Abstract
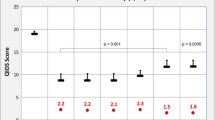
Gabapentin is a new adjunctive medication to antiseizure therapies. Anecdotal evidence suggests that it may also help to alleviate mood symptoms in patients with bipolar illness. An open-label study examined the effects of adjunctive gabapentin in bipolar patients with mixed symptoms who had previously demonstrated only partial treatment responses. Mood ratings and side-effect profiles were followed weekly in 10 patients for 1 month. Decreases in Hamilton depression (P < 0.05) and Bech mania ratings (P < 0.01) were evident in the first week of treatment and were sustained. Potent early improvements were noted in early, middle, and late insomnia. The results suggest that gabapentin may be of benefit to bipolar patients who only partially respond to other mood stabilizers. A favorable side-effect profile and rapid action make this drug an attractive choice as an adjunctive therapy.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Post RM, Rubinow DR, Uhde TW, et al: Dysphoric mania. Clinical and biological correlates. Arch Gen Psychiatry 1989; 46(4):353–358
Swann AC: Mixed or dysphoric manic states: psychopathology and treatment. J Clin Psychiatry 1995; 56(suppl 3):6–10
Hlastala SA, Frank E, Mallinger AG, et al: Bipolar depression: an underestimated treatment challenge. Depression and Anxiety 1997; 5(2):73–83.
Altshuler LL, Post RM, Leverich GS, et al: Antidepressant-induced mania and cycle acceleration: a controversy revisited. Am J Psychiatry 1995; 152(8):1130–1138
Pickar D, Cowdry RW, Zis AP, et al: In: Post RM, Ballenger J, eds. Mania and hypomania during antidepressant pharmacotherapy: Clinical and Research Implications in Neurobiology of Mood Disorders. Baltimore: Williams & Wilkins; 1984
Wehr TA, Goodwin FK: Can antidepressants cause mania and worsen the course of affective illness? Am J Psychiatry 1987; 144(11):1403–1411
Peet M: Induction of mania with selective serotonin re-uptake inhibitors and tricyclic antidepressants. Br J Psychiatry 1994; 164(4):549–550
Stoll AL, Mayer PV, Kolbrener M, et al: Antidepressant-associated mania: a controlled comparison with spontaneous mania. Am J Psychiatry 1994; 151(11):1642–1645
Dilsaver SL, Swann AC: Mixed mania: apparent induction by a tricyclic antidepressant in five consecutively treated patients with bipolar depression. Biol Psychiatry 1995; 37(1):60–62
Solomon DA, Keitner GI, Miller IW, et al: Course of illness and maintenance treatments for patients with bipolar disorder. J Clin Psychiatry 1995; 56(1):5–13
Howland RH: Induction of mania with serotonin reuptake inhibitors. J Clin Psychopharmacol 1996; 16(6):425–427
Solomon RL, Rich CL, Darko DF: Antidepressant treatment and the course of mania in bipolar patients admitted for depression. J Affective Disord 1998; 18:253–257
Young LT, Robb JC, Patelis-Siotis I, et al: Acute treatment of bipolar depression with gabapentin. Biol Psychiatry 1997; 42:851–853
McElroy SL, Soutullo CA, Keck Jr, et al: A pilot trial of adjunctive gabapentin in the treatment of bipolar disorder. Ann Clin Psychiatry 1997; 9(2):99–103
Bruni J, Saunders M, Anhut H, et al: Efficacy and safety of gabapentin (Neurontin): a multicenter placebo controlled, double-blind study. Neurology 1991; 41(suppl 1):330–331
Andrews CO, Fischer JH: Gabapentin: A new agent for the management of epilepsy. Ann Pharmacother 1994; 28:1188–1196
Taylor CP: Emerging perspectives on the mechanism of action of gabapentin. Neurology 1994; 44(suppl 5):510–516
Bennet J, Goldman WT, Suppes T: Gabapentin for treatment of bipolar and schizoaffective disorders (letter). J Clin Psychopharmacol 1997; 17:141–142
Ryback RS, Brodsky L, Munasifi F: Gabapentin in bipolar disorder. J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci 1997; 9(2):301
Schaffer CB, Schaffer LC. Gabapentin in the treatment of bipolar disorder (letter). Am J Psychiatry 1997; 154(2):291–292
Stanton SP, Keck PE Jr, McElroy SL: Treatment of acute mania with gabapentin (letter). Am J Psychiatry 1997; 54:287
Ghaemi SN, Katzow JJ, DeSai SP, Goodwin FK: Gabapentin treatment of mood disorders: a preliminary study. J Clin Psychiatry 1998; 8:426–429
Spitzer RL, Williams JBW, Mirron G: Structured Clinical Interview for DSM-IV. New York: New York State Psychiatric Institute; 1994
Hamilton M: Development of a rating scale for primary depressive illness. Br J Soc Clin Psychol 1967; 6:278–296
Bech P, Bolvig TG, Kramp P, et al: The Bech-Rafaelsen Mania Scale and the Hamilton Depression Scale. Acta Psychiatr Scand 1979; 59(4):420–430
Wehr TA: Sleep-loss as a possible mediator of diverse causes of mania. Br J Psychiatry 1991; 159:576–578
Wehr TA, Goodwin FK: Rapid cycling in manic-depressives induced by tricyclic antidepressants. Arch Gen Psychiatry 1979; 36:555–559
Frances AJ, Kahn DA, Carpenter D, et al: The expert consensus guidelines for treating depression in bipolar disorder. J Clin Psychiatry 1998; 59(suppl 4):73–79
Wehr TA: Can antidepressants induce rapid cycling? (letter, comment). Arch Gen Psychiatry 1993; 50(6):495–496
Short C, Cooke L: Hypomania induced by gabapentin. Br J Psychiatry 1995; 166:679–680
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sokolski, K.N., Green, C., Maris, D.E. et al. Gabapentin as an Adjunct to Standard Mood Stabilizers in Outpatients with Mixed Bipolar Symptomatology. Ann Clin Psychiatry 11, 217–222 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022361412956
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022361412956