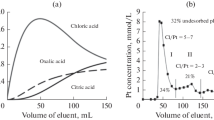
Abstract
The point of zero charge (PZC) of common oxide catalyst supports such as alumina and silica can be altered by doping with anions such as Cl-, which lower the ZPC, or cations such as Na+ or K+, which raise the PZC. In a prior work it was shown that such alterations did not influence the properties of either support toward the adsorption of either cationic amine or anionic chloride complexes of Pt(IV) [1]. This follow-up work explored the hypothesis that in the pH range of interest (low pH over cation-doped silica, high pH over anion-doped alumina) the dopant is dissolved and the surface behaves as pure.
The PZCs of doped silica and alumina washed in acidic, neutral, and basic solutions was measured by the EpHL (equilibrium pH at high loading) technique. Repeated acid washes of K+-doped, PZC-raised silica quickly brought the PZC back to that of the pure oxide, and the same was observed for basic washed, PZC-lowered Cl--doped alumina. Thus, ion doping of silica and alumina does not appear to create irreversible changes in the materials' PZC and cannot be used to influence adsorptive properties.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
W. A. Spieker and J. R. Regalbuto, Stud. Surf. Sci. Catal. 130 (2000) 203.
J. P. Brunelle, Pure Appl. Chem. 50 (1978) 1211.
C. Contescu and M. I. Vass, Appl. Catal. 33 (1987) 259.
A. Shah and J. R. Regalbuto, Langmuir 10 (1994) 500.
N. Santhanam, T. A. Conforti, W. A. Spieker and J. R. Regalbuto, Catal. Today, 21 (1994) 141.
J. R. Regalbuto, A. Navada, S. Shadid, M. L. Bricker and Q. Chen, J. Catal. 184 (1999) 335.
W. A. Spieker and J. R. Regalbuto, Chem. Eng. Sci. 56 (2000) 2365.
B. Shelimov, J.-F. Lambert, M. Che and B. Didillon, J. Mol. Catal. 158 (2000) 91.
W. A. Spieker, J. Liu, X. Hao, J. T. Miller, A. J. Kropf and J. R. Regalbuto, Appl. Catal. A: Gen., in press.
J. A. Mieth, J. A. Schwarz, Y.-J. Huangand S. C. Fung, J. Catal. 122 (1990) 202.
K.Ch. Akratopulu, L. Vordonis and A. Lycourghiotis, J. Catal. 109 (1988) 41.
J. Park and J. R. Regalbuto, J. Coll. Interf. Sci. 175 (1995) 239.
J. R. Regalbuto, M. Schrier, X. Hao, W. A. Spieker, J. G. Kim, J. T. Miller and A. J. Kropf, Stud. Surf. Sci. Catal. 143 (2002) 45.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Korah, J., Spieker, W. & Regalbuto, J. Why Ion-Doped, PZC-Altered Silica and Alumina Fail to Influence Platinum Adsorption. Catalysis Letters 85, 123–127 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022189312386
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022189312386