Abstract
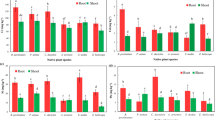
An attempt has been made to study the physiological andbiochemical responses and to evaluate the bioaccumulationpotential of moss Sphagnum to environmental lead. Supply of0.1 to 100 mM lead acetate caused a loss in chlorophyll andnitrogen content of moss and in nitrate reductase activity in themoss, although the peroxidase activity was increased. Partialrecovery in the above parameters was recorded upon simultaneoustreatment with glutathione. Results also indicate that treatmentwith glutathione increased the bioaccumulation potential bylowering the lead toxicity, which could be the result of inductionof metal binding capabilities of cells as the heavy metal alsoinduced the synthesis of phytochelatins. The moss accumulated asignificant amounts of Pb under both experimental and fieldconditions. The heavy metal accumulated by moss was positivelycorrelated to the soil metal content. The experiments demonstratethat Sphagnum is able to accumulate and tolerate higheramounts of Pb and therefore, it can be used as a bioindicator andphytoremediator of lead contaminated environment.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alscher, R. G.: 1989, 'Biosynthesis and antioxidant function of glutathione in plants', Plant Physiol. 77, 457–464.
Arnon, D. I.: 1949, 'Copper enzymes in isolated chloroplasts. Polyphenol oxidase in Beta vulgaris', Plant Physiol. 24, 1–15.
Bhandal, I. S. and Kaur, H.: 1992, 'Heavy metal inhibition of nitrate uptake and in vivo nitrate reductase in roots of wheat, Triticum aestivum', Indian J. Plant Physiol. 35, 281–284.
Bhattacharya, M., Choudhury, M. A. and Bhattacharya, M.: 1995, 'Heavy metal (Pb2+ and Cd2+) stress induced damages in Vigna seedings and possible involvement of phytochelatin like substances in mitigation of heavy metal stress', Indian J. Exper. Biol. 33(3), 236–238.
Bruns, I., Friese, K., Friese, K., Markert, B. and Krauss, G. J.: 1997, 'The use of Fontinalis antipyretica L. ex Hedw. as a bioindicator for heavy metals. 2. Heavy metal accumulation and physiological reaction of Fontinalis antipyretica L. ex Hedw. in active biomonitoring in the river Elbe', Sci. Total Environ. 204(2), 161–176.
Chen, S. L. and Kao, S. H.: 1995, 'Glutathione reduces the inhibition of rice seeding root growth catalyzed by cadmium', Plant Growth Regul. 16, 249–252.
Chitkara, S.: 1998, 'Air Pollution in India - An Exploratory Study', In Proceedings of National Workshop on Environmental Statistics, Goa, India, 12- 13 January, 1998, pp. 117–127.
Crist, R. H., Martin, J. R. and Chonko, J. D. R.: 1996, 'Uptake of metals on peat moss: An ion exchange process', Environ. Sci. Technol. 30(8), 2456–2461.
Echols, R. and Kisailus, E.: 1992, 'Cell Fractionation in Plants', in J. G. Chirikjian, (ed.), Biotechnology: Theory and Techniques. Plant Biotechnology, Animal Cell Culture and Immunobiotechnology.
Gallego, S. M., Benavides, M. P. and Tomaro, M. L.: 1996, 'Oxidative damage caused by cadmium chloride in sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.) plants', Phyton Buenos Aires 58, 41–52.
Glime, J. M. and Saxena, D. K.: 1991, Uses of Bryophytes, Today's and Tomorrow Printers and Publishers, New Delhi.
Godbold, D. L: 1994, 'Aluminium and Heavy Metal Stress: From the Rhizosphere to the Whole Plant', in D. L. Godbold, and Z. Zhutterman, (eds), Effects of Acid Rain on Forest Processes, Wiley-Liss, New York, pp. 232–264.
Grill, E., Winnacker, E. L. and Zenk, M. H.: 1991, 'Phytochelatins', in J. F. Riordon and B. L. Valle (eds), Methods in Enzymology, Vol. 205, Academic Press, New York, pp. 333–341
Gupta, M., Raj, U. N., Tripathi, R. D. and Chandra, P.: 1995, 'Induced changes in glutathione and phytochelatin in Hydrilla verticillata (L. f.) Royle', Chemosphere 30(10), 2011–2020.
Gupta, M., Tripathi, R. D., Raj, U. N. and Haq, W.: 1999, 'Lead induced synthesis of metal binding peptides (phytochelatins) in the submerged macrophyte Vallisneria spiralis L.', Physiol. Molec. Biol. Plants 5, 173–180.
Jackson, M. L.: 1962, 'Nitrogen Determination from Soil and Plant Tissue' in Soil and Chemical Analysis, Prentice Hall, U.S.A., pp. 185–191.
Jita, P., Panda, B. B. and Pantra, J.: 1998, 'A comparison of biochemical responses to oxidative and metal stress in seedlings of barley, Hordeum vulgare L.', Environ. Pollut. 101, 99–105.
Leopold, I., Gunther, D. M., Schinidt, J. and Neumann, D.: 1999, 'Phytochelatins and heavy metal tolerance', Phytochem. 50, 1323–1325.
Lowry, O. H., Rose, N. J., Brough, A. L. and Randall, N. R. J.: 1951, 'Protein measurement with foline phenol reagent', J. Biol. Chem. 193, 265–275.
Nakazawa, A. and Takenaga, H.: 1998, 'Interactions between cadmium and several heavy metals in the activation of the catalytic activity of phytochelatin synthase', Soil Sci. Plant Nutrit. 44, 265.
Nag, P., Paul, A. K. and Mukherjee, S. K.: 1981, 'Heavy metal effects in plants tissues involving chlorophyll, chlorophyllase, Hill reaction activity and gel electrophoretic patterns of soluble proteins', Indian J. Experim. Biol. 19, 702–706.
Putter, J.: 1974, Methods of Enzymatic Analysis 2, in Bergmeyer (ed.), Academic Press, New York, pp. 685.
Rauser, W. E.: 1995, 'Phytochelatins and related peptide: Structure, biosynthesis and function', Plant Physiol. 109, 1141–1149.
Saxena, D. K. and Thomas, S.: 1998, 'Possible Involvement of Phytochelatin like Substances in Mitigation of Heavy Metal Stress in Bryophytes', in 'Moss 98', International Conference held at T. I. F. R., Mumbai.
Saxena, D. K., Saxena, A. and Srivastava, H. S.: 1999, 'Heavy Metal Accumulation and In Vivo Nitrate Reductase Activity in the Sphagnum squarrosum Cram Samml.', Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, India 69(B) III and IV, pp. 307–312.
Shimwell, D.W. and Laurie, A. E.: 1972, 'Lead and zinc contamination of vegetation in the Southern Pennines', Environ. Pollut. 3, 291–301.
Sinha, S. K., Srivastava, H. S. and Mishra, S. N.: 1988, 'Nitrate assimilation in intact and excised maize leaves in the presence of lead', Bull. Environ. Contamin. Toxicol. 41, 419–426.
Srivastava, H. S.: 1975, 'Distribution of nitrate reductase in aging bean seedlings', Plant Cell Physiol. 16, 995–999.
Steffens, J. C.: 1990, 'The heavy metal binding peptides of plants', Ann. Rev. Plant Physiol. Plant Molec. Biol. 41, 553–575.
Steinnes, E.: 1996, 'Heavy Metals in NorwegianWildlife: Contributions from Natural and Anthropogenic Sources', in J. Lag (ed.), Chemical Data of Plant, Animal and Human Tissue as a Basis of Geomedical Investigations, The Norwegian Academy of Science and Letters, Oslo, pp. 101–113.
Steinnes, E.: 1997, 'Monitoring of Contaminants in the Arctic by Means of Terrestrial Mosses and Surface Soils', in AMAP International Symposium on Environmental Pollution in the Arctic, Vol. 1, Tromso, Norway, pp. 151–152.
Stobart, A. K., Griffiths, W. T., Ameen-Bukhari, I. and Sherwood, R. P.: 1985, 'The effect of Cd2+ on the biosynthesis of chlorophyll in leaves of barley', Plant Physiol. 63, 293–298.
Syso, A. S.: 1998, 'Using the Cr, Ni relationship for monitoring environmental pollution', Agrokhimiya 4, 76–83.
Thapa, D., Srivasatava, H. S. and Ormrod, D. I.: 1988, 'Physiological and biochemical effects of lead on higher plants', Vegetos 1, 107–119.
Van Assche, F. and Clijsters J.: 1990, 'Effects of metals on enzyme activity in plants', Plant Cell Environ. 13, 195–206.
Vasconcelos, M. T. S. D. and Taveres, H. M. F.: 1998, 'Atmospheric metal pollution (Cr, Cu, Fe,Mn, Ni, Pb and Zn) in Oporto city derived from results for low volume aerosol samplers and for the moss Sphagnum auriculatum bioindicator', Sci. Total Environ. 212(1), 11–20.
Vile, M., Wieder, P. K. and Martin, N.: 1999, '200 Years of Pb deposition throughout the Czech Republic patterns and source', Environ. Sci. Technol. 34(1), 12–21.
Weiss, D., Shotyk, W., Cheburkin, A. K., Gloor, M. and Reese, S.: 1997, 'Atmospheric lead deposition from 12400 to 2000 years B.C. in a peat bog profile, in Jura mountains, Switzerland', Water, Air, and Soil Pollut. 100(3- 4), 311–324.
Zenk, M. H.: 1996, 'Heavy metal detoxification in higher plants - A review', Gene 179, 21–30.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saxena, A., Saxena, D.K. & Srivastava, H.S. The Influence of Glutathione on Physiological Effects of Lead and its Accumulation in Moss Sphagnum Squarrosum . Water, Air, & Soil Pollution 143, 351–361 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022856807592
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022856807592