Abstract
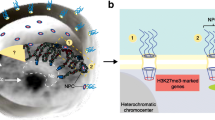
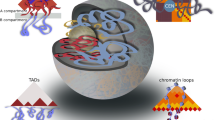
The eukaryotic nucleus represents a complex arrangement of heterochromatic and euchromatic domains, each with their specific nuclear functions. Somatic cells of a multicellular organism are genetically identical, yet they may differ completely in nuclear organization and gene expression patterns. Stable changes in gene expression without modifying the sequence are the result of epigenetic changes and include covalent modifications in cytosine residues of DNA and in histone tails giving rise to altered chromatin protein complexes, remodeling of chromatin and changes in chromatin compaction. Large-scale differences in chromatin structure are visible at the microscopic level as euchromatin and heterochromatin. Arabidopsis thaliana chromosomes display a relatively simple distribution of euchromatic and heterochromatic segments overlapping with gene-rich and repeat-rich regions, respectively. Recently, we have shown that Arabidopsis provides a well-defined system to study individual chromosomes and chromatin domains in interphase nuclei as well as the relationship between chromatin condensation and epigenetic mechanisms of gene silencing. This overview focuses on the organization and composition of heterochromatin in Arabidopsis nuclei.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amedeo P, Habu Y, Afsar K et al. (2000) Disruption of the plant gene MOM releases transcriptional silencing of methylated genes. Nature 405: 203‐206.
Ananiev EV, Phillips RL, Rines HW (1998) Complex structure of knob DNA on maize chromosome 9. Retrotransposon invasion into heterochromatin. Genetics 149: 2025‐2037.
Arabidopis Genome Initiative (2000) Analysis of the genome sequence of the flowering plant Arabidopsis thaliana. Nature 408: 796‐815.
Brown SW (1966) Heterochromatin. Science 151: 417‐425.
Campell BR, Song Y, Posch TE et al. (1992) Sequence and organization of 5S ribosomal RNA‐encoding genes of Arabidopsis thaliana. Gene 112: 225‐228.
Cao X, Jacobsen SE (2002) Role of the Arabidopsis DRM methyltransferases in de novo DNA methylation and gene silencing. Curr Biol 12: 1138‐1144.
Czermin B, Melfi R, McCabe D et al. (2002) Drosophila enhancer of Zeste/ESC complexes have a histone H3 methyltransferase activity that marks chromosomal Polycomb sites. Cell 111: 185‐196.
Cloix C, Tutois S, Mathieu O et al. (2000) Analysis of 5S rDNA arrays in Arabidopsis thaliana: physical mappinga nd chromosome‐specific polymorphisms. Genome Res 10: 679‐690.
Copenhaver GP, Pikaard CS (1996) RFLP and physical mappingwi th an rDNA‐specific endonuclease reveals that nucleolus organizer regions of Arabidopsis thaliana adjoin the telomeres on chromosomes 2 and 4. Plant J 9: 259‐272.
CSHL/WUGSC/PEB Arabidopsis Sequencing Consortium (2000) The complete sequence of a heterochromatic island from a higher eukaryote. Region. Cell 100: 377‐386.
Choo KHA (2001) Domain organization at the centromere and neocentromere. Dev Cell 1: 165‐177.
de Jong J H, Fransz PF, Zabel P (1999) High resolution FISH in plant — techniques and applications. Trends Genet 4: 258‐263.
Eberl DF, Duyf BJ, Hilliker AJ (1993) The role of heterochromatin in the expression of a heterochromatic gene, the rolled locus of Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics 134: 277‐292.
Finnegan EF, Genger RK, Peacock WJ et al. (1998) DNA methylation in plants. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 49: 223‐247.
Francastel C, Schubeler D, Martin DI et al. (2000) Nuclear compartmentalization and gene activity. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 1: 137‐143.
Fransz PF, Armstrong S, Alonso‐Blanco C et al. (1998) Cytogenetics for the model system Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 13: 867‐876.
Fransz P, Armstrong S, de Jong J H et al. (2000) Integrated cytogenetic map of chromosome arm 4S of A. thaliana: Structural organization of heterochromatic knob and centromere region. Cell 100: 367‐376.
Fransz P, De Jong J H, Lysak M et al. (2002) Interphase chromosomes in Arabidopsis are organised as well‐defined chromocenters from which euchromatin loops emanate. Proc Natl Acad Sci 99: 14584‐14589.
Furner IJ, Sheikh MA, Collett CE (1998) Gene silencing and homology‐dependent gene silencing in Arabidopsis: genetic modifiers and DNA methylation. Genetics 149: 651‐662.
Haaf T, Schmid M (1989) 5‐Azadeoxycytidine induced undercondensation in the giant X chromosomes of Microtus agrestis. Chromosoma 98: 93‐98.
Haupt W, Fischer TC, Winderl S et al. (2001) The CENTROMERE1 (CEN1) region of Arabidopsis thaliana: architecture and chromatin and its impact on gene expression, recombination and size estimation of centromeres. Plant J 27: 285‐297.
Heitz E (1928) Das Heterochromatin der Moose. I Jahrb Wiss Botanik 69: 762‐818.
Henikoff S (2000) Heterochromatin function in complex genomes. Biochim Biophys Acta 1470: O1‐8.
Henikoff S, Comai L (1998) A DNA methyltransferase homologw ith a chromodomain exists in multiple polymorphic forms in Arabidopsis. Genetics 149: 307‐318.
Hennig W (1999) Heterochromatin. Chromosoma 108: 1‐9.
Heslop‐Harrison JS, Brandes A, Schwarzacher T (2003) Tandemly repeated DNA sequences and centromeric chromosomal regions of Arabidopsis species. Chromosome Res 11: 241‐253.
Jackson JP, Lindroth AM, Cao X et al. (2002) Control of CpNpG DNA methylation by the KRYPTONITE histone H3 methyltransferase. Nature 416: 556‐560.
Jasencakova Z, Soppe W, Meister A et al. (2002) Histone modifications in Arabidopsis — high methylation of H3 lysine 9 is dispensable for chromocenter formation. Plant J (in press).
Jeddeloh JA, Stokes TL, Richards EJ (1999) Maintenance of genomic methylation requires a SWI2/SNF2‐like protein. Nat Genet 22: 94‐97.
Kakutani T, Munakata K, Richards EJ et al. (1999)Meiotically and mitotically stable inheritance of DNA hypomethylation induced by ddm1 mutation of Arabidopsis thaliana. Genetics 151: 831‐838.
Karpen GH, Allshire RC (1997) The case for epigenetic effects on centromere identity and function. Trends Genet 13: 489‐496.
Koornneef M, Fransz P, de Jong H (2003) Cytogenetic tools for Arabidopsis thaliana. Chromosome Res 11: 183‐194.
Kulikova O, Gualtieri G, Geurts R et al. (2001) Integration of the FISH pachytene and genetic maps of Medicago truncatula. Plant J 21: 49‐58.
Laibach F (1907) Zur Frage nach der Individualitat der Chromosomen im Pflanzenreich. Beiheft zum Bot. Centralblatt 22: 191‐210.
Lindroth AM, Cao X, Jackson JP et al. (2001) Requirement of CHROMOMETHYLASE3 for maintenance of CpXpG methylation. Science 292: 2077‐2080.
Lohe AR, Hilliker AJ (1995) Return of the H‐word (heterochromatin). Curr Opin Genet Dev 5: 746‐755.
Maison C, Bailly D, Peters AH et al. (2002) Higher‐order structure in pericentric heterochromatin involves a distinct pattern of histone modification and an RNA component. Nat Genet 30: 329‐334.
Martienssen RA, Colot V (2001) DNA methylation and epigenetic inheritance in plants and filamentous fungi. Science 293: 1070‐1074.
Miklos GL, Cotsell JN (1990) Chromosome structure at interfaces between major chromatin types: alpha‐and beta‐heterochromatin. Bioessays 12: 1‐6.
Mittelsten Scheid O, Probst AV, Afsar K et al. (2002) Two regulatory levels of transcriptional gene silencing in Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci 99: 13659‐13662.
Miura A, Yonebayashi S, Watanabe K et al. (2001). Mobilization of transposons by a mutation abolishingf ull DNA methylation in Arabidopsis. Nature 411: 212‐214.
Probst AV, Mittelsten Scheid O, Fransz PF et al. (2002) Transcriptional reactivation can modify or maintain properties and organization of heterochromatin. Plant J (in press).
Ré dei GP (1962) Single locus heterosis. Z Vererbungsl 93: 164‐170.
Ronemus MJ, Galbiati M, Ticknor C et al. (1996) Demethylation‐induced developmental pleiotropy in Arabidopsis. Science 273: 654‐657.
Sewalt RGAB, Lachner M, Vargas M et al. (2002) Selective interactions between vertebrate Polycomb homologs and the SUV39H1 histone lysine methyltransferase suggest that histone H3‐K9 methylation contributes to chromosomal targeting of Polycomb group proteins. Mol Cell Biol 22: 5539‐5553.
Soppe WJJ, Jasencakova Z, Houben A et al. (2002) DNA methylation controls histone H3 lysine 9 methylation and heterochromatin assembly in Arabidopsis. EMBO J 21: 6549‐6559.
Steimer A, Amedeo P, Fransz P et al. (2000) Endogenous targets of transcriptional gene silencing in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell 12: 1165‐1178.
Volpe TA, Kidner C, Hall IM et al. (2002) Regulation of heterochromatic silencinga nd histone H3 lysine‐9 methylation by RNAi. Science 297: 1833‐1837.
Volpi EV, Chevret E, Jones T et al. (2000) Large‐scale chromatin organization of the major histocompatibility complex and other regions of human chromosome 6 and its response to interferon in interphase nuclei. J Cell Sci 113: 1565‐1576.
Vongs A, Kakutani T, Martienssen RA et al. (1993) Arabidopsis thaliana DNA methylation mutants. Science 260: 1926‐1928.
Yoder JA, Walsh CP, Bestor TH (1997) Cytosine methylation and the ecology of intragenomic parasites. Trends Genet 13: 335‐340.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fransz, P., Soppe, W. & Schubert, I. Heterochromatin in interphase nuclei of Arabidopsis thaliana . Chromosome Res 11, 227–240 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022835825899
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022835825899