Abstract
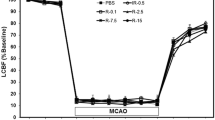
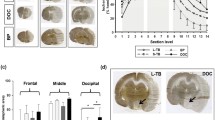
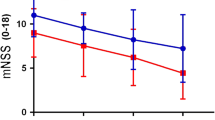
In view of the protective effect of brain derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) against metabolic/excitotoxic insults in vitro, we investigated whether BDNF could limit infarct size after permanent occlusion of the middle cerebral artery in rat (MCAO). BDNF was delivered into the territory of the middle cerebral artery via an osmotic mini-pump (1 μg/h). Infusion of BDNF was started shortly after MCAO, and 24 h later brains were removed for infarct volume determination. Intraoperative and postoperative measurements of physiological variables revealed no differences among vehicle-treated and BDNF-infused animals. However, we found a 33% reduction in total infarct volume in BDNF-treated animals (p<0.05), and a 37% reduction in cortical infarct volume (p<0.05).
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Beck, T., Lindholm, D., Castren, E., and Wree, A. (1994). Brain-derived neurotrophic factor protects against ischemic cell damage in rat hippocampus. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 4:689–692.
Campagne, M.V., and Gill, R. (1996). Ultrastructural morphological changes are not characteristic of apoptotic cell death following focal cerebral ischaemia in the rat. Neurosci. Lett. 213:111–114.
Castrén, E., Berzaghi, M.P., Lindholm, D., and Thoenen, H. (1993). Differential effect of MK-801 on BDNF mRNA levels in different parts of rat brain. Exp. Neurol. 122:244–252.
Dalkara, T. and Moskowitz, M.A. (1994). The complex role of nitric oxide in the pathophysiology of focal cerebral ischemia. Brain Pathol. 4:49–57.
Fisher, M., Meadows, M.E., Do, T., Weise, J., Trubetskoy, V., Charette, M., and Finklestein, S.P. (1995). Delayed treatment with intravenous basic fibroblast growth factor reduces infarct size following permanent focal cerebral ischemia in rats. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 15:953–959.
Ghosh, A., Carnahan, J., and Greenberg, M.E. (1994). Requirement for BDNF in activity-dependent survival of cortical neurons. Science 263:1618–1623.
Hofer, M., Paglinsi, S.R., Hohn, A., Leibrock, J., and Barde, Y.-A. (1990). Regional distribution of brain derived neurotrophic factor mRNA in the adult mouse brain. EMBO J. 9:2459–2464.
Hossmann, K.-A. (1994). Glutamate-mediated injury in focal cerebral ischemia — The excitotoxin hypothesis revised. Brain Pathol. 4:23–36.
Isackson, P.J., Huntsman, M.M., Murray, K.D., and Gall, C.M. (1991). BDNF mRNA expression is increased in adult rat forebrain after limbic seizures: temporal pattern of induction distinct from NGF. Neuron 6:937–948.
Jones, K.R., Farinas, I., Backus, C., and Reichard, L.F. (1994). Targeted disruption of the BDNF gene perturbs brain and sensory neuron development but not motor neuron development. Neuron 76:989–999.
Kawahara, N., Ruetzler, C.A., Wiegand, S., Croll, S., Mies, G., and Klatzo, I. (1994). Effects of spreading depression and of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in cardiac arrest cerebral ischemia. Pharmacol. Cereb. Isch. 389–396.
Kokaia, Z., Zhao, Q., Kokaia, M., Elmér, E., Metsis, M., Smith, M.-L., et al. (1995). Regulation of brain-derived neurotrophic factor gene expression after transient middle cerebral artery occlusion with and without brain damage. Exp. Neurol. 136:73–88.
Koroshetz, W.J., and Moskowitz, M.A. (1996). Emerging treatments for stroke in humans. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 17:227–233.
Leibrock, J., Lottspeich, F., Hohn, A., Hofer, M., Hengerer, B., Masiakowski, P., et al. (1989). Molecular cloning and expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor. Nature 341:149–152.
Lindholm, D., Carroll, P., Tzimagiorgis, G., and Thoenen, H. (1996). Autocrine-paracrine regulation of hippocampal neuron survival by IGF-1 and the neurotrophins, BDNF, NT-3 and NT-4. Eur. J. Neurosci. 8:1452–1460.
Lindholm, D., Dechant, G., Heisenberg, C.-P., and Thoenen, H. (1993). Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) is a survival factor for cultured granule neurons and protects them against glutamate-induced neurotoxicity. Eur. J. Neurosci. 5:1455–1464.
Lindsay, R.M., Wiegand, S.J., Altar, C.A., and DiStefano, P.S. (1994). Neurotrophic factors: from molecules to man. Trends Neurol. Sci. 17:182–190.
Lindvall, O., Ernfors, P., Bengzon, J., Kokaia, Z., Smith, M. L., Siesjö, B. K., and Persson, H. (1992). Differential regulation of mRNAs for nerve growth factor, brain-derived neurotrophic factor, and neurotrophin 3 in the adult rat brain following cerebral ischemia and hypoglycemic coma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 89:648–652.
Linnik, M.D., Zobrist, R.H., and Hatfield, M.D. (1993). Evidence supporting a role for programmed cell death in focal cerebral ischemia in rats. Stroke 24:2002–2008.
Mies, G., Ishimaru, S., Xie, Y., Seo, K., and Hossmann, K.-A. (1991). Ischemic thresholds of cerebral protein synthesis and energy state following middle cerebral artery occlusion in rat. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 11:753–761.
Novikov, L., Novikova, L., and Kellerth, J.O. (1995). Brain-derived neurotrophic factor promotes survival and blocks nitric oxide synthase expression in adult rat spinal motoneurons after ventral root avulsion. Neurosci. Lett. 200:45–48.
Swanson, R.A., Morton, M.T., Tsao-Wu, G., Savalos, R.A., Davidson, C., and Sharp, F.A. (1990). A semiautomated method for measuring brain infarct volume. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 10:290–293.
Valenzuela, D.M., Maisonpierre, P.C., Glass, D.J., Rojas, E., Nunez, L., Kong, Y., et al. (1993). Alternative forms of rat TrkC with different functional capabilities. Neuron 10:963–974.
Yamashita, K., Vogel, P., Fritze, K., Back, T., Hossmann, K.-A., and Paschen, W. (1996). Monitoring the temporal and spatial activation pattern of astrocytes in focal cerebral ischemia using in situ hybridization to GFAP mRNA: comparison with spg-2 and hsp70 mRNA and the effect of glutamate receptor antagonists. Brain Res. 735:285–297.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yamashita, K., Wiessner, C., Lindholm, D. et al. Post-Occlusion Treatment with BDNF Reduces Infarct Size in a Model of Permanent Occlusion of the Middle Cerebral Artery in Rat. Metab Brain Dis 12, 271–280 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022322025000
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022322025000