Abstract
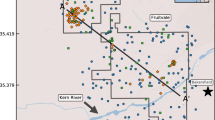
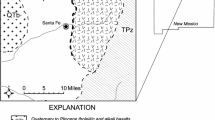
A geographic information system was used to map and analyze nitrate, chloride, sulfate, and fluoride concentrations in 110 wells tapping the Woodbine Aquifer. The study area, covering ninecounties in north-central Texas, includes large percentages of both urban and agricultural land uses. Land use maps were compared with solute concentration data, and statistics were applied to detect associations between solutes, well depth, andland use. Anthropogenic sources such as fertilizer applications and natural sources such as gypsum, lignite, and clay deposits controlled nitrate, chloride, and sulfate concentrations, each inversely correlated with well depth. However, only one nitrate observation – from a shallow well in the aquifer's outcrop zone – surpassed the maximum contaminant level (MCL) of 44.3 mg L-1. By comparison, nearly half of the sulfate and several of the chloride observations surpassed the MCL of 250 mg L-1for each of those ions. Volcanic ash deposits influenced fluorideconcentrations, which directly correlated with well depth. There were no statistically significant associations between solute concentrations and land use. Low recharge rates and confining layers have mitigated anthropogenic impacts on solute levels in the aquifer.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agrawal, V., Vaish, A. K. and Vaish, P.: 1997, 'Groundwater quality: Focus on fluoride and fluorosis in Rajasthan', Current Sci. 73(9), 743-746.
Baker, B., Duffin, G., Flores, R. and Lynch, T.: 1990, Evaluation of Water Resources in Part of North-Central Texas, Texas Water Development Board, Austin, TX.
Bouwer, H.: 1978, Groundwater Hydrology, McGraw-Hill, New York, NY.
Driscoll, F. G.: 1986, Groundwater and Wells, Johnson Division, St. Paul, MN.
EPA (U.S. Environmental Protection Agency): 2000, Drinking Water Standards, U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Washington, DC.
Feth, J. H.: 1981, 'Chloride in natural continental water: A review', U.S. Geolog. Survey Water-Supply Paper 2176, 1-30.
Freeze, R. A. and Cherry, J. A.: 1979, Groundwater, Prentice Hall, Englewood Cliffs, NJ.
Hem, J. D.: 1985, 'Study and interpretation of the chemical characteristics of natural water', U.S. Geolog. Survey Water-Supply Paper 2254, 1-263.
Hopkins, J.: 1996, Water Quality in the Woodbine Aquifer, Texas Water Development Board, Austin, TX.
Jenkins, G. N.: 1982, 'Fluoride and Fluoridation of Water', in A. Neuberger and T. H. Jukes (eds), Human Nutrition, Burgess, Englewood, NJ, pp. 23-72
Johnson, C. J., Bonrod, R. A., Dosch, T. I., Kilness, A. W., Senger, K. A., Busch, D. C. and Meyer, M. R.: 1987, 'Fatal outcome of methemoglobinemia in an infant', J. Amer. Med. Assoc. 256, 2796-2797.
Langley, L.: 1999, Updated Evaluation of Water Resources in Part of North-Central Texas, Texas Water Development Board, Austin, TX.
Mace, R. E., Dutton, A. R. and Nance, H. S.: 1994, 'Water-level declines in the Woodbine, Paluxy, and Trinity Aquifers of North-Central Texas', Gulf Coast Assoc. Geolog. Soc. Trans. 44, 413-420.
Nordstrom, P. L. and Quincy, R.: 1997, Ground-Water Data System Dictionary, Texas Water Development Board, Austin, TX.
Peckham, R. C., Souders, V. L., Dillard, J. W. and Baker, B.: 1963, Reconnaissance Investigation of the Ground-Water Resources of the Trinity River Basin, Texas, Texas Water Commission, Austin, TX.
Ryan, F. R., Joiner, B. L. and Ryan, T. A.: 1992, MINITAB Handbook, 2nd ed., PWS-Kent, Boston, MA.
Scott, J. M. and Jennings, M. D.: 1997, A Description of the National GAP Analysis Program, U.S. Geological Survey, Reston, VA.
Stephenson, L. W.: 1952, 'Larger invertebrate fossils of the Woodbine Formation (Cenomanian) of Texas', U.S. Geolog. Survey Profes. Paper 242, 4-17.
TWC (Texas Water Commission): 1989, Ground-Water Quality of Texas, Texas Water Commission, Austin, TX.
USCB (U.S. Census Bureau): 2001, United States Census 2000, U.S. Census Bureau, Washington, DC.
Ward, M. H., Zahm, S. H. and Blair, A.: 1994, 'Dietary factors and non-Hodgkin's lymphoma', Cancer Caus. Contr. 5(5), 422-432.
Winton, W. M. and Adkins, W. S.: 1919, The Geology of Tarrant County, Bureau of Economic Geology, Austin, TX.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hudak, P.F., Sanmanee, S. Spatial Patterns of Nitrate, Chloride, Sulfate, and Fluoride Concentrations in the Woodbine Aquifer of North-Central Texas. Environ Monit Assess 82, 311–320 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1021946402095
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1021946402095