Abstract
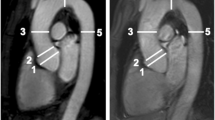
Objective: To investigate if a simple axial spin echo (SE) image can be used for reliable assessment of pulmonary artery dimensions in patients with Marfan syndrome. Methods: Fifty Marfan patients (mean age 33 ± 10 years; 34 men, 16 women) and 15 normal subjects (mean age 28 ± 4 years; nine men, six women) underwent cardiac magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Pulmonary artery dimensions were obtained on axial SE images at two different levels: (1) the level of the pulmonary artery root, and (2) the level of the pulmonary artery bifurcation. To evaluate the accuracy of axial plane measurements 10 Marfan patients also underwent contrast-enhanced MR angiography (CE-MRA). Results: In the 10 Marfan patients who also underwent CE-MRA, the mean diameter at the pulmonary bifurcation assessed with CE-MRA (31.5 ± 3.6 mm) was almost equal to mean diameter assessed with axial SE (30.7 ± 3.6 mm). Agreement of methodology according to Bland and Altman analysis showed a 95% confidence interval ranging from −2.6 to +4.4 mm for all distances of the pulmonary artery root. In Marfan patients the mean right-left diameter measured on both axial SE images and CE-MRA was approximately 2.5 mm larger than the anterior-right and anterior-left diameters (p < 0.001). Conclusions: Axial SE MRI is a reliable and easy acquisition to measure pulmonary artery dimensions in patients with Marfan syndrome, and could be used for follow-up, especially in patients with severe involvement of the cardiovascular system. Not only the pulmonary artery trunk but also the asymmetric pulmonary root should be measured, although the clinical relevance of the asymmetric root is not yet known.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pyeritz RE, McKusick VA. The Marfan syndrome: diagnosis and management. N Engl J Med 1979; 300: 772–777.
Beighton P, de Paepe A, Danks D, Hennekam RC, Pyeritz RE. International nosology of heritable disorders of connective tissue, Berlin 1986. Am J Med Genet 1988; 29: 581–594.
De Paepe A, Devereux RB, Dietz HC, Hennekam RC, Pyeritz RE. Revised diagnostic criteria for the Marfan syndrome. Am J Med Genet 1996; 62: 417–426.
Roman MJ, Devereux RB, Kramer-Fox R, O'Loughlin J. Two-dimensional echocardiographic aortic root dimensions in normal children and adults. Am J Cardiol 1989; 64: 507–512.
Edwards PD, Bull RK, Coulden R. CT measurement of main pulmonary artery diameter. Br J Radiol 1998; 71: 1018–1020.
Paz R, Mohiaddin RH, Longmore DB. Magnetic resonance assessment of the pulmonary arterial trunk anatomy, flow, pulsatility and distensibility. Eur Heart J 1993; 14: 1524–1530.
Solowiejczyk DE, Bourlon F, Apfel HD, et al. Serial echocardiographic measurements of the pulmonary autograft in the aortic valve position after the Ross operation in a pediatric population using normal pulmonary artery dimensions as the reference standard. Am J Cardiol 2000; 85: 1119–1123.
Snider RS, Enderlein MA, Teitel DF, Juster RP. Two-dimensional echocardiographic determination of aortic and pulmonary artery sizes from infancy to adulthood in normal subjects. Am J Cardiol 1984; 53: 218–224.
Morgan VL, Graham TP, Roselli RJ, Lorenz CH. Alterations in pulmonary artery flow patterns and shear stress determined with three-dimensional phase-contrast magnetic resonance imaging in Fontan patients. J Thorac Cardiov Sur 1998; 116: 294–303.
Kuriyama K, Gamsu G, Stern RG, Cann CE, Herfkens RJ, Brundage BH. CT-determined pulmonary artery diameters in predicting pulmonary hypertension. Invest Radiol 1984; 19: 16–22.
Nollen GJ, Timmermans J, Groenink M, Barentsz JO, van der Wall EE, Mulder BJ. Pulmonary artery root dilation in Marfan syndrome: quantative assessment of an unknown criterion. Heart 2002; 87: 470–471.
Kirklin JW. Cardiac Surgery. 2nd ed. New York: John Wiley, 1993; 3–60.
Meijboom LJ, Groenink M, van der Wall EE, Romkes H, Stoker J, Mulder BJ. Aortic root asymmetry in Marfan patients; evaluation by magnetic resonance imaging and comparison with standard echocardiography. Int J Card Imaging 2000; 16: 161–168.
Beekman RP, Beek FJ, Meijboom EJ. Usefulless of MRI for the pre-operative evaluation of the pulmonary arteries in Tetralogy of Fallot. Magn Reson Imaging 1997; 15: 1005–1015.
van Erkel AR, van Rossum AB, Bloem JL, Kievit J, Pattynama PM. Spiral CT angiography for suspected pulmonary embolism: a cost-effectiveness analysis. Radiology 1996; 201: 29–36.
Stein PD, Athanasoulis C, Alavi A, et al. Complications and validity of pulmonary angiography in acute pulmonary embolism. Circulation 1992; 85: 462–468.
Meaney JF, Weg JG, Chenevert TL, Stafford-Johnson D, Hamilton BH, Prince MR. Diagnosis of pulmonary embolism with magnetic resonance angiography. N Engl J Med 1997; 336: 1422–1427.
Gupta A, Frazer CK, Ferguson JM, et al. Acute pulmonary embolism: diagnosis with MR angiography. Radiology 1999; 210: 353–359.
Sloth E, Veien M, Kure HH, Nygaard H, Hasenkam JM. Diameter and cross-sectional area relationship of the human main pulmonary artery. Scand Cardiov J 1998; 32: 269–275.
Grande KJ, Cochran RP, Reinhall PG, Kunzelman KS. Stress variations in the human aortic root and valve: the role 146 of anatomic asymmetry. Ann Biomed Eng 1998; 62: 534–545.
Bartter T, Irwin RS, Nash G. Aneurysms of the pulmonary arteries. Chest 1988; 94: 1065–1075.
Mastroroberto P, Chello M, Zofrea S, Del Negro G, De Fransesca F, Maltese G. Pulmonary artery aneurysm. Ann Thorac Surg 1997; 64: 585–586.
Nair KK, Cobanoglu AM. Idiopathic main pulmonary artery aneurysm. Ann Thorac Sur 2001; 71: 1688–1690.
Ugolini P, Mousseaux E, Sadou Y, et al. Idiopathic dilatation of the pulmonary artery: report of four cases. Magn Reson Imaging 1999; 17: 933–937.
Arom KV, Richardson JD, Grover FL, Feris G, Trinkle JK. Pulmonary artery aneurysm. Am Sur 1978; 44: 688–692.
Disler LJ, Manga P, Barlow JB. Pulmonary arterial aneurysms in Marfan's syndrome. Int J Cardiol 1988; 21: 79–82.
Deterling RA, Clagett OT. Aneurysm of the pulmonary artery: review of the literature and a report of a case. Am Heart J 1947; 34: 471–498.
Andrews R, Colloby P, Hubner PJB. Pulmonary artery dissection in a patient with idiopathic dilatation of the pulmonary artery: a rare cause of sudden cardiac death. Br Heart J 1993; 69: 268–269.
Senbaklavaci O, Kaneko Y, Bartunek A, et al. Rupture and dissection in pulmonary artery aneurysms: incidence, cause, and treatment-review and case report. J Thorac Cardiov Sur 2001; 121: 1006–1008.
Potter KA, Besser TE. Cardiovascular lesions in bovine Marfan's syndrome. Vet Pathol 1994; 31: 501–509.
Kuwaki K, Morishita K, Sato H, et al. Surgical repair of the pulmonary trunk aneurysm. Eur J Cardiothor Sur 2000; 18: 535–539.
Kuwaki K, Morishita K, Komatsu K, et al. Graft replacement for huge aneurysm of the main pulmonary artery. Ann Thorac Sur 2000; 70: 1714–1716.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nollen, G., van Schijndel, K., Timmermans, J. et al. Magnetic resonance imaging of the main pulmonary artery: reliable assessment of dimensions in marfan patients on a simple axial spin echo image. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging 19, 141–147 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022860919684
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022860919684