Abstract
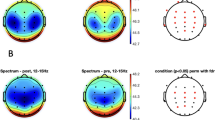
The present piece of research studied the spontaneous alpha rhythm of the human brain by combining the use of a whole-cortex neuromagnetometer and Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Single trials of spontaneous brain activity were recorded from ten human subjects asked to rest, with their eyes either closed or open, in relaxed wakefulness. MEG measurements were conducted over a period of one and a half years. The replicability of the results was confirmed for eight subjects out of ten. For three subjects, the alpha rhythm did not show any reductions due to the opening of the eyes. Both field map pattern and location of the estimated source were persistently stationary during each of the bursts of oscillations of the alpha rhythm. Dipoles were concentrated in clusters, indicating the existence of several spatially distributed sources. The calcarine fissure, the parieto-occipital sulcus and the surrounding occipital and parieto-occipital areas were identified as cortical sites of the brain where the alpha rhythm may originate. For four subjects, the majority of the sources were located near or in the calcarine fissure, while for five subjects, they were located near or in the parieto-occipital sulcus and for the remaining subject they were equally divided between the two generation sites.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chapman, R.M., Ilmonemi, R.J., Barbanera, S. and Romani, G.L. Selective localization of alpha brain activity with neuromagnetic measurements. Electroenceph. clin. Neurophysiol., 1984, 58: 569–572.
Duffy, F.H., Iyer, V.G. and Surwillo, W.W. The normal EEG. In: F.H. Duffy, V.G. Iyer and W.W. Surwillo (Eds.), Clinical Electroencephalography and Topographic mapping. (Springer Verlag), 1989: 99–132.
Gharib, S., Sutherling, W.W., Nakasato, N., Barth, D.S., Baumgartner, C.A., Alexopoulos, N., Taylor, S. and Rogers, R.L. MEG and ECoG localization accuracy test. Electroenceph. clin. Neurophysiol., 1995, 94: 109–114.
Lehmann, D., Ozaki, H. and Pal, I. EEG alpha map series: brain micro-states by space-oriented adaptive segmentation. Electroenceph. clin. Neurophysiol., 1987, 67: 271–288.
Lehmann, D. and Koenig, T. Spatio-temporal dynamics of alpha brain electric fields, and cognitive modes. International Journal of Psychophysiology, 1997, 26: 99–112.
Lopes da Silva, F.H., Van Lierop, T.H.M.T., Schrijer, C.F. and Storm Van Leeuwen. Organization of thalamic and cortical alpha rhythms: Spectra and Coherences. Electroenceph. clin. Neurophysiol., 1973, 35: 627–639.
Lopes da Silva, F.H. and Storm Van Leeuwen, W. The cortical source of the alpha rhythm. Neurosci. Lett., 1977, 6: 237–241.
Lopes da Silva, F.H., Vos, J.E., Mooibroek, J. and Van Rooterdam, A. Relative contributions of intracortical and thalamo-cortical processes in the generation of alpha rhythms, revealed by partial coherence analysis. Electroenceph. clin. Neurophysiol., 1980, 50: 449–456.
Rodin, E.A. and Rodin, M.J. Dipole sources of the human alpha rhythm. Brain Topography, 1995, 7: 201–208.
Salenius, S., Kajola, M., Thompson, W.L., Kosslyn, S. and Hari, R. Reactivity of magnetic parieto-occipital alpha rhythm during visual imagery. Electroenceph. clin. Neurophysiol., 1995, 95: 453–462.
Salmelin, R. and Hari, R. Characterization of spontaneous MEG rhythms in healthy adults. Electroenceph. clin. Neurophysiol., 1994, 91: 237–248.
Salmelin, R., Hari, R., Lounasmaa, O. and Sams, M. Dynamics of brain activation during picture naming. Nature, 1994, 368: 463–465.
Steriade, M., Gloor, P., Llinas, R.R., Lopes da Silva, F.H. and Mesulam, M.M. Basic mechanisms of cerebral rhythmic activities. Electroenceph. clin. Neurophysiol., 1990, 76: 481–508.
Wieringa, H.J. Integration of the MEG and EEG with the MRI. In: MEG, EEG and the integration with Magnetic Resonance Images. (Enschede, The Netherlands), 1993: 57–72.
Williamson, S. and Kaufmann, L. Advances in neuromagnetic instrumentation and studies of spontaneous brain activity. Brain Topography, 1989, 2: 129–139.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ciulla, C., Takeda, T. & Endo, H. MEG Characterization of Spontaneous Alpha Rhythm in the Human Brain. Brain Topogr 11, 211–222 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022233828999
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022233828999