Abstract
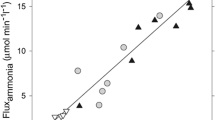
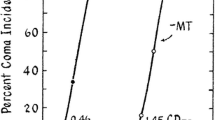
Glutamatergic dysfunction has been suggested to play an important role in the pathogenesis of hepatic encephalopathy (HE) in acute liver failure (ALF). Increased extracellular brain glutamate concentrations have consistently been described in different experimental animal models of ALF and in patients with increased intracranial pressure due to ALF. High brain ammonia levels remain the leading candidate in the pathogenesis of HE in ALF and studies have demonstrated a correlation between ammonia and increased concentrations of extracellular brain glutamate both clinically and in experimental animal models of ALF. Inhibition of glutamate uptake or increased glutamate release from neurons and/or astrocytes could cause an increase in extracellular glutamate. This review analyses the effect of ammonia on glutamate release from (and uptake into) both neurons and astrocytes and how these pathophysiological mechanisms may be involved in the pathogenesis of HE in ALF.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENECES
Araque, A., Li, N., Doyle, R.T., and Haydon, P. (2000). Snare protein-dependent glutamate release from astrocytes. J. Neurosci. 20:666-673.
Bates, T.E., Williams, S.R., Kauppinen, R.A., and Godian, D.G. (1989). Observation of cerebral metabolites in an animal model of acute liver failure in vivo: 1H and 31P nuclear magnetic resonance study. J. Neurochem. 53:102-110.
Bélanger, M., Chan, H., Hazell, A.S., and Butterworth, R.F. (2001). Increased lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) expression and activity in cultured astrocytes exposed to ammonia. J. Neurochem. 78(Suppl. 1):25.
Bender, A.S., and Norenberg, M.D. (1996). Effects of ammonia on L-glutamate uptake in cultured astrocytes. Neurochem. Res. 21:567-573.
Bezzi, P., Carmignoto, G., Pasti, L., Vesce, S., Rossi, D., Rizzini, B.L., et al. (1998). Prostaglandins stimulate calcium-dependent glutamate release in astrocytes. Nature 391:281-285.
Blei, A.T., Olafsson, S.M., Therrien, G., and Butterworth, R.F. (1994). Ammonia-induced cerebral edema and intracranial hypertension in rats after portacaval anastomosis. Hepatology 19:1431-1444.
Bosman, D.K., Deutz, N.E.P., Maas, M.A.W., van Eijk, H.M.H., Smit, J.J.H., de Hann, J.G., et al. (1992). Amino acid release from cerebral cortex in experimental acute liver failure, studied by in vivo cerebral cortex microdialysis. J. Neurochem. 59:591-599.
Bradford, H.F., Ward, H.K., and Foley, P. (1989). Glutaminase inhibition and release of neurtransmitter glutamate from synaptosomes. Brain Res. 476:29-34.
Chan, H., Hazell, A.S., Desjardins, P., and Butterworth, R.F. (2000). Effects of ammonia on glutamate transporter (GLAST) protein and mRNA in cultured rat cortical astrocytes. Neurochem. Int. 37:243-248.
Chatauret, N., Rose, C., Therrien, G., and Butterworth, R.F. (2001). Mild hypothermia prevents cerebral edema and CSF lactate accumulation in acute liver failure. Metab. Brain Dis. 16:95-102.
Clemmensen, J.O., Larsen, F.S., Kondrup, J., Hansen, B.A., and Ott, P. (1999). Cerebral herniation in patients with acute liver failure is correlated with arterial ammonia concentration. Hepatology 29:648-653.
Cordoba, J., Crespin, J., Gottstein, J., and Blei, A.T. (1999). Mild hypothermia modifies ammonia-induced brain edema in rats after portacaval anastomosis. Gastroenterology 116:686-693.
de Knegt, R.J., Kornhuber, J., Schalm, S.W., Rusche, K., Riederer, P., and Tan, J. (1993). Binding of the ligand [3H]MK-801 to the MK-801 binding site of the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor during experimental encephalopathy from acute liver failure and from acute hyperammonemia in the rabbit. Metab. Brain Dis. 8:81-94.
de Knegt, R.J., Schalm, S.W., van der Rijt, C.C.D., Fekkes, D., Dalm, E., and Hekking-Weyma, I. (1994). Extracellular brain glutamate during acute liver failure and during acute hyperammonemia simulating acute liver failure: An experimental study based on in vivo brain dialysis. J. Hepatol. 20:19-26.
Fan, P., Lavoie, J., Lé, N.L.O., Szerb, J.C., and Butterworth, R.F. (1990). Neurochemical and electrophysiological studies on the inhibitory effect of ammonium ions on synaptic transmission in slices of rat hippocampus: Evidence for a postsynaptic action. Neuroscience 37:327-334.
Fan, P., and Szerb, J.C. (1993). Effects of ammonium ions on synaptic transmission and on responses to quisqualate and N-methyl-D-aspartate in hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurons in vitro. Brain Res. 632:225-231.
Ferenci, P., Pappas, S.C., Munson, P.J., Henson, K., and Jones, E.A. (1984). Changes in the status of neurotransmitter receptors in a rabbit model of hepatic encephalopathy. Hepatology 4:186-191.
Hamberger, A., Hedquist, B., and Nystrom, B. (1979). Ammonium ion inhibition of evoked release of endogenous glutamate from hippocampal slices. J. Neurochem. 33:1295-1302.
Hamberger, A., Lindroth, P., and Nystrom, B. (1982). Regulation of glutamate biosynthesis and release in vitro by low levels of ammonium ions. Brain Res. 237:339-350.
Hansson, E., Blomstrand, F., Khabiti, S., Olsson, T., and Rönnback, L. (1997). Glutamate induced astroglial swelling-methods and mechanisms. Acta Neurochir. 70:148-151.
Hawkins, R.A., Miller, A.L., Nielsen, R.C., and Veech, R.L. (1973). The acute action of ammonia on rat brain metabolism in vivo. Biochem. J. 134:1001-1008.
Hilgier, W., Zielinska, M., Borkowska, H.D., Gadamski, R., Walski, M., Oja, S.S., et al. (1999). Changes in the extracellular profiles of neuroactive amino acids in the rat striatum at the symptomatic stage of hepatic failure. J. Neurosci. Res. 56:76-84.
Innocenti, B., Parpura, V., and Haydon, P.G. (2000). Imaging extracellular waves of glutamate during calcium signalling in cultured astrocytes. J. Neurosci. 20:1800-1808.
Jeremic, A., Jeftinija, K., Stevanovic, J., Glavaski, A., and Jeftinija, S. (2001). ATP stimulates calcium-dependent glutamate release from cultured astrocytes. J. Neurochem. 77:664-675.
Kimelberg, H.K., Goderie, S.K., Higman, S., Pang, S., and Waniewski, R.A. (1990). Swelling-induced release of glutamate, aspartate and taurine from astrocyte culture. J. Neurosci. 10:1583-1591.
Knecht, K., Michalak, A., Rose, C., Rothstein, J.D., and Butterworth, R.F. (1997). Decreased glutamate transporter (GLT-1) expression in frontal cortex of rats with acute liver failure. Neurosci. Lett. 229:201-203.
Lai, J.C.K., and Cooper, A.J.L. (1986). Brain α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase complex: Kinetic properties, regional distribution and effects of inhibitors. J. Neurochem. 47:1376-1386.
Marcaida, G., Felipo, V., Hermenegildo, C., Minana, M.-D., and Grisolia, S. (1992). Acute ammonia toxicity is mediated by the NMDA type of glutamate receptors. FEBS Lett. 296:67-68.
Michalak, A., and Butterworth, R.F. (1997). Selective loss of binding sites for the non-NMDA(glutamate) receptor ligands [3H]-kainate and (S)-[3H]-5-fluorowillardiine in the brains of rats with acute liver failure. Hepatology 25:631-635.
Michalak, A., Rose, C., Butterworth, J., and Butterworth, R.F. (1996). Neuroactive amino acides and glutamate (NMDA) receptors in frontal cortex of rats with experimental acute liver failure. Hepatology 24:908-914.
Minelli, A., Lyons, S., Nolte, C., Verkhratsky, A., and Kettenmann, H. (2000). Ammonium triggers calcium elevation in cultured mouse astroglial cells by initiating Ca2+ release from thapsigargin-densitive intracellular stores. Eur. J. Physiol. 439:370-377.
Moroni, F., Mannaioni, G., Cherici, G., Leonardi, P., Carla, V., and Lombardi, G. (1995). Excitatory amino acid neurotransmission and ammonia toxicity. In: Capocaccia, L., Merli, M., and Riggio, O. (eds.), Advances in Hepatic Encephalopathy and Metabolic Nitrogen Exchange, CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL, Chap. 22, pp. 130-139.
Mort, D., Marcaggi, P., Grant, J., and Attwell, D. (2001). Effect of acute exposure to ammonia on glutamate transport in glial cells isolated from the salamander retina. J. Neurophysiol. 86:836-844.
Nicholls, D.G., and Sihra, T.S. (1986). Synaptosomes possess an exocytotic pool of glutamate. Nature 321:772-773.
renbergM.D.BakerL.renbergL.O.B.BlicharskaJ.Bruce-GregarioH.H.andNearyJ.T.1991.Ammonia-inducedastrocyteswellinginprimaryculture.Neurochem.Res. 16:833-836
Norenberg, M.D., Huo, Z., Neary, J.T., and Roig-Cantesano, A. (1997). The glial glutamate transporter in hyperammonemia and hepatic encephalopathy: Relation to energy metabolism and glutamatergic neurotransmission. Glia 21:124-133.
Oppong, K.N.W., Bartlett, K., Record, C.O., and Al Mardini, H. (1995). Synaptosomal glutamate transport in thioacetamide-induced hepatic encephalopathy. Hepatology 22:553-558.
Papura, V., Basarsky, T.A., Liu, F., Jeftinija, K., Jeftinija, S., and Haydon, P.G. (1994). Glutamate-mediated astrocyte-neuron signalling. Nature 369:744-749.
Pasti, L., Zonta, M., Pozzan, T., Vicini, S., and Carmignoto, G. (2001). Cytosolic calcium oscillations in astrocytes may regulate exocytotic release of glutamate. J. Neurosci. 21:477-484.
Raabe,W. (1989). Ammoniumdecreases excitatory synaptic transmission in cat spinal cord in vivo. J. Neurophysiol. 62:1461-1473.
Rose, C., Michalak, A., Rama Rao, K.V., Quack, G., Kircheis, G., and Butterworth, R.F. (1999). L-ornithine-L-aspartate lowers plasma and cerebrospinal fluid ammonia and prevents brain edema in rats with acute liver failure. Hepatology 30:636-640.
Rose, C., Michalak, A., Rambaldi, A., Chatauret, N., Pannunzio, M., and Butterworth, R.F. (2000). Mild hypothermia delays the onset of coma and prevents brain edema and extracellular brain glutamate accumulation in rats with acute liver failure. Hepatology 31:872-877.
Schmidt,W., Wolf, G., Grungreiff, K., Meier, M., and Reum, T. (1990). Hepatic encephalopathy influences high-affinity uptake of transmitter glutamate and aspartate into the hippocampal formation. Metab. Brain Dis. 5:19-31.
Sugden, P.H., and Newsholme, E.A. (1975). The effects of ammonium, inorganic phosphate and potassium ions on the activity of phosphofructokinases from muscle and nervous tissues of vertebrates and invertebrates. Biochem. J. 150:113-122.
Swain, M., Butterworth, R.F., and Blei, A.T. (1992a). Ammonia and related amino acids in the pathogenesis of brain edema in acute liver failure in rats. Hepatology 15:449-453.
Swain, M., Bergeron, M., Audet, R., Blei, A.T., and Butterworth, R.F. (1992b). Monitoring of neurotransmitter amino acids by means of indwelling cisterna magna catheter:Acomparison of two rodent models of fulminant hepatic failure. Hepatology 16:1028-1035.
Szatkowski, M., Barbour, B., and Attwell, D. (1990). Nonvesicular release of glutamate from glial cells by reversed electrogenicglutamate uptake. Nature 348:443-446.
Szerb, J.C., and Butterworth, R.F. (1992). Effect of ammonium ions on synaptic transmission in the mammalian nervous system. Prog. Neurobiol. 39:135-153.
Takahashi, H., Koehler, R.C., Brusilow, S.W., and Traystman, R.J. (1991). Inhibition of brain glutamine accumulation prevents cerebral edema in hyperammonemic rats. Am. J. Physiol. 281:H825-H829.
Tanaka, K., Watase, K., Manabe, T., Yamada, K., Watanabe, M., Takahashi, K., et al. (1997). Epilepsy and exacerbation of brain injury in mice lacking the glutamate transporter GLT-1. Science 276:1699-1702.
Tofteng, F., Jorgensen, L., Ansen, B.A., Ott, P., Kondrup, J., and Larsen, F. (2001). Cerebral microdialysis of glutamate and lactate in patients with fulminant hepatic failure. Hepatology 34:658A. (Abstract No. 1943.)
Vesce, S., Bezzi, P., and Volterra, A. (2001). Synaptic transmission with the glia. News Physiol. Sci. 16:178-184.
Vogels, B.A.P., Maas, M.A.W., Daalhuisen, J., Quack, G., and Chamuleau, R.A.F.M. (1997). Memantine, a noncompetitive NMDA-receptor antagonist improves hyperammonemia-induced encephalopathy and acute hepatic encephalopathy in rats. Hepatology 25:820-827.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rose, C. Increased Extracellular Brain Glutamate in Acute Liver Failure: Decreased Uptake or Increased Release?. Metab Brain Dis 17, 251–261 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1021945515514
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1021945515514