Abstract
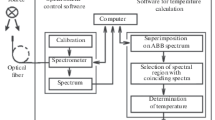
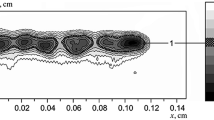
Two experimental approaches dealing with the determination of melting at high static pressures are described and analyzed. With the sample squeezed inside a diamond anvil cell, high temperatures up to the solid–liquid transition are obtained using Nd:YAG laser heating. Two methods have been investigated. In the first technique, the heating is accomplished with a pulsed laser and the brief radiation variations (t<10 ms) emitted from the sample are recorded with two high-speed infrared detectors. The melting location is defined by a plateau or changes of slope of the signals, and the temperatures are calculated by assuming a constant value of emissivity factor at the end of the transition over the studied pressure range. The second system employs a continuous laser and a two-dimensional CCD detector to measure temperatures using multispectral pyrometry. Melting is detected from criteria related either to textural change in the sample involving interference contrast under a laser illumination or to the specific variations of temperature and emissivity as a function of laser power. Thermal radiation is fitted to Planck's law with temperature and emissivity as the free parameters. Advantages and drawbacks are presented from results obtained on pure uranium.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
E. Tonkov, High Pressure Phase Transformations, Vols. 1 and 2 (Gordon and Breach, Amsterdam, 1992).
D. Adams and A. Christy, High Temp.-High Press. 24:1 (1992).
N. Dahan, R. Couty, A. Lefèvre, A. Berthault, J. Boutroux, and J. Péré, Cellule à enclume de diamant, French Patent No. 9005814 (1990).
H. Mao, J. Xu, and P. Bell, J. Geophys. Res. 91:4673 (1986).
B. Sitaud, J. Péré, and Th. Thévenin, High Press. Res. 12:175 (1994).
C. Yoo, J. Akella, and J. Moriarty, Phys. Rev. B 48:15529 (1993).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sitaud, B., Thévenin, T. Melting-Point Measurements at High Static Pressures from Laser Heating Methods: Application to Uranium. International Journal of Thermophysics 20, 1189–1198 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022619323705
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022619323705