Abstract
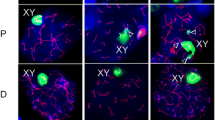
During meiosis in male mammals, the X and Y chromosomes become heterochromatic and transcriptionally silent, and form the XY body. Although the HP1 proteins are known to be involved in the packaging of chromosomal DNA into repressive heterochromatin domains, their involvement in facultative heterochromatinization has not been precisely determined. Here, we analyse, for the first time in humans, the subcellular distribution of the heterochromatin protein HP1α, HP1β and HP1γ isoforms, in male pachytene spermatocytes, and the XY body facultative heterochromatin in particular. Our results demonstrate that HP1β and HP1γ, but not the HP1α isoforms, decorate the entire XY body in half the pachytene nuclei observed. In some nuclei, the XY body appears to be only partially labelled. In these cases, the HP1β and HP1γ signals are adjacent to the Yq12 constitutive heterochromatin and signal appears to originate in this region before spreading over the entire XY body. This distribution suggests that HP1β and HP1γ proteins, which are components of the constitutive heterochromatin, may also be involved in the facultative heterochromatinization of the XY body. Nevertheless, their absence from the early pachytene substage, even though the XY body is already condensed, suggests that these proteins are not involved in the initiation of this process.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ayoub N, Richler C, Wahrman J (1997) Xist RNA is associated with the transcriptionally inactive XY body in mammalian male meiosis. Chromosoma 106: 1-10.
Bannister AJ, Zegerman P, Partridge JF et al. (2001) Selective recognition of methylated lysine 9 on histone H3 by the HP1 chromo domain. Nature 410(6824): 120-124.
Barlow AL, Benson FE, West SC, Hulten MA (1997) Distribution of the Rad 51 recombinase in human and mouse spermatocytes. EMBO J 16(17): 5207-5215.
Cowell IG, Aucott R, Mahadevaiah SK et al. (2002) Heterochromatin, HP1 and methylation at lysine 9 of histone H3 in animals. Chromosoma 111: 22-36.
Eissenberg JC, Elgin S (2000) The HP1 protein family: getting a grip on chromatin. Curr Opin Genet Dev 10(2): 204-210.
Furuta K, Chan EK, Kiyosawa K, Reimer G, Luderschmidt C, Tan EM (1997) Heterochromatin protein HP1Hsbeta (p25beta) and its localization with centromeres in mitosis. Chromosoma 106(1): 11-19.
Hoyer-Fender S, Costanzi C, Pehrson JR (2000) Histone macroH2A1.2 is concentrated in the XY-body by the early pachytene stage of spermatogenesis. Exp Cell Res 258(2): 254-260.
Kellum R, Alberts BM (1995) Heterochromatin protein 1 is required for correct chromosome segregation in Drosophila embryos. J Cell Sci 108(Pt 4): 1419-1431.
Kralewski M, Novello A, Bennavente R (1997) A novel Mr 77,000 protein of the XY body of mammalian spermatocytes: its localization in normal animals and in Searle's translocation carriers. Chromosoma 106: 160-167.
Lachner M, O'Carroll D, Rea S, Mechtler K, Jenuwein T (2001) Methylation of histone H3 lysine 9 creates a binding site for HP1 proteins. Nature 410(6824): 116-120.
McKee BD, Handel MA (1993) Sex chromosomes, recombination, and chromatin conformation. Chromosoma 102(2): 71-80.
Metzler-Guillemain C, Mignon C, Depetris D, Guichaoua MR, Mattei MG (1999) Bivalent 15 regularly associates with the sex vesicle in normal male meiosis. Chromosome Res 7: 369-378.
Metzler-Guillemain C, Usson Y, Mignon C et al. (2000) Organization of the X and Y chromosomes in human, chimpanzee and mouse pachytene nuclei using molecular cytogenetics and three-dimensional confocal analyses. Chromosome Res 8(7): 571-584.
Minc E, Allory Y, Worman HJ, Courvalin JC, Buendia B (1999) Localization and phosphorylation of HP1 proteins during the cell cycle in mammalian cells. Chromosoma 108(4): 220-234.
Minc E, Courvalin JC, Buendia B (2000) HP1gamma associates with euchromatin and heterochromatin in mammalian nuclei and chromosomes. Cytogenet Cell Genet 90(3-4): 279-284.
Motzkus D, Singh PB, Hoyer-Fender S (1999) M31, a murine homolog of drosophila HP1, is concentrated in the XY body during spermatogenesis. Cytogenet Cell Genet 86: 83-88.
Muchardt C, Guilleme M, Seeler JS, Trouche D, Dejean A, Yaniv M (2002) Coordinated methyl and RNA binding is required for heterochromatin localization of mammalian HP1{alpha}. EMBO Rep 3(10): 975-981.
Nielsen AL, Oulad-Abdelghani M, Ortiz JA, Remboutsika E, Chambon P, Losson R (2001) Heterochromatin formation in mammalian cells: interaction between histones and HP1 proteins. Mol Cell 7(4): 729-739.
O'Carroll D, Scherthan H, Peters AH et al. (2000) Isolation and characterization of Suv39h2, a second histone H3 methyltransferase gene that displays testis-specific expression. Mol Cell Biol 20(24): 9423-9433.
Perche PY, Vourch C, Konecny L et al. (2000) Higher concentrations of histone macroH2A in the Barr body are correlated with higher nucleosome density. Curr Biol 10(23): 1531-1534.
Peters AH, Mermoud JE, O'Carroll D et al. (2002) Histone H3 lysine 9 methylation is an epigenetic imprint of facultative heterochromatin. Nat Genet 30(1): 77-80.
Salido EC, Yen PH, Mohandas TK, Shapiro LJ (1992) Expression of the X-inactivation-associated gene Xist during spermatogenesis. Nat Genet 2: 196-199.
Smith A, Benavente R (1992) Meiosis-specific protein selectively associated with sex chromosomes of rat pachytene spermatocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89: 6938-6942.
Solari AJ (1980) Synaptonemel complexes and associated structures in microspread human spermatocytes. Chromosoma 81: 315-337.
Solari AJ (1989) Sex chromosome pairing and fertility in the heterogametic sex of mammals and birds. In: Gillies CB, ed. Fertility and Chromosome pairing. Recent Studies in Plants and Animals. Boca Raton, Fla.: CRC Press, pp 77-107.
Turner JM, Mahadevaiah SK, Benavente R, Offenberg HH, Heyting C, Burgoyne PS (2000) Analysis ofmalemeiotic ''sex body'' proteins during XY female meiosis provides new insights into their functions. Chromosoma 109(6): 426-432.
Turner JM, Burgoyne PS, Singh PB (2001) M31 and macroH2A1.2 colocalise at the pseudoautosomal region during mouse meiosis. J Cell Sci 114(Pt 18): 3367-3375.
Turner JM, Mahadevaiah SK, Elliott DJ et al. (2002) Meiotic sex chromosome inactivation in male mice with targeted disruptions of Xist. J Cell Sci 115 (Pt 21): 4097-4105.
Wreggett KA, Hill F, James PS, Hutchings A, Butcher GW, Singh PB (1994) A mammalian homologue of Drosophila heterochromatin protein 1 (HP1) is a component of constitutive heterochromatin. Cytogenet Cell Genet 66(2): 99-103.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Metzler-Guillemain, C., Luciani, J., Depetris, D. et al. HP1β and HP1γ, but not HP1α, decorate the entire XY body during human male meiosis. Chromosome Res 11, 73–81 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022014217196
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022014217196