Abstract
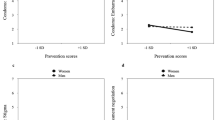
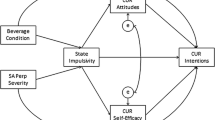
Using the AIDS risk reduction model as a conceptual framework, we conducted a multivariate prospective test of psychosocial antecedents of unprotected sex by 155 female and 134 male heterosexual injection drug users. For both women and men, stronger intentions to use condoms predicted subsequent reductions in unprotected sex. For women, but not men, higher perceived self-efficacy also led to reductions in unprotected sex. These results suggest that explicit formation of risk-reduction intentions is an important antecedent to sexual behavior change by drug users of either gender and that change by drug-using women is also influenced by their perceived control over sexual risk-taking.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Ajzen, I. (1987). Attitudes, traits, and actions: Dispositional prediction of behavior in personality and social psychology. In L. Berkowitz (Ed.), Advances in experimental social psychology (pp. 1-63). New York: Academic Press.
Ajzen, I. (1991). The theory of planned behavior. Organizational Behavior and Human Decision Processes, 50, 179-211.
Ajzen, I., and Fishbein, M. (1980). Understanding attitudes and predicting social behavior. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice-Hall.
Amaro, H. (1995). Love, sex, and power. American Psychologist, 50, 437-447.
Bagozzi, R. P. (1981). Attitudes, intentions and behavior: A test of some key hypotheses. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 41, 607-627.
Bandura, A. (1986). Social foundations of thought and action: A social cognitive theory. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice-Hall.
Bandura, A. (1989). Perceived self-efficacy in the exercise of control over AIDS infection. In V.M. Mays, G. W. Albee, and S. F. Schneider (Eds.), Primary prevention of AIDS: Psychological approaches (pp. 128-141). Newbury Park, CA: Sage.
Bandura, A. (1994). Social cognitive theory and exercise of control over HIV infection. In R.J. DiClemente and J. L. Peterson (Eds.), Preventing AIDS: Theories and methods of behavioral interventions (pp. 25-59). New York: Plenum Press.
Basen-Enquist, K. (1992). Psychosocial predictors of safer sex behaviors in young adults. AIDS Education and Prevention, 4, 120-134.
Bentler, P. M. (1990). Comparative fit indexes in structural models. Psychological Bulletin, 107, 238-246.
Bentler, P. M. (1995). EQS structural equations programs manual. Encino, CA: Multivariate Software, Inc.
Bentler, P. M., and Dudgeon, P. (1996). Covariance structure analysis: Statistical practice, theory, and directions. Annual Review of Psychology, 47, 563-592.
Bentler, P. M., and Stein, J. A. (1992). Structural equation modeling in medical research. Statistical Methods in Medical Research, 1, 159-181.
Bollen, K. A., and Long, J. S. (1993). Testing structural equation models. Newbury Park, CA: Sage.
Catania, J. A., Kegeles, S. M. and Coates, T. J. (1990). Towards an understanding of risk behavior: An AIDS risk reduction model (ARRM). Health Education Quarterly, 17, 53-72.
Chou, C.-P., and Bentler, P. M. (1990). Model modification in covariance structure modeling: A comparison among likelihood ratio, Lagrange multiplier, and Wald tests. Multivariate Behavioral Research, 25, 115-136.
Colon, H. M., Robles, R. R., Sahai, H., and Matos, T. (1992). Changes in HIV risk behaviors among intravenous drug users in San Juan, Puerto Rico. British Journal of Addiction, 87, 585-590.
Corby, N. H., Jamner, M. S., and Wolitski, R. (1996). Using the theory of planned behavior to predict intentions to use condoms among male and female injecting drug users. Journal of Applied Social Psychology, 26, 52-75.
Curran, P. J., West, S. G., and Finch, J. F. (1996). The robustness of test statistics to nonnormality and specification error in confirmatory factor analysis. Psychological Methods, 1, 16-29.
Decker, S., and Rosenfeld, R. (1995). 'My wife is married and so is my girlfriend': Adaptations to the threat of AIDS in an arrestee population. Crime and Delinquency, 41, 37-53.
DiClemente, R. J., and Peterson, J. L. (1994). Changing HIV/AIDS risk behaviors: The role of behavioral interventions. In R. J. DiClemente and J. L. Peterson (Eds.), Preventing AIDS: Theories and methods of behavioral interventions (pp. 1-4). New York: Plenum Press.
Elias, C. J., and Coggins, C. (1996). Female-controlled methods to prevent sexual transmission of HIV. AIDS, 10, S43-S51.
Fishbein, M., Bandura, A., Triandis, H. C., Kanfer, F., Becker, M. H., and Middlestadt, S. E. (1991). Factors influencing behavior and behavior change: Final report—Theorists' workshop. Unpublished.
Fisher, J. D., and Fisher, W. A. (1992). Changing AIDS-risk behavior. Psychological Bulletin, 111, 455-474.
Fisher, W. A., and Fisher, J. D. (1993). A general social psychological model for changing AIDS risk behavior. In J. B. Pryor and G. D. Reeder (Eds.), The social psychology of HIV infection (pp. 127-153). Hillsdale, NJ: Erlbaum.
Fisher, W. A., Fisher, J. D., and Rye, B. J. (1995). Understanding and promoting AIDS-preventive behavior: Insights from the theory of reasoned action. Health Psychology, 14, 255-264.
Fisher, W. A., and Gray, J. (1988). Erotophobia-erotophilia and sexual behavior during pregnancy and postpartum. Journal of Sex Research, 25, 379-396.
Flores-Ortiz, Y. G. (1994). The role of cultural and gender values in alcohol use patterns among Chicana/Latina high school and university students: Implications for AIDS prevention. International Journal of the Addictions, 19, 1149-1171.
French, J., and Raven, B. H. (1959). The bases of social power. In D. Cartwright (Ed.), Studies in social power (pp. 150-167). Ann Arbor, MI: University of Michigan Press.
Friedman, S. R. (1993). AIDS as a sociohistorical phenomenon. In G. L. Albrecht and R. S. Zimmerman (Eds.), The social and behavioral aspects of AIDS (pp. 19-36). Greenwich, CT: JAI Press.
Gerrard, M., Gibbons, F. X., and Bushman, B. J. (1996). Relation between perceived vulnerability to HIV and precautionary sexual behavior. Psychological Bulletin, 119, 390-409.
Hammer, J. C., Fisher, J. D., Fitzgerald, P., and Fisher, W. A. (1996). When two heads aren't better than one: AIDS risk behavior in college-age couples. Journal of Applied Social Psychology, 26, 375-397.
Hobfoll, S. E., Jackson, A. P., Lavin, J., Britton, P. J., and Shepherd, J. B. (1994). Women's barriers to safer sex. Psychology and Health, 9, 233-252.
Hospers, H. J., and Kok, G. (1995). Determinants of safe and risk-taking behavior among gay men: A review. AIDS Education and Prevention, 7, 74-94.
Huang, K. H. C., Watters, J. K., and Case, P. (1989). Predicting compliance with HIV risk reduction behaviors among heterosexual intravenous drug users: Relative contributions of health beliefs and situational factors. Paper presented at the Fifth International Conference on AIDS, Montreal.
King, V. L., Brooner, R. K., Bigelow, G. E., Schmidt, C. W., Felch, L., and Gazaway, P. M. (1994). Condom use rates for specific sexual behaviors among opioid abusers entering treatment. Drug and Alcohol Dependence, 35, 231-238.
Kline, A., Kline, E., and Oken, E. (1992). Minority women and sexual choice in the age of AIDS. Social Science and Medicine, 34, 447-457.
Kok, G., de Vries, H., Mudde, A. N., and Strecher, V. J. (1991). Planned health education and the role of self-efficacy: Dutch research. Health Education Research, 6, 231-238.
Lear, D. (1995). Sexual communication in the age of AIDS: The construction of risk and trust among young adults. Social Science and Medicine, 41, 1311-1323.
Longshore, D. (1992). AIDS education for drug users: Existing research and new directions. Journal of Drug Issues, 22, 1-16.
Longshore, D., and Anglin, M. D. (1992). Seroprevalence low and seroconversions rare among Los Angeles injection drug users. Journal of Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndromes, 5, 212-213.
Longshore, D., and Anglin, M. D. (1994). HIV prevalence and incidence among injection drug users in Los Angeles. Journal of Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndromes, 7, 738-739.
Longshore, D., and Anglin, M. D. (1996). HIV incidence among injection drug users in Los Angeles. Journal of Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndromes and Human Retrovirology, 11, 308-309.
Longshore, D., Anglin, M. D., Annon, K., and Hsieh, S. (1993). Trends in behavioral indicators of HIV risk: Injection drug users in Los Angeles. Journal of Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndromes, 6, 82-90.
Longshore, D., Hseih, S., and Anglin, M. D. (1994). Reducing HIV risk among injection drug users: Effect of methadone maintenance on number of sex partners. International Journal of the Addictions, 29, 741-758.
Longshore, D., Stein, J. A., and Anglin, M. D. (1996). Ethnic differences in the psychosocial antecedents of needle/syringe disinfection by drug users. Drug and Alcohol Dependence, 42, 183-196.
Longshore, D., Stein, J. A., and Anglin, M. D. (1997). Psychosocial antecedents of needle/syringe disinfection: A theory-based prospective analysis. AIDS Education and Prevention, 9, 442-457.
Magura, S., Kang, S., Shapiro, J., and O'Day, J. (1995). Evaluation of an AIDS education model for women drug users in jail. International Journal of the Addictions, 30, 259-273.
Magura, S., Shapiro, J., Siddiqi, Q., and Lipton, D. S. (1990). Variables influencing condom use among intravenous drug users. American Journal of Public Health, 80, 82-84.
Malow, R. M., Corrigan, S. A., Cunningham, S. C., West, J. A., and Pena, J. M. (1993). Psychosocial factors associated with condom use among African-American drug abusers in treatment. AIDS Education and Prevention, 5, 244-253.
Malow, R. M., West, J. A., Corrigan, S. A., Pena, J. M., and Cunningham, S. C. (1994). Outcome of psychoeducation for HIV risk reduction. AIDS Education and Prevention, 6, 113-125.
Mantell, J. E., Karp, G., Majidi, K., Ramos, S. E., Glover-Walton, C., Gonzales, V., and Brown, L. S. (1992). Do power and powerlessness affect condom use among inner-city women? Paper presented at the Annual Meeting of the American Public Health Association.
McCusker, J., Stoddard, A. M., Zapka, J. G., and Lewis, B. F. (1993a). Behavioral outcomes of AIDS educational interventions for drug users in short-term treatment. American Journal of Public Health, 83, 1463-1466.
McCusker, J., Stoddard, A. M., Zapka, J. G., and Zorn, M. (1993b). Use of condoms by heterosexually active drug abusers before and after AIDS education. Sexually Transmitted Diseases, 20, 81-88.
Miller, L. C., Bettencourt, A., DeBro, S. C., and Hoffman, V. (1993). Negotiating safer sex: Interpersonal dynamics. In J. B. Pryor and G. D. Reeder (Eds.), The social psychology of HIV infection (pp. 85-123). Hillsdale, NJ: Erlbaum.
Moore, M. M. (1985). Nonverbal courtship patterns in women: Context and consequences. Ethology and Sociobiology, 6, 237-247.
Norris, A. E., and Ford, K. (1995). Condom use by low-income African American and Hispanic youth with a well-known partner: Integrating the health belief model, theory of reasoned action, and the construct accessibility model. Journal of Applied Social Psychology, 25, 1801-1830.
O'Sullivan, L. F., and Allgeier, E. R. (1994). Disassembling a stereotype: Gender differences in the use of token resistance. Journal of Applied Social Psychology, 24, 1035-1055.
Peplau, L. A., Hill, C. T., and Rubin, Z. (1993). Sex role attitudes in dating and marriage: A 15-year follow-up of the Boston Couples Study. Journal of Social Issues, 49, 31-52.
Peplau, L. A., Rubin, Z., and Hill, C. T. (1977). Sexual intimacy in dating relationships. Journal of Social Issues, 33, 86-109.
Ramos, S., Mantell, J., Majidi, K., Glover-Walton, C., Gonzales, V., and Brown, L. S. (1992). Gender variations in contraceptive and reproductive attitudes, intentions and practices among New York City injecting drug users. Paper presented at the Eighth International Conference on AIDS, Amsterdam.
Rhodes, T., Stimson, G. V., and Quirk, A. (1996). Sex, drugs, intervention, and research: From the individual to the social. Substance Use and Misuse, 31, 375-407.
Robles, R., Cancel, L. I., Colon, H. M., Matos, T. D., Freeman, D. H., and Sahai, H. (1995). Prospective effects of perceived risk of developing HIV/AIDS on risk behaviors among injection drug users in Puerto Rico. Addiction, 90, 1105-1111.
Roehrich, L., Wall, T. L., and Sorensen, J. L. (1994). Behavioral interventions for in-treatment injection drug users. In R. J. DiClemente and J. L. Peterson (Eds.), Preventing AIDS: Theories and methods of behavioral interventions (pp. 189-208). New York: Plenum Press.
Rosenstock, I. M. (1990). The health belief model: Explaining health behavior through expectancies. In K. Glanz, F. M. Lewis, and B. K. Rimer (Eds.), Health behavior and education (pp. 39-62). San Francisco: Jossey-Bass.
Rosenstock, I. M., Strecher, V. J., and Becker, M. H. (1994). The health belief model and HIV risk behavior change. In R. J. DiClemente and J. L. Peterson (Eds.), Preventing AIDS: Theories and methods of behavioral interventions (pp. 5-24). New York: Plenum Press.
Schilling, R. F., El-Bassell, N., Schinke, S., Nichols, S., Botvin, G. J., and Orlandi, M. A. (1991). Sexual behavior, attitudes toward safer sex, and gender among a cohort of 244 recovering IV drug users. International Journal of the Addictions, 26, 859-877.
Sibthorpe, B., Fleming, D., Tesselaar, H., and Gould, J. (1991). Needle use and sexual practices: Difference in perception of personal risk of HIV among intravenous drug users. Journal of Drug Issues, 21, 699-712.
Sobo, E. J. (1995). Choosing unsafe sex: AIDS-risk denial among disadvantaged women. Philadelphia: University of Pennsylvania Press.
Sorensen, J. L., Wermuth, L. A., Gibson, D. R., Choi, K., Guydish, J. R., and Batki, S. L., Eds. (1991). Preventing AIDS in drug users and their sexual partners. New York: Guilford Press.
Strecher, V. J., Seijts, G. H., Kok, G. J., Latham, G. P., Glasgow, R., DeVellis, B., Meertens, R. M., and Bulger, D. W. (1995). Goal setting as a strategy for health behavior change. Health Education Quarterly, 22, 190-200.
Terry, D. (1993). Self-efficacy expectancies and the theory of reasoned action. In D.J. Terry, C. Gallois, and M. McCamish (Eds.), The theory of reasoned action: Its application to AIDS preventive behaviour (pp. 135-151). Oxford: Pergamon Press.
Vlahov, D., Anthony, J. C., Celantano, D., Solomon, L., and Chowdhury, N. (1991). Trends of HIV-1 risk reduction among initiates into intravenous drug use (1982–1987). American Journal of Drug and Alcohol Abuse, 17, 39-48.
Wermuth, L., Ham, J., and Robbins, R. L. (1992). Women don't wear condoms: AIDS risk among sexual partners of IV drug users. In J. Huber and B. E. Schneider (Eds.), The social context of AIDS (pp. 72-94). Newbury Park, CA: Sage.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Longshore, D., Stein, J.A., Kowalewski, M. et al. Psychosocial Antecedents of Unprotected Sex by Drug-Using Men and Women. AIDS Behav 2, 293–306 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022618008009
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022618008009