Abstract
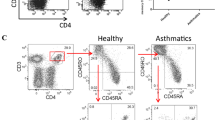
The helper (Th)2 cell-attracting chemokines thymus and activation-regulated chemokine (TARC)4 and macrophage-derived chemokine (MDC) are ligands for the chemokine receptor CCR4. A number of cellular sources of TARC and MDC have been identified, including not only macrophages, dendritic cells, and natural killer cells, but also bronchial epithelial cells. Recent studies report that TARC and MDC may serve as pivotal chemokines for the development of Th2-dominated experimental allergen-induced asthma. This study was designed to assess TARC and MDC production by CD4+ T cells, including naive T cells and memory/effector T cells, purified from peripheral blood mononuclear cells in patients with asthma. Asthmatic subjects included in this study had mild asthmatic symptoms, positive skin test responses to house dust mite allergen, and elevated level of Dermatophagoides farinae immunoglobulin E in the sera. CD4+ T cells—CD45RA+CD4+ T cells—as naive T cells and CD45RO+CD4+ T cells—as memory/effector T cells—were purified by negative selection from peripheral blood mononuclear cells obtained from asthmatic patients (n = 6) and healthy controls (n = 6). These cells and established Th1/Th2 cell lines were then cultured in the presence of both anti-CD3 and -CD28 antibodies. After 48 hr of incubation, concentrations of TARC, MDC, interleukin (IL)-4, IL-5, and interferon-γ in the supernatants were measured by enzyme-linked immunoadsorbent assay. Reverse transcriptase–polymerase chain reaction was performed to analyze mRNA expression of TARC and MDC. Our results clearly showed that TARC and MDC were produced by activated CD45RA+CD4+ T cells rather than by activated CD45RO+CD4+ T cells, and the levels of these chemokines in the asthmatic patients were higher than those in the healthy controls. Furthermore, these chemokines production by Th2 cell lines were greater than those by Th1 cell lines, but the level were smaller than those by naive T cells. Our studies suggest that TARC and MDC are produced by naive T cells rather than by memory/effector T cells, including Th2 cells, in asthmatic patients, and these chemokines were produced at modest levels in any T-cell populations from healthy controls. Taken together, naive T cells in asthma have a peculiar function to produce TRAC and MDC, which contribute to local migration of Th2 cells into lung and lymphoid tissues, along with a function as precursor for memory/effector T cell. This novel function of naive T cells may be implicated in the development of asthma.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Carroll N, Elliot J, Morton A, James A: The structure of large and small airways in nonfatal and fatal asthma. Am Rev Respir Dis 147:405-410, 1993
Haley KJ, Sunday ME, Wiggs BR, Kozakewich HP, Reilly JJ, Mentzer SJ, Sugarbaker DJ, Doerschuk CM, Drazen JM: Inflammatory cell distribution within and along asthmatic airways. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 158:565-572, 1998
Tournoy KG, Kips JC, Pauwels RA: The allergen-induced airway hyperresponsiveness in a human—mouse chimera model of asthma is T cell and IL-4 and IL-5 dependent. J Immunol 166:6982-6991, 2001
Tomkinson, A, Duez C, Cieslewicz G, Pratt JC, Joetham A, Shanafelt, MC, Gundel R, Gelfand EW: A murine IL-4 receptor antagonist that inhibits IL-4-and IL-13-induced responses prevents antigen-induced airway eosinophilia and airway hyperresponsiveness. J Immunol 166:5792-5800, 2001
Kawasaki S, Takizawa H, Yoneyama H, Nakayama T, Fujisawa R, Izumizaki M, Imai T, Yoshie O, Homma I, Yamamoto K, Matsushima K: Intervention of thymus and activation-regulated chemokine attenuates the development of allergic airway inflammation and hyperresponsiveness in mice. J Immunol 166:2055-2062, 2001
Garlisi CG, Falcone A, Hey JA, Paster TM, Fernandez X, Rizzo CA, Minnicozzi M, Jones H, Billah MM, Egan RW, Umland SP: Airway eosinophils, T cells, Th2-type cytokine mRNA, and hyperreactivity in response to aerosol challenge of allergic mice with previously established pulmonary inflammation. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 17:642-651, 1997
Lee SY, Kim SJ, Kwon SS, Kim YK, Kim KH, Moon HS, Song JS, Park SH: Distribution and cytokine production of CD4 and CD8 T-lymphocyte subsets in patients with acute asthma attacks. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol 86:659-664, 2001
Yoshida N, Arima M, Cheng G, Eda F, Hirata H, Honda K, Fukushima F, Fukuda T: Interleukin (IL)-4/IL-9 and exogenous IL-16 induce IL-16 production by BEAS-2B cells, a bronchial epithelial cell line. Cell Immunol 207:75-80, 2001
Jaffar Z, Roberts K, Pandit A, Linsley P, Djukanovic R, Holgate S: B7 costimulation is required for IL-5 and IL-13 secretion by bronchial biopsy tissue of atopic asthmatic subjects in response to allergen stimulation. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 20:153-162, 1999
Crimi E, Gaffi D, Frittoli E, Borgonovo B, Burastero SE: Depletion of circulating allergen-specific TH2 T lymphocytes after allergen exposure in asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol 99:788-797, 1997
Imai T, Chantry D, Raport CJ, Wood CL, Nishimura M, Godiska R, Yoshie O, Gray PW: Macrophage-derived chemokine is a functional ligand for the CC chemokine receptor 4. J Biol Chem 16:1764-1768, 1998
Imai T, Nagira M, Takagi S, Kakizaki M, Nishimura M, Wang J, Gray PW, Matsushima K, Yoshie O: Selective recruitment of CCR4-bearing Th2 cells toward antigen-presenting cells by the CC chemokines thymus and activation-regulated chemokine and macrophage-derived chemokine. Int Immunol 11:81-88, 1999
Hashimoto S, Suzuki T, Dong HY, Nagai S, Yamazaki N, Matsushima K: Serial analysis of gene expression in human monocyte-derived dendritic cells. Blood 94:845-852, 1999
Inngjerdingen M, Damaj, B Maghazachi AA: Human NK cells express CC chemokine receptors 4 and 8 and respond to thymus and activation-regulated chemokine, macrophage-derived chemokine, and I-309. J Immunol 164:4048-4054, 2000
Sekiya T, Miyamasu M, Imanishi M, Yamada H, Nakajima T, Yamaguchi M, Fujisawa T, Pawankar R, Sano Y, Ohta K, Ishii A, Morita Y, Yamamoto K, Matsushima K, Yoshie O, Hirai K: Inducible expression of a Th2-type CC chemokine thymus-and activation-regulated chemokine by human bronchial epithelial cells. J Immunol 165:2205-2213, 2000
Goebeler M, Trautmann A, Voss A, Brocker EW, Toksoy A, Gillitzer R: Differential and sequential expression of multiple chemokines during elicitation of allergic contact hypersensitivity. Am J Pathol 158:431-440, 2001
Vestergaard C, Yoneyama H, Murai M, Nakamura K, Tamaki K, Terashima Y, Imai T, Yoshie O, Irimura T, Mizutani H, Matsushima K: Overproduction of Th2-specific chemokines in NC/Nga mice exhibiting atopic dermatitis-like lesions. J Clin Invest 104:1097-1105, 1999
Panina-Bordignon P, Papi A, Mariani M, Di Lucia P, Casoni G, Bellettato C, Buonsanti C, Miotto D, Mapp C, Villa A, Arrigoni G, M.Fabbri L, Sinigaglia F: The C-C chemokine receptors CCR4 and CCR8 identify airway T cells of allergen-challenged atopic asthmatics. J Clin Invest 107:1357-1364, 2001
Berin MC, Eckmann L, Broide DH, Kagnoff MF: Regulated production of the T helper 2-type T-cell chemoattractant TARC by human bronchial epithelial cells in vitro and in human lung xenografts. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 24:382-389, 2001
National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute: International Consensus Report on diagnosis and treatment of asthma. Eur Respir J 5:601-641, 1992
Chantry D, Romagnani P, Raport CJ, Wood CL, Epp A, Romagnani S, Gray PW: Macrophage-derived chemokine is localized to thymic medullary epithelial cells and is a chemoattractant for CD3(+), CD4(+), CD8(low) thymocytes. Blood. 94:1890-1898, 1999
Chomczynski P: A reagent for the single-step simultaneous isolation of RNA, DNA and proteins from cell and tissue samples. Biotechniques 15: 532-534, 536-537, 1993
Arima M, Plitt J, Stellato C, Bickel C, Motojima S, Makino M, Fukuda T, Schleimer RP: Expression of interleukin-16 by human epithelial cells. Inhibition by dexamethasone. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 21:684-692, 1999
Viola A, Salio M, Tuosto L, Linkert S, Acuto O, Lanzavecchia A: Quantitative contribution of CD4 and CD8 to T cell antigen receptor serial triggering. J Exp Med 186:1775-1779, 1997
Andrew DP, Ruffing N, Kim CH, Miao W, Heath H, Li Y, Murphy K, Campbell JJ, Butcher EC, Wu L: C-C chemokine receptor 4 expression defines a major subset of circulating nonintestinal memory T cells of both Th1 and Th2 potential. J Immunol 166:103-111, 2001
Galli G, Chantry D, Annunziato F, Romagnani P, Cosmi L, Lazzeri E, Manetti R, Maggi E, Gray PW, Romagnani S: Macrophage-derived chemokine production by activated human T cells in vitro and in vivo: Preferential association with the production of type 2 cytokines. Eur J Immunol 30:204-210, 2000
Lenschow DJ, Walunas TL, Bluestone JA: CD28/B7 system of T cell costimulation. Annu Rev Immunol 14:233-258, 1996
D'Ambrosio D, Iellem A, Bonecchi R, Mazzeo D, Sozzani S, Mantovani A, Sinigaglia F: Selective up-regulation of chemokine receptors CCR4 and CCR8 upon activation of polarized human type 2 Th cells. J Immunol 161: 5111-5115, 1998
Zhang S, Lukacs NW, Lawless VA, Kunkel SL, Kaplan MH: Cutting edge: Differential expression of chemokines in Th1 and Th2 cells is dependent on Stat6 but not Stat4. J Immunol 165:10-14, 2000
Sallusto F, Palermo B, Lenig D, Miettinen M, Matikainen S, Julkunen I, Forster R, Burgstahler R, Lipp M, Lanzavecchia A: Distinct patterns and kinetics of chemokine production regulate dendritic cell function. Eur J Immunol 29:1617-1625, 1999
Topham DJ, Castrucci MR, Wingo FS, Belz GT, Doherty PC: The role of antigen in the localization of naive, acutely activated, and memory CD8(+) T cells to the lung during influenza pneumonia. J Immunol 167:6983-6990, 2001
Luettig B, Kaiser M, Bode U, Bell EB, Sparshott SM, Bette M, Westermann J: Naive and memory T cells migrate in comparable numbers through the normal rat lung: Only effector T cells accumulate and proliferate in the lamina propria of the bronchi. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 25:69-77, 2001
Turner SJ, Cross R, Xie W, Doherty PC: Concurrent naive and memory CD8 (+) T cell responses to an influenza A virus. J Immunol 167:2753-2758, 2001
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hirata, H., Arima, M., Cheng, G. et al. Production of TARC and MDC by Naive T Cells in Asthmatic Patients. J Clin Immunol 23, 34–45 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1021948214742
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1021948214742