Abstract
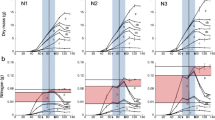
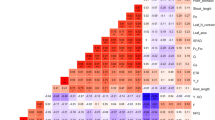
Contrasting rice genotypes differing in leaf mass ratio (LMR) and leaf nitrogen content were screened. A strong inverse relationship was observed between ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase (Rubisco) content and its efficiency estimated as the ratio of net photosynthetic rate (PN) to Rubisco content. Similarly, an inverse relationship between the specific activity of fully activated Rubisco and its content was observed. This suggests that a down regulation of Rubisco may occur if the efficiency of the enzyme is superior. Genotypes IET 12989 and IET 13567 recorded higher PN together with lower Rubisco content in comparison with other genotypes measured. These genotypes showed low LMR and low nitrogen content and hence could be considered as efficient nitrogen users.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Besford, R.T., Hand, D.W.: The effects of CO2 enrichment and nitrogen oxides on some Calvin cycle enzymes and nitrite reductase in glasshouse lettuce.-J. exp. Bot. 40: 329–336, 1989.
Bradford, M.M.: A rapid and sensitive method for the quantification of utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding.-Anal. Bot. 72: 248–254, 1976.
Cheng, S.H., Moore, D., Seeman, J.R.: Effect of short-and long-term elevated CO2 on the expression of ribulose-1,5–bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase genes and carbohydrate accumulation in leaves of Arabidopsis thaliana.-Plant Physiol. 116: 715–723, 1998.
Debabrata Ray: Genetic variability in net carbon gain per unit leaf nitrogen in rice: An approach to identify efficient Rubisco types with high nitrogen use efficiency.-M.Sc. Thesis. University of Agricultural Sciences, Bangalore 1998.
Evans, J.R.: The relationship between carbon-dioxide-limited photosynthetic rate and ribulose-1,5–bisphosphate carboxylase content in two nuclear-cytoplasm-substitution lines of wheat, and the co-ordination of ribulose-1,5–bisphosphate carboxylase and electron transport capacities.-Planta 167: 351–358, 1986.
Evans, J.R.: Photosynthesis and nitrogen relationships in leaves of C3 plants.-Oecologia 78: 9–19, 1989.
Ishimaru, K., Kobayashi, N., Ono, K., Ohsugi, R.: Are contents of Rubisco, soluble protein and nitrogen in flag leaves of rice controlled by the same genetics?-J. exp. Bot. 52: 1827–1833, 2001.
Krishnaprasad, B.T, Sheshshayee, M.S, Nataraja, K.N, Shankar, A.G, Prasad, T.G., Udaya Kumar, M.: Regulation of carboxylation by Rubisco content and its efficiency in sunflower and soybean.-Curr. Sci. 70: 675–680, 1996.
Makino, A., Harada, M., Kaneko, K., Mae, T., Shimada, T., Yamamoto, N.: Whole-plant growth and N allocation in transgenic rice plants with decreased content of ribulose-1,5–bisphosphate carboxylase under different CO2 partial pressures.-Aust. J. Plant Physiol. 27: 1–12, 2000.
Makino, A., Harada, M., Sato, T., Nakano, H., Mae, T.: Growth and nitrogen allocation in rice plants under CO2 enrichment.-Plant Physiol. 115: 199–203, 1997.
Makino, A., Mae, T., Ohira, K.: Relation between nitrogen and ribulose-1,5–bisphosphate carboxylase in rice from emergence through senescence.-Plant Cell Physiol. 25: 429–437, 1984.
Makino, A., Mae, T., Ohira, K.: Photosynthesis and ribulose-1,5–bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase in rice leaves from emergence through senescence. Quantitative analysis by carboxylation/oxygenation and regeneration of ribulose-1,5–bisphosphate.-Planta 166: 414–420, 1985.
Makino, A., Sakashita, H., Hidema, J., Mae, J., Ojima, K., Osmond, B.: Distinctive response of ribulose-1,5–bisphosphate carboxylase and carbonic anhydrase in wheat leaves to nitrogen nutrition and their possible relationships to CO2 transfer resistance.-Plant Physiol. 100: 1737–1743, 1992.
Mate, C.J., Hudson, G.S., Caemmerer, S. von, Evans, J.R. Andrews, T.J.: Reduction of ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase activase levels in tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum) by antisense RNA reduces ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase carbamylation and impairs photosynthesis.-Plant Physiol. 102: 1119–1128, 1993.
Mate, C.J., Caemmerer, S. von, Evans, J.R., Hudson, G.S., Andrews, T.J.: The relationship between CO2-assimilation rate, Rubisco carbamylation and Rubisco activase content in activase-deficient transgenic tobacco suggests a simple model of activase action.-Planta 198: 604–613, 1996.
Moore, B.d., Cheng, S.-H., Rice, J., Seeman, J.R.: Sucrose cycling, Rubisco expression, and prediction of photosynthetic acclimation to elevated atmospheric CO2.-Plant Cell Environ. 21: 905–915, 1998.
Morrel, M.K., Paul, K., Kane, H.J., Andrews, T.J.: Rubisco: Maladapted or misunderstood?-Aust. J. Bot. 40: 431–441, 1992.
Nakano, H., Makino, A., Mae, T.: The effect of elevated partial pressure of CO2 on the relationship between capacity and N content in rice leaves.-Plant Physiol. 115: 191–198. 1997.
Nataraja, K.N.: Influence of CO2 enrichment on seedling growth and gas exchange parameters in few forest tree species.-MSc. Thesis. University of Agricultural Sciences, Bangalore 1991.
Nie, G.Y., Hendrix, D.L., Webber, A.N., Kimball, B.A., Long, S.P.: Increased accumulation of carbohydrates and decreased photosynthetic gene transcript levels in wheat grown at an elevated CO2 concentration in the field.-Plant Physiol. 108: 975–983, 1995.
Ono, K., Watanabe, A.: Levels of endogenous sugars, transcript of rbcS and rbcL, and of Rubisco protein in senescing sunflower leaves.-Plant Cell Physiol. 38: 1032–1038, 1997.
Osada, A.: Relationship between photosynthetic activity and dry matter production in rice varieties especially as influenced by nitrogen supply.-Bull. nat. Inst. agr. Sci. Jap. D14: 117–188, 1966.
Piper, C.S. (ed.): Soil and Plant Analysis.-InterScience Publishers, New York 1957.
Sage, R.F.: Acclimation of photosynthesis to increasing atmospheric CO2: The gas exchange perspective.-Photosynth. Res. 39: 351–368, 1994.
Sage, R.F., Sharkey, T.D., Seemann, J.R. Acclimation of photosynthesis to elevated CO2 in five C3 species.-Plant Physiol. 89: 590–596. 1989.
Sheshshayee, M.S., Krishnaprasad, B.T., Nataraja, K.N., Shankar, A.G., Udaya Kumar, M., Prasad, T.G.: Ratio of intercellular CO2 concentration to stomatal conductance is a reflection of mesophyll efficiency.-Curr. Sci. 70: 672–675, 1996.
Stitt, M.: Rising CO2 levels and their potential significance for carbon flow in photosynthetic cells.-Plant Cell Environ. 14: 741–762, 1991.
Stitt, M., Krapp, A.: The interaction between elevated carbon dioxide and nitrogen nutrition: the physiological and molecular background.-Plant Cell Environ. 22: 583–621, 1999.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ray, D., Sheshshayee, M., Mukhopadhyay, K. et al. High Nitrogen Use Efficiency in Rice Genotypes is Associated with Higher Net Photosynthetic Rate at Lower Rubisco Content. Biologia Plantarum 46, 251–256 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022858828972
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022858828972