Abstract
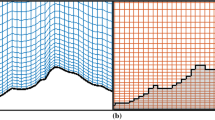
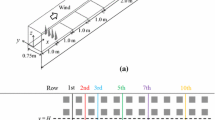
A multiple-cell flat-level tracer dispersion model is developed for atmospheric pollution study. The horizontal domain may be constructed with multiple-sized cells for varied resolution. The sequence of cells is arbitrary, as in unstructured grids, as long as no holes are left in the horizontal domain, which may be tailored in shape according to local orography. The vertical levels are truly flat and the level spacing may vary from level to level. The surface orography is included by removing cells from the bottom of the three-dimensional cell block. The arrangement of wind velocity and tracer concentration is similar to the Arakawa C grid. Advection and horizontal diffusion are formulated on each cell face, using tracer concentrations in the two cells that share the cell face. Pointer-orientated numerical loops are used to facilitate the arbitrary horizontal cell arrangement and orographic variation of vertical levels. A second-order upstream upper limiter advection scheme is developed for this model and numerically tested to be positive-definite and mass conserving. Vertical diffusion is solved with an implicit scheme and simplified vertical diffusivity, which is parameterised as a function of the mixing layer depth. The model is fast, compact, easy to implement and highly portable. It is suitable for studies ofmesoscale and small-scale atmospheric tracer dispersion over complex terrain, including steep slopes. The model is used to simulate traffic pollution in London, UK, and is compared with available observations.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barratt, B., Beevers, S., Buckingham, C., Carslaw, D., Fuller, G., Hedley, S., Hutchinson, D., and Rice, J.: 1997, The AIM Project and Air Quality in London 1996, South East Institute of Public Health, Tunbridge Wells, Kent TN3 0XT, U.K., 216 pp.
Berger, M. and Oliger, J.: 1984, 'Adaptive Mesh Refinement for Hyperbolic Partial Differential Equations', J. Comput. Phys. 53, 484–512.
Blayo, E. and Debreu, L.: 1999, 'Adaptive Mesh Refinement for Finite-Difference Ocean Models: First Experiments', J. Phys. Oceanog. 29, 1239–1250.
Bott, A.: 1993, 'The Monotone Area-Preserving Flux-Form Advection Algorithm: Reducing the Time-Splitting Error in Two-Dimensional Flow Fields', Mon. Wea. Rev. 121, 2637–2641.
Carpenter, K. M.: 1979, 'An Experimental Forecast Using a Non-Hydrostatic Mesoscale Model', Quart. J. Roy. Meteorol. Soc. 105, 629–655.
Cox, M. D.: 1985, 'An Eddy-Resolving Numerical Model of the Ventilated Thermocline', J. Phys. Oceanog. 15, 1312–1324.
Crowley, W. P.: 1968, 'Numerical Advection Experiments', Mon. Wea. Rev. 96, 1–11.
Derwent, R. G., Middleton, D. R., Field, R. A., Goldstone, M. E., Lester, J. N., and Perry, R.: 1995, 'Analysis and Interpretation of Air Quality Data from an Urban Roadside Location in Central London over the Period from July 1991 to July 1992', Atmos. Environ. 29, 923–946.
Gifford, F. A.: 1985, 'Atmospheric Diffusion in the Range 20–2000 km', in C. De Wispelaere et al. (eds.), Air Pollution Modelling and its Application, Vol. V, Plenum Press, New York, pp. 247–252.
Godowitch, J. M., Ching, J. K. S., and Clarke, J. F.: 1985, 'Evolution of the Nocturnal Inversion Layer at an Urban and Nonurban Location', J. Clim. Appl. Meteorol. 24, 791–804.
Golding, B. W.: 1987, 'The U.K. Meteorological Office Mesoscale Model', Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 41, 91–107.
Leonard, B. P.: 1996, 'Conservative Explicit Unrestricted-Time-Step Multidimensional Constancy-Preserving Advection Scheme', Mon. Wea. Rev. 124, 2588–2606.
Leone, Jr. J. M. and Lee, R. L.: 1989, 'Numerical Simulation of Drainage Flow in Brush Creek, Colorado', J. Appl. Meteorol. 28, 530–542.
Li, J. G. and Atkinson, B. W.: 1999, 'Transition Regimes in Valley Airflows', Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 91, 385–411.
Li, J. G. and Atkinson, B. W.: 2000, 'An Inert Tracer Dispersion Scheme for Use in a Mesoscale Atmospheric Model', Atmos. Environ. 34, 4011–4018.
Mesinger, F., Janjic, A. I., Nickovic, S., Gavrilov, D., and Deaven, D. G.: 1988, 'The Step-Mountain Coordinate: Model Description and Performance for Cases of Alpine Lee Cyclogenesis and for a Case of an Appalachian Redevelopment', Mon. Wea. Rev. 116, 1493–1518.
Peters, L. K., Berkowitz, C. M., Carmichael, G. R., Easter, R. C., Fairweather, G., Gham, S. J., Hales, J. M., Leung, L. R., Pennell, W. R., Potra, F. A., Saylor, R. D., and Tsang, T. T.: 1995, 'The Current State and Future Direction of Eulerian Models in Simulating the Tropospheric Chemistry and Transport of Trace Species: A Review', Atmos. Environ. 29, 189–222.
Pielke, R. A.: 1984, Mesoscale Meteorological Modeling, Academic Press, Orlando, FL, 612 pp.
Pielke, R. A., Cotton, W. R., Walko, R. L., Tremback, C. J., Lyons, W. A., Grasso, L. D., Nicholls, M. E., Moran, M. D., Wesley, D. Z., Lee, T. J., and Copeland, J. G.: 1992, 'A Comprehensive Meteorological Modeling System-RAMS', Meteorol. Atmos. Phys. 49, 69–91.
Skamarock, W. C. and Klemp, J. B.: 1993, 'Adaptive Grid Refinement for 2D and 3D Nonhydrostatic Atmospheric Flowes', Mon. Wea. Rev. 121, 788–804.
Smolarkiewicz, P. K.: 1982, 'The Multi-Dimensional Crowley Advection Schemes', Mon. Wea. Rev. 110, 1968–1983.
Smolarkiewicz, P. K. and Grabowski, W. W.: 1990, 'The Multidimensional Positive Definite Advection Transport Algorithm: Nonoscillatory Option', J. Comput. Phys. 86, 355–375.
Staniforth, A., Cote, J., and Pudykiewicz, J.: 1987, 'Comments on “Smolarkiewicz's Deformation Flow”', Mon. Wea. Rev. 115, 894–900.
Stull, R. B.: 1988, An Introduction to Boundary Layer Meteorology, Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, 666 pp.
Tapp, M. C. and White, P.W.: 1976, 'A Non-Hydrostatic Mesoscale Model', Quart. J. Roy. Meteorol. Soc. 102, 277–296.
Thuburn, J.: 1997, 'TVD Schemes, Positive Schemes, and the Universal Limiter', Mon. Wea. Rev. 125, 1990–1993.
Tremback, C. J., Powell, J., Cotton, W. R., and Pielke, R. A.: 1987, 'The Forward-in-Time Upstream Advection Scheme: Extension to Higher Orders', Mon. Wea. Rev. 115, 540–555.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, JG. A Multiple-Cell Flat-Level Model for Atmospheric Tracer Dispersion over Complex Terrain. Boundary-Layer Meteorology 107, 289–322 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022115808637
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022115808637