Abstract
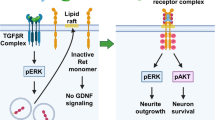
1. Glial cell-derived neurothrophic factor (GDNF) interacts with a cell surface receptor, GFRα1, that is linked via a glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol (GPI) lipid to the cell membrane. The neurotrophic activities of GDNF are mediated by binding to GFRα1 and further interaction of the GDN–GFRα1 complex with a coreceptor tyrosine kinase encoded by the c-Ret protooncogene. There is also evidence for the existence of cell signaling by GDNF and GFRα1 in the absence of Ret.
2. To further delineate the Ret-dependent and -independent functions of GDNF, cellular internalization of GDNF and GFRα1 was examined in cells lines and primary neurons.
3. Relative to other GPI-anchored receptors, efficient endocytosis ( 30–40% of total surface-bound ligand internalized after 2 min) of GNDF and GFRα1 was observed in neuroblastoma and transfected-fibroblast cell lines that lack Ret. Primary hippocampal neurons from transgenic mice that express a wild-type GFRα1 together with a mutant, tyrosine kinase-inactive Ret also internalized GDNF efficiently ( 20% of total surface-bound ligand internalized after 2 min). We also observed a ligand dependence for GFRα1 internalization in the cell lines that lack Ret. Furthermore, a comparison in the presence and absence of Ret indicates that this coreceptor tyrosine kinase slows internalization at early time points.
4. The data suggest different mechanisms of internalization for GDNF–GFRα1 in the absence and presence of the Ret coreceptor.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Airaksinen, M. S., Titievsky, A., and Saarma, M. (1999). GDNF family neurotrophic factor signaling: Four masters, one servant? Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 13:313–325.
Alberti, L., Borrello, M. G., Ghizzoni, S., Torriti, F., Rizzetti, M. G., and Pierotti, M. A. (1998). Grb2 binding to the different isoforms of Ret tyrosine kinase. Oncogene 17:1079–1087.
Arighi, E., Alberti, L., Torriti, F., Ghizzoni, S., Rizzetti, M. G., Pelicci, G., Pasini, B., Bongarzone, I., Piutti, C., Pierotti, M. A., and Borrello, M. G. (1997). Identification of Shc docking site on Ret tyrosine kinase. Oncogene 14:773–782.
Asai, N., Murakami, H., Iwashita, T., and Takahashi, M. (1996). A mutation at tyrosine 1062 in MEN2A-Ret and MEN2B-Ret impairs their transforming activity and association with Shc adaptor proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 271:17644–17649.
Baloh, R. H., Gorodinsky, A., Golden, J. P., Tansey, M. G., Keck, C. L., Popescu, N. C., Johnson, E. M., Jr., and Milbrandt, J. (1998a). GFRα3 is an orphan member of the GDNF/neurturin/persephin receptor family. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 95:5801–5806.
Baloh, R. H., Tansey, M. G., Golden, J. P., Creedon, D. J., Heuckeroth, R. O., Keck, C. L., Zimonjic, D. B., Popescu, N. C., Johnson, E. M., Jr., and Milbrandt, J. (1997). TrnR2, a novel receptor that mediates neurturin and GDNF signaling through Ret. Neuron 18:793–802.
Baloh, R. H., Tansey, M. G., Lampe, P. A., Fahrner, T. J., Enomoto, H., Simburger, K. S., Leitner, M. L., Araki, T., Johnson, E. M., and Milbrandt, J. (1998b). Artemin, a novel member of the GDNF ligand family, supports peripheral and central neurons and signals through the GFRα3-RET receptor complex. Neuron 21:1291–1302.
Borrello, M. G., Alberti, L., Arighi, E., Bongarzone, L., Battistini, C., Bardelli, A., Pasini, B., Piutti, C., Rizzetti, M. G., Mondellini, P., Radice, M. T., and Pierotti, M. A. (1996). The full oncogenic activity of Ret/ptc2 depends on tyrosine 539, a docking site for phospholipase Cγ. Mol. Cell. Biol. 16:2151–2163.
Creedon, D. J., Tansey, M. G., Baloh, R. H., Osborne, P. A., Lampe, P. A., Fahrner, T. J., Heuckeroth, R. O., Milbrandt, J., and Johnson, E. M., Jr. (1997). Neurturin shares receptors and signal transduction pathways with glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor in sympathetic neurons. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 94:7018–7023.
Daaka, Y., Luttrell, L. M., Ahn, S., Della Rocca, G. J., Ferguson, S. S. G., Caron, M. G., and Lefkowitz, R. J. (1998). Essential role for G protein-coupled receptor endocytosis in the activaton of mitogen activated protein kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 273:685–688.
Durbec, P., Marcos-Gutierrez, C. V., Kilkenny, C., Grigoriou, M., Wartiowaara, K., Suvanto, P., Smith, D., Ponder, B., Costantini, F., Saarma, M., Sariola, H., and Pachnis, V. (1996). GDNF signalling through the Ret receptor tyrosine kinase. Nature 381:789–793.
Durick, K., Gill, G. N., and Taylor, S. S. (1996). Mitogenic signaling by Ret/ptc2 requires association with enigma via a LIM domain. J. Biol. Chem. 271:12691–12694.
Durick, K., Gill, G. N., and Taylor, S. S. (1998). She and Enigma are both required for mitogenic signaling by Ret/pt2. Mol. Cell. Biol. 18:2298–2308.
Friedrichson, T., and Kurzchalia, T. V. (1998). Microdomains of GPI-anchored proteins in living cells revealed by crosslinking. Nature 394:802–805.
Green, J. M., Schreiber, A. D., and Brown, E. J. (1997). Role for a glycan phosphoinositol anchor in Fc gamma receptor synergy. J. Cell Biol. 139:1209–1217.
Hiltunen, J. O., Laurikainen, A., Vakeva, A., Meri, S., and Saarma, M. (2001). Nerve growth factor and brain-derived neurotrophic factor mRNAs are regulated in distinct cell populations of rat heart after ischaemia and reperfusion. J. Pathol. 194:247–253.
Hiwasa, T., Kondo, K., Hishiki, T., Koshizawa, S., Umezawa, K., and Nakagawara, A. (1997). GDNF–induced neurite formation was stimulated by protein kinase inhibitors and suppressed by Ras inhibitors. Neurosci. Lett. 238:115–118.
Horger, B. A., Nishimura, M. C., Armanini, M. P., Wang, L. C., Poulsen, K. T., Rosenblad, C., Kirik, D., Moffat, B., Simmons, L., Johnson, E. M., Jr., Milbrandt, J., Rosenthal, A., Bjorklund, A., Vandlen, R. A., Hynes, M. A., and Phillips, H. S. (1998). Neurturin exerts potent actions on survival and function of midbrain dopaminergic neurons. J. Neurosci. 18:4929–4937.
Iwashita, T., Asai, N., Murakami, H., Matsuyama, M., and Takahashi, M. (1996). Identification of tyrosine residues that are essential for transforming activity of the ret proto-oncogene with MEN2A or MEN2B mutation. Oncogene 12:481–487.
Jings, S. Q., Spencer, T., Miller, K., Hopkins, C., and Trowbridge, I. S. (1990). Role of the human transferrin receptor cytoplasmic domain in endocytosis: Localization of a specific signal sequence for internalization. J. Cell. Biol. 110(2):283–294.
Jing, S., Wen, D., Yu, Y., Holst, P. L., Luo, Y., Fang, M., Tamir, R., Antonio, L., Hu, Z., Cupples, R., Louis, J. C., Hu, S., Altrock, B. W., and Fox, G. M. (1996). GDNF-induced activation of the ret protein tyrosine kinase is mediated by GDNFR-alpha, a novel receptor for GDNF. Cell 85:1113–1124.
Jing, S., Yu, Y., Fang, M., Hu, Z., Holst, P. L., Boone, T., Delaney, J., Schultz, H., Zhou, R., and Fox, G. M. (1997). GFRα-2 and GFRα-3 are two new receptors for ligands of the GDNF family. J. Biol. Chem. 272:33111–33117.
Kaplan, D. R., and Miller, F. D. (1997). Signal transduction by the neurotrophin receptors. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 9:213–221.
Klein, R. D., Sherman, D., Ho, W. H., Stone, D., Bennett, G. L., Moffat, B., Vandlen, R., Simmons, L., Gu, Q., Hongo, J. A., Devaux, B., Poulsen, K., Armanini, M., Nozaki, C., Asai, N., Goddard, A., Phillips, H., Henderson, C. E., Takahashi, M., and Rosenthal, A. (1997). A GPI-linked protein that interacts with Ret to form a candidate neurturin receptor. Nature 387:717–721.
Kotzbauer, P. T., Lampe, P. A., Heuckeroth, R. O., Golden, J. P., Creedon, D. J., Johnson, E. M., Jr., and Milbrandt, J. (1996). Neurturin, a relative of glial-cell-line-derived neurotrophic factor. Nature 384:467–470.
Lin, L. F., Doherty, D. H., Lile, J. D., Bektesh, S., and Collins, F. (1993). GDNF: A glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor for midbrain dopaminergic neurons. Science 260:1130–1132.
Lindahl, M., Poteryaev, D., Yu, L., Arumae, U., Timmusk, T., Bongarzone, I., Aiello, A., Pierotti, M. A., Airaksinen, M. S., and Saarma, M. (2001). Human glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor receptor alpha 4 is the receptor for persephin and is predominantly expressed in normal and malignant thyroid medullary cells. J. Biol. Chem. 276:9344–9351.
Lorenzo, M. J., Gish, G. D., Houghton, C., Stonehouse, T. J., Pawson, T., Ponder, B. A., and Smith, D. P. (1997). RET alternate splicing influences the interaction of activated RET with the SH2 and PTB domains of Shc, and the SH2 domain of Grb2. Oncogene 14:763–771.
Mayor, S., Sabharanjak, S., and Maxfield, F. R. (1998). Cholesterol-dependent retention of GPI-anchored proteins in endosomes. EMBO J. 17:4626–4638.
Milbrandt, J., de Sauvage, F. J., Fahrner, T. J., Baloh, R. H., Leitner, M. L., Tansey, M. G., Lampe, P. A., Heuckeroth, R. O., Kotzbauer, P. T., Simburger, K. S., Golden, J. P., Davies, J. A., Vejsada, R., Kato, A. C., Hynes, M., Sherman, D., Nishimura, M., Wang, L. C., Vandlen, R., Moffat, B., Klein, R. D., Poulsen, K., Gray, C., Garces, A., and Johnson, E. M., Jr. (1998). Persephin, a novel neurotrophic factor related to GDNF and neurturin. Neuron 20:245–253.
Naveilhan, P., ElShamy, W. E., and Ernfors, P. (1997). Differential regulation of mRNAs for GDNF and its receptors Ret and GDNFRa after sciatic nerve lesion in the mouse. Eur. J. Neurosci. 9:1450–1460.
Neet, K. E., and Campenot, R. B. (2001). Receptor binding, internalization, and retrograde transport of neurotrophic factors. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 58(8):1021–1035.
Ohiwa, M., Murakami, H., Iwashita, T., Asai, N., Iwata, Y., Imai, T., Funahashi, H., Takagi, H., and Takahashi, M. (1997). Characterization of Ret–Shc–Grb2 complex induced by GDNF, MEN 2A, and MEN 2B mutations. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 237:747–751.
Pezeshki, G., Franke, B., and Engele, J. (2001). Evidence for a ligand specic signaling through GFRalpha-1, but not GFRalpha-2, in the absence of Ret. J. Neurosci. Res. 66:390–395.
Pong, K., Xu, R. Y., Baron, W. F., Louis, J. C., and Beck, K. D. (1998). Inhibition of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase activity blocks cellular differentiation mediated by glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor in dopaminergic neurons. J. Neurochem. 71:1912–1919.
Poteryaev, D., Titievsky, A., Sun, Y. F., Thomas-Crusells, J., Lindahl, M., Billaud, M., Arumae, U., and Saarma, M. (1999). GDNF triggers a novel ret-independent Src kinase family-coupled signaling via a GPI-linked GDNF receptor alpha1. FEBS Lett. 463:63–66.
Saarma M. (2000). GDNF—A stranger in the TGF-beta superfamily? Eur. J. Biochem. 267:6968–6971.
Sanicola, M., Hession, C., Worley, D., Carmillo, P., Ehrenfels, C., Walus, L., Robinson, S., Jaworski, G., Wei, H., Tizard, R., Whitty, A., Pepinsky, R. B., and Cate, R. L. (1997). Glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor-dependent RET activation can be mediated by two different cell-surface accessory proteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 94:6238–6243.
Schaefer, A. W., Kamiguchi, H., Wong, E. V., Beach, C. M., Landreth, G., and Lemmon, V. (1999). Activation of the MAPK signal cascade by the neural cell adhesion molecule L1 requires L1 internalization. J. Biol. Chem. 274:37965–37973.
Smythe, E., Redelmeier, T. E., and Schmid, S. L. (1992). Receptor-mediated endocytosis in semiintact cells. Methods Enzymol. 219:223–234.
Treanor, J. J., Goodman, L., de Sauvage, F., Stone, D. M., Poulsen, K. T., Beck, C. D., Gray, C., Armanini, M. P., Pollock, R. A., Hefti, F., Phillips, H. S., Goddard, A., Moore, M. W., Buj-Bello, A., Davies, A. M., Asai, N., Takahashi, M., Vandlen, R., Henderson, C. E., and Rosenthal, A. (1996). Characterization of a multicomponent receptor for GDNF. Nature 382:80–83.
Trupp, M., Arenas, E., Fainzilber, M., Nilsson, A. S., Sieber, B. A., Grigoriou, M., Kilkenny, C., Salazar-Grueso, E., Pachnis, V., Arumäe, U., Sariola, H., Saarma, M., and Ibáñez, C. (1996). Functional receptor for GDNF encoded by the c-ret proto-oncogene. Nature 381:785–788.
Trupp, M., Belluardo, N., Funakoshi, H., and Ibáñez, C. F. (1997). Complementary and overlapping expression of glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF), c-ret proto-oncogene, and GDNF receptor-alpha indicates multiple mechanisms of trophic actions in the adult rat CNS. J. Neurosci. 17:3554–3567.
Trupp, M., Raynoschek, C., Belluardo, N., and Ibáñez, C. F. (1998). Multiple GPI-anchored receptors control GDNF-dependent and independent activation of the c-ret receptor tyrosine kinase. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 11:47–63.
Trupp, M., Scott, R., Whittemore, S. R., and Ibanez, C. F. (1999). Ret-dependent and-independent mechanisms of glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor signaling in neuronal cells. J. Biol. Chem. 274:20885–20894.
van Weering, D. H., and Bos, J. L. (1997). Glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor induces Ret-mediated lamellipodia formation. J. Biol. Chem. 272:249–254.
Varma, R., and Mayor, S. (1998). GPI-anchored proteins are organized in submicron domains at the cell surface. Nature 394:798–801.
Vieira, A. V., Lamaze, C., and Schmid, S. L. (1996). Control of EGF receptor signaling by clathrin-mediated endocytosis. Science 274:2086–2089.
Worby, C. A., Vega, Q. C., Zhao, Y., Chao, H. H. J., Seasholtz, A. F., and Dixon, J. E. (1996). Glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor signals through the RET receptor and activates mitogen-activated protein kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 271:23619–23622.
Xavier, R., Brennan, T., Li. Q., McCormack, C., and Seed, B. (1998). Membrane compartmentation is required for efficient T cell activation. Immunity 8:723–732.
Xing, S., Furminger, T. L., Tong, Q., and Jhiang, S. M. (1998). Signal transduction pathways activated by RET oncoproteins in PC12 pheochromocytoma cells. J. Biol. Chem. 273:4909–4914.
Ylikoski, J., Pirvola, K., Virkkala, J., Suvanto, P., Liang, X.-Q., Magal, E., Altschuler, R., Miller, J. M., and Saarma, M. (1998). Guinea pig auditory neurons are protected by glial cell line-derived growth factor from degeneration after noise trauma. Hear. Res. 124:17–26.
Yu, T., Scully, S., Yu, Y., Fox, G. M., Jing, S., and Zhou, R. (1998). Expression of GDNF family receptor components during development: Implications in the mechanisms of interaction. J. Neurosci. 18:4684–4696.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vieira, P., Thomas-Crusells, J. & Vieira, A. Internalization of Glial Cell-Derived Neurotrophic Factor Receptor GFRα1 in the Absence of the Ret Tyrosine Kinase Coreceptor. Cell Mol Neurobiol 23, 43–55 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022593001155
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022593001155