Abstract
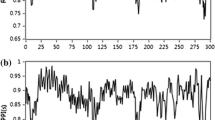
Biofeedback methods are well established as behavioral techniques for the therapy of various psychophysiological diseases. The forms of feedback generally employed are muscle activity (electromyogram), skin temperature, brain activity (electroencephalogram), and vasomotoricity. The latter technique, which employs plethysmographic feedback, has been studied most extensively in the therapy of migraine (vasoconstriction training, blood volume pulse training). Although the clinical efficacy has been demonstrated in several studies, little is known about the psychometric properties of this technique. This study examined the intrasession and intersession reliability of the pulse volume amplitude (PVA). The results showed that the PVA measurements within a single biofeedback session were highly reliable. Repositioning of the probe within the session resulted in a lower correlation coefficient, but one that was still sizable and significant. The PVA values from different sessions were not reliable (or comparable).
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Andrasik,F.,& Gerber,W.D.(1993).Relaxation,biofeedback,and stress-coping therapies.In J.Olesen, P.Tfelt-Hansen,& K.M.A.Welch (Eds.),The headaches (pp.833–842).New York: Raven Press.
Arena,J.G.(1984).Inter-and intrasession reliability of psychophysiological poststress adaptation periods.Journal of Behavioral Assessment,6,247–260.
Arena,J.G., Blanchard,E.B., Andrasik,F., Cotch,P.A.,& Myers,P.E.(1983).Reliability of psychophysiological assessment.Behaviour Research and Therapy,21,447–460.
Blanchard,E.B.,& Andrasik,F.(1987).Biofeedback treatment of vascular headache.In J.P.Hatch, J.G.Fisher, & J.D.Rugh (Eds.),Biofeedback-Studies in clinical efficacy (pp.1–79).New York: Plenum Press.
Drummond,P.D.,& Lance,J.W.(1983).Extracranial vascular changes and the source of pain in migraine headache.Annals of Neurology,13,32–37.
Duckro,P.N.(1991).Biofeedback in the management of headache:I.Headache Quarterly,1,290–298.
Gerber,W.D., Gothe,L., Speckenbach,U.,& Winzer,O.(1993).Psychobiological mechanisms of BVP-and MCA-selfregulation-training in migraine attacks.In A.Lehmenkuhler, K.-H.Grotemeyer,& F.Tegtmeier (Eds.),International Symposium Migraine held in Munster,March 8–11,1992.Migraine:Basic mechanisms and treatment (pp.41–54).Munchen: Urban &Schwarzenberg.
Haynes,S.N.(1980).Muscle contraction headache:A psychophysiological perspective of etiology and treatment. In S.N.Haynes & L.R.Gannon (Eds.),Psychosomatic disorders:A psychophysiological approach to etiology and treatment.New York: Garner Press.
Haynes,S.N., Gannon,L.R., Cuevas,J., Heiser,P., Hamilton,J.,& Katranides,M.(1983).The psychophysio-logical assessment of muscle contraction headache subjects during headache and non-headache conditions. Psychophysiology,20,393–399.
Haynes,S.N., Gannon,L.R., Bank,J., Shelton,D.,& Goodwin,J.(1991).Cephalic blood flow correlates of induced headaches.Journal of Behavioral Medicine,13,467–480.
Holroyd,K.A.,& Penzien,D.B.(1990).Pharmacological versus non-pharmacological prophylaxis of recurrent migraine headache:A meta-analytic review of clinical trials.Pain,42,1–13.
Holroyd,K.A.,& Penzien,D.B.(1994).Psychosocial interventions in the management of recurrent headache disorders:I.Overview and effectiveness.Behavioral Medicine,20,53–63.
Jennings,J.R., Tahmoush,A.J.,& Redmond,D.P.(1980).Non-invasive measurement of peripheral vascular activity.In I.Martin & P.H.Venbles (Eds.),Technics in psychophysiology.New York: Willey.
Kropp,P., Gerber,W.D., Keinath-Specht,A., Kopal,T.,& Niederberger,U.(1997).Behavioral treatment in migraine:Cognitive-behavioral therapy and blood-volume-pulse biofeedback:A cross-over study with a two year followup.Functional Neurology,12,17–24.
Leone,M., Grazzi,L., D'Amico,D., Moschiano,F.,& Bussone,G.(1995).A review of the treatment of primary headaches.I:Migraine.Italian Journal of Neurological Science,16,577–586.
Penzien,D.B.,& Holroyd,K.A.(1994).Psychosocial interventions in the management of recurrent headache disorders:II.Description of treatment techniques.Behavioral Medicine,20,64–73.
Raskin,D.C., Kotses,H.,& Bever,J.(1969).Cephalic vasomotor and heard rate measures of orienting and defense reflexes.Psychophysiology,6,149–158.
Reid,G.J.,& McGrath,P.J.(1996).Psychological treatments for migraine.Biomedicine &Phannacotherapy, 50,58–63.
Saxena,P.R.,& Den Boer, M.O.(1991).Pharmacology of antimigraine drugs.Journal of Neurology,238, S28-S35.
Schwartz,M.S. (Ed.) (1995).Biofeedback.A practioner's guide.New York: Guilford Press.
Silberstein,S.D.,& Lipton,R.B.(1994).Overview of diagnosis and treatment of migraine.Neurology,44 (10, Suppl.7),S6-S16.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Speckenbach, U., Gerber, W.D. Reliability of Infrared Plethysmography in BVP Biofeedback Therapy and the Relevance for Clinical Application. Appl Psychophysiol Biofeedback 24, 261–265 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022286930738
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022286930738