Abstract
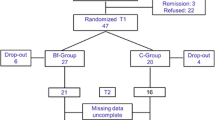
The relative efficacy of EMG-frontalis feedback and progressive relaxation was examined in children with tension-type or combined headaches (8–14 yrs. old). Furthermore, the influence of parent involvement, in the form of a three-session educational approach, on training outcome was systematically explored (2 × 2 factor design). Fifty children took part in the study, 40 were randomly assigned to the four different treatment conditions, 10 children participated in the self-monitoring control group. The training comprised 6 sessions of 1 hr each in the relaxation treatment and 12 sessions of 1/2 hr duration in the biofeedback group. Headache diaries were kept by children and parents for 4-week period prior to therapy, and for a similar length of time at post-treatment and follow-up (6 months). Multivariate analyses of variance on the headache diary data yield no significant main or interaction effects of treatment format or of parent involvement, but only a main effect of period, indicating a general efficacy of the four treatment conditions. At follow-up the reduction of headache activity is even more prominent. A different evaluative approach points to the superiority of biofeedback revealing a mean effect size for biofeedback training that reflects a good to excellent improvement rate. Correlations between headache data from children and parents are high.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Andrasik, F., Blanchard, E. B., Edlund, S. R., & Attanasio, V. (1983). EMG-biofeedback treatment of a child with muscle contraction headache. American Journal of Clinical Biofeedback, 6, 96–102.
Andrasik, F., Burke, E. J., Attanasio, V., & Rosenblum, E. L. (1985). Child, parent, and physician reports of a child's headache pain: relationships prior to and following treatment. Headache, 25, 421–425.
Beames, L., Sanders, M. R., & Bor, W. (1992). The role of parent training in the cognitive behavioral treatment of children's headaches. Behavioural Psychotherapy, 20, 167–180.
Bille, B. (1981). Migraine in childhood and its prognosis. Cephalalgia, 1, 71–75.
Blanchard, E. B., & Andrasik, F. (1985). Management of chronic headaches—a psychological approach. New York: Pergamon Press.
Burke, E. J., & Andrasik, F. (1989). Home versus clinic-based biofeedback treatment for pediatric migraine results of treatment through one year follow-up. Headache, 29, 434–440.
Bussone, G., Grazzi, L., & D'Amico, D. (1991). Electromyographic biofeedback (EMG-BFB) treatment for children and adolescent headache. Abstract presented at International Juvenile Headache Congress, Rome. 178–180.
Cautela, H. & Groden, J. (1978). Relaxation: A comprehensive manual for adults, children and children with special needs. Champaign, IL: Research Press.
Davis, J. F. (1959). Manual of surface electromyography. WADC Technical Report, 59–184.
Dooley, J., & Bagnell, A. (1995). The prognosis and the treatment of headaches in children—A ten year follow-up. Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences, 22, 47–49.
Duckro, P.N., & Cantwell-Simmons, E. (1989). A review of studies evaluating biofeedback and relaxation training in the management of pediatric headache. Headache, 29, 428–433.
Engel, J. M., Rapoff, M. A., & Pressman, A. R. (1994). The durability of relaxation training in pediatric headache management. Occupational Therapy Journal of Research, 14, 183–190.
Grazzi, L., Leone, M., Frediani, F., & Bussone, G. (1990). A therapeutic alternative for tension headache in children: treatment and 1-year follow-up results. Biofeedback and Self-Regulation, 15, 1–6.
Guarnieri, P., & Blanchard, E. B. (1990). Evaluation of home based thermal biofeedback treatment of pediatric migraine headache. Biofeedback and Self-Regulation, 15, 179–184.
Griffith, J. D., & Martin, P. R. (1996). Clinical-versus home-based treatment formats for children with chronic headache. British Journal of Health Psychology, 1, 151–167.
Hartmann, A., & Herzog, T. (1995). Varianten der Effektstärkenberechnung in Meta-analysen: Kommt es zu variablen Ergebnissen? (Different methods of calculating effect sizes in meta-analysis: do results differ?) Zeitschrift für Klinische Psychologie, 24, 337–343.
Headache Classification Committee of the International Headache Society (1988). Classification and diagnostic criteria for headache disorders, cranial neuralgias and facial pain. Cephalalgia, 8supplement 7, 1–96.
Hermann, C., Kim, M., & Blanchard, E. B. (1995). Behavioral and prophylactic pharmacological intervention studies of pediatric migraine: An exploratory meta-analysis. Pain, 60, 239–256.
Hermann, C., Blanchard, E. B., & Flor, H. (1997). Biofeedback treatment for pediatric migraine prediction of treatment outcome. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 65, 611–616.
Kristjansdottir, G., & Wahlberg, V. (1993). Sociodemographic differences in the prevalence of self-reported headache in Icelandic school children. Headache, 33, 381–385.
Kröner-Herwig, B., Plump, U., & Pothmann, R. (1992). Progressive Relaxation und EMG-Biofeedback in der Therapie von chronischem Kopfschmerz bei Kindern: Ergebnisse einer explorativen Studie (Progressive relaxation and EMG-biofeedback in pediatric headache therapy: results of an exploratory study). Der Schmerz, 6, 121–127.
Kröner-Herwig, B., & Ehlert, U. (1992). Relaxation und Biofeedback in der Behandlung von chronischem Kopfscherz bei Kindern und Jugendlichen: Ein Überblick (Progressive relaxation and biofeedback in the treatment of recurrent headache in children and adolescents: A review). Der Schmerz, 6, 171–181.
Labbée, E. L., & Williamson, D. A. (1984). Treatment of childhood migraine using autogenic feedback training. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 52, 968–976.
McGrath, P. J., Humphreys, P., Goodman, J. T., Keene, D., Firestone, P., Jacob, B., & Cunningham, S. J. (1988). Relaxation prophylaxis for childhood migraine: a randomized placebo-controlled trial. Developmental Medicine and Child Neurology, 30, 626–631.
McGrath, P. J., & Humphreys, P. (1989). Recurrent headaches in children and adolescents: Diagnosis and treatment. Pediatrician, 16, 71–77.
McGrath, P. J., Cunningham, S. J., Lascelles, M. A. & Humphreys, P. (1990). Help yourself. A treatment for migraine headaches. Ottawa: University of Ottawa Press.
McGrath, P. J., Humphreys, P., Keene, D., Goodman, J. T., Lascelles, M. A., Cunningham, S. J., & Firestone, P. (1992). The efficacy and efficiency of a self-administered treatment for adolescent migraine. Pain, 49, 321–324.
Passchier, J., & Orlebeke, J. F. (1985). Headache and stress in school children: An epidemiological study. Cephalalgia, 5, 167–176.
Ramsden, R., Friedmann, B. & Williamson, D. (1983). Treatment of childhood headache reports with contingency management procedures. Journal of Clinical Child Psychology, 12, 202–206.
Richardson, G. M., McGrath, P. J., Cuningham, S. J., & Humphreys, O. (1983). Validity of the headache diary for children. Headache, 23, 184–187.
Richter, I. L., McGrath, P. J., Humphreys, P. J., Goodman, J. T., Firestone, P., & Keene, D. (1986). Cognitive and relaxation treatment of paediatric migraine. Pain, 25, 195–203.
Rosenstock, H. A., & Cambor, C. G. (1979). Family therapy approach to incapacitating migraine. International Journal of Family Therapy, 1, 46–55.
Rowan, A. B., & Andrasik, F. (1996). Efficacy and cost-effectiveness of minimal therapist contact treatments of chronic headaches: A review. Behavior Therapy, 27, 207–234.
Sillanpää, M. (1976). Prevalence of migraine and other headache in Finnish children starting school. Headache, 15, 288–290.
Warranch, H., & Keenan, D. M. (1985). Behavioral treatment of children with recurrent headaches. Journal of Behavior Therapy and Experimental Psychiatry, 16, 31–38.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kröner-Herwig, B., Mohn, U. & Pothmann, R. Comparison of Biofeedback and Relaxation in the Treatment of Pediatric Headache and the Influence of Parent Involvement on Outcome. Appl Psychophysiol Biofeedback 23, 143–157 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022267104369
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022267104369