones & D. Kioussis, 1996. Locus control region function and heterochromatin-induced position effect variegation. Science 271: 1123-1125.
Hassig, C.A. & S.L. Schreiber, 1997. Nuclear histone acetylases and deacetylases and transcriptional regulation: HATs off to HDACs. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 1: 300–308.
Hebbes, T.R., A.W. Thorne & C. Crane-Robinson, 1988. A direct link between core histone acetylation and transcriptionally active chromatin. Embo J. 7: 1395-1402.
Heitz, E., 1928. Das Heterochromatin der Moose. Jb.Wiss. Bot. 69: 728–730.
Hwang, K.K., J.C. Eissenberg & H.J. Worman, 2001. Transcriptional repression of euchromatic genes by Drosophila heterochromatin protein 1 and histone modifiers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 98: 11423-11427.
Imhof, A. & P.B. Becker, 2001. Modifications of the histone N-terminal domains. Evidence for an “epigenetic code”. Mol. Biotechnol. 17: 1–13.
Ivanova, A.V., M.J. Bonaduce, S.V. Ivanov & A.J. Klar, 1998. The chromo and SET domains of the Clr4 protein are essential for silencing in fission yeast. Nat. Genet. 19: 192–195.
Jacobs, S.A., S.D. Taverna, Y. Zhang, S.D. Briggs, J. Li, J.C. Eissenberg, C.D. Allis & S. Khorasanizadeh, 2001. Specificity of the HP1 chromo domain for the methylated N-terminus of histone H3. Embo J. 20: 5232-5241.
James, T.C., J.C. Eissenberg, C. Craig, V. Dietrich, A. Hobson & S.C. Elgin, 1989. Distribution patterns of HP1, a heterochromatin-associated nonhistone chromosomal protein of Drosophila. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 50: 170–180.
Jenuwein, T. & C.D. Allis, 2001. Translating the histone code. Science 293: 1074-1080.
Kuo, M.H., J.E. Brownell, R.E. Sobel, T.A. Ranalli, R.G. Cook, D.G. Edmondson, S.Y. Roth & C.D. Allis, 1996. Transcriptionlinked acetylation by Gcn5p of histones H3 and H4 at specific lysines. Nature 383: 269–272.
Lachner, M., D. O'Carroll, S. Rea, K. Mechtler & T. Jenuwein, 2001. Methylation of histone H3 lysine 9 creates a binding site for HP1 proteins. Nature 410: 116–120.
Litt, M.D., M. Simpson, M. Gaszner, C.D. Allis & G. Felsenfeld, 2001. Correlation between histone lysine methylation and developmental changes at the chicken beta-globin locus. Science 293: 2453-2455.
Milot, E., J. Strouboulis, T. Trimborn, M. Wijgerde, E. de Boer, A. Langeveld, K. Tan-Un, W. Vergeer, N. Yannoutsos, F. Grosveld & P. Fraser, 1996. Heterochromatin effects on the frequency and duration of LCR-mediated gene transcription. Cell. 87: 105–114.
Moore, G.D., J.D. Procunier, D.P. Cross & T.A. Grigliatti, 1979. Histone gene deficiencies and position-effect variegation in Drosophila. Nature 282: 312–314.
Mottus, R., R. Reeves & T.A. Grigliatti, 1980. Butyrate suppression of position-effect variegation in Drosophila melanogaster. Mol. Gen. Genet. 178: 465–469.
Mottus, R., R.E. Sobel & T.A. Grigliatti, 2000. Mutational analysis of a histone deacetylase in Drosophila melanogaster: missense mutations suppress gene silencing associated with position effect variegation. Genetics 154: 657–668.
Nakayama, J., J.C. Rice, B.D. Strahl, C.D. Allis & S.I. Grewal, 2001. Role of histone H3 lysine 9 methylation in epigenetic control of heterochromatin assembly. Science 292: 110–113.
Nielsen, S.J., R. Schneider, U.M. Bauer, A.J. Bannister, A. Morrison, D. O'Carroll, R. Firestein, M. Cleary, T. Jenuwein, R.E. Herrera & T. Kouzarides, 2001. Rb targets histone H3 methylation and HP1 to promoters. Nature 412: 561–565.
Nightingale, K.P., R.E. Wellinger, J.M. Sogo & P.B. Becker, 1998. Histone acetylation facilitates RNA polymerase II transcription of the Drosophila hsp26 gene in chromatin. Embo J. 17: 2865-2876.
Noma, K., C.D. Allis & S.I. Grewal, 2001. Transitions in distinct histone H3 methylation patterns at the heterochromatin domain boundaries. Science 293: 1150-1155.
Rea, S., F. Eisenhaber, D. O'Carroll, B.D. Strahl, Z.W. Sun, M. Schmid, S. Opravil, K. Mechtler, C.P. Ponting, C.D. Allis & T. Jenuwein, 2000. Regulation of chromatin structure by sitespecific histone H3 methyltransferases [see comments]. Nature 406: 593–599.
Reuter, G., R. Dorn & H.J. Hoffmann, 1982. Butyrate sensitive suppressor of position-effect variegation mutations in Drosophila melanogaster. Mol. Gen. Genet. 188: 480–485.
Sherman, J.M. & L. Pillus, 1997. An uncertain silence. Trends Genet. 13: 308–313.
Spofford, J.B., 1967. Single-locus modification of position-effect variegation in Drosophila melanogaster. I. White variegation. Genetics 57: 751–766.
Steger, D.J., A. Eberharter, S. John, P.A. Grant & J.L. Workman, 1998. Purified histone acetyltransferase complexes stimulate HIV-1 transcription from preassembled nucleosomal arrays. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95: 12924-12929.
Sterner, R., L.C. Boffa, T.A. Chen & V.G. Allfrey, 1987. Cell cycle-dependent changes in conformation and composition of nucleosomes containing human histone gene sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 15: 4375-4391.
Strahl, B.D. & C.D. Allis, 2000. The language of covalent histone modifications. Nature 403: 41–45.
Tie, F., T. Furuyama, J. Prasad-Sinha, E. Jane & P.J. Harte, 2001. The Drosophila Polycomb Group proteins ESC and E(Z) are present in a complex containing the histone-binding protein p55 and the histone deacetylase RPD3. Development 128: 275–286.
Turner, B.M., 2000. Histone acetylation and an epigenetic code. BioEssays 450: 1–10.
Turner, B.M., A.J. Birley & J. Lavender, 1992. Histone H4 isoforms acetylated at specific lysine residues define individual chromosomes and chromatin domains in Drosophila polytene nuclei. Cell 69: 375–384.
Waterborg, J.H., 1993. Dynamic methylation of alfalfa histone H3. J. Biol. Chem. 268: 4918-4921.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Czermin, B., Imhof, A. The Sounds of Silence – Histone Deacetylation Meets hisTone Methylation. Genetica 117, 159–164 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022927725945
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022927725945