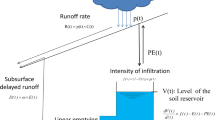
Abstract
This article is a preliminary report of a research activityfocusing on the effects of the crop potentialevapotranspiration (ETp) generation methods on boththe performance of a distributed catchment model as well ason the magnitude of its main effective parameters. Thereferred effects were assessed on the basis of theindependent Multi-Calibration (MC) of the distributed modelfor which three different ETp scenarios were generatedas follows: (A) FAO-24 standard approach;(B) FAO-24 approach but used with coefficients of the wind function and of the Stefan-Boltzmann equation selected according to local conditions; and (C) FAO-56 standard approach. ETp was estimated as a function of the reference crop evapotranspiration (ETo) by means of the k c-ETo approach. For assessing the performance of theestimation approach, the ETo outputs of the three scenarioswere compared to local ETo constraints derived from a previous research. The outputs of scenario B and scenario C showed a close agreement with the local ETo constraints. Their effect on the performance of the hydrological model alsoseemed to be comparable. The output of scenario A producedhigher estimates than the outputs of the other two scenarios, inthe order of 200 mm per year. The best model performance was obtained by using the estimates of scenario A. The research alsorevealed the weak dependency of the model effective parametersinspected in this preliminary research on the ETpestimating methods.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen, G. R., Pereira, L. S., Raes, D. and Martin, S.: 1998, FAO Irrigation and Drainage Paper 56: Crop Evapotranspiration-Guidelines for Computing Crop Water Requirements, FAO, Rome, p. 300.
Anderson, M. P. and Woessner, W. W.: 1992, Applied Groundwater Modelling Simulation of Flow and Advective Transport, University Press, U.S.A., p. 296.
Bagarello, V. and Iovino, M.: 1999, ‘Spatial and Temporal Variability of Saturated Hydraulic Conductivity in a Central Sicily Soil’ in Proceedings of the International Workshop of EurAgEng's Field of Interest on Soil and Water ‘Modelling of Transport Processes in Soils at Various Scales in Time and Space’ Leuven, pp. 249–256.
Beven, K.: 1997, ‘Topmodel: A critique’ Hydrol. Processes 11, 1069–1085.
Boons-Prins, E. R., De Koning, G. H. J., Van Diepen, C. A. and Penning de Vries, F. W. T.: 1993, in Simulation Report CABO-TT (Vol. 32), Crop Specific Simulation Parameters for Yield Forecasting Across the European Community, Centre for Agrobiological Research and Winand Staring Centre for Integrated Land, Soil and Water Research, Wageningen, The Netherlands.
Chow, V. T., Maidment, D. R. and Mays, L. W.: 1988, Applied Hydrology, McGraw-Hill International Editions, Singapore, p. 572.
DHI: 1998, in MIKE-SHE v.5.3 User Guide and Technical Reference Manual, Danish Hydraulic Institute, Denmark, p. 50.
Doorenbos, J. and Pruitt, W. O.: 1977, FAO Irrigation and Drainage Paper 24: Crop Water Requirements, FAO, Rome, p. 156.
Edwards, W. R. N.: 1986, ‘Precision weighing lysimetry for trees, using a simplified tared-balance design’ Tree Physiol. 1, 127–144.
Engman, E. T.: 1986, ‘Roughness coefficients for routing surface runoff’ J. Irrigat. Drainage Engineer. 112(1), 39–53.
Feyen, L., Vázquez, R., Christiaens, K., Sels, O. and Feyen, J.: 2000, ‘Application of a distributed physically-based hydrological model to a medium size catchment’ Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 4(1), 47–63.
Gellens-Meulenberghs, F. and Gellens, D.: 1992, in Internal Publication (A 130) L'evapotranspiration Potentielle en Belgique: Variabilité Spatiale et Temporelle, Belgian Meteorological Institute, Brussels, p. 23.
Groot, J. J. R.: 1987, in Simulation Report CABO-TT Vol. (13) Simulation of Nitrogen Balance in a System of Winter Wheat and Soil, Centre for Agrobiological Research and Department of Theoretical Production Ecology, Wageningen, p. 50.
Gupta, H. V., Sorooshian, S. and Yapo, P. O.: 1998, ‘Toward improved calibration of hydrologic models: Multiple and noncommensurable measures of information’ Water Resour. Res. 34(4), 751–763.
Hubrechts, L., Vlassak, V., Van Criekingen, A. and Feyen, J.: 1997, in Internal Publication (48) Handleiding bij AARDEWERK-SISBIS: Bevraginssysteem voor Bodemprofielgegevens, Bodemoppervlaktegegevens en Bodemgeschiktheids-gegevens, Institute for Land and Water Management (K.U. Leuven), Leuven, p. 56.
Hupet, F. and Vanclooster, M.: 2001, ‘Effect of the sampling frequency of meteorological variables on the estimation of the reference evapotranspiration’ J. Hydrol. 243, 192–204.
Jensen, M. E., Burman, R. D. and Allen, R. G.: 1990, ASCE Manuals and Reports on Engineeering Practice 70: Evapotranspiration and Irrigation Water Requirements, ASCE, New York, p. 332.
Katz, R. W.: 1999, ‘Extreme value theory for precipitation: Sensitivity analysis for climate change’ Advan. Water Resour. 23(2), 133–139.
Kristensen, K. J. and Jensen, S. E.: 1975, ‘A model for estimating actual evapotranspiration from potential evapotranspiration’ Nordic Hydrol. 6, 170–188.
Legates, D. R. and McCabe, G. J.: 1999, ‘Evaluating the use of ‘goodness-of-fit’ measures in hydrologic and hydroclimate model validation’ Water Resour. Res. 35(1), 233–241.
Loague, K. and Green, R. E.: 1991, ‘Statistical and graphical methods for evaluating solute transport models: Overview and applications’ J. Contam. Hydrol. 7, 51–73.
Lundberg, A., Calder, I. and Harding, R.: 1998, ‘Evaporation of intercepted snow: Measurement and modelling’ J. Hydrol. 206, 151–163.
Morton, F. I.: 1978, ‘Estimating evapotranspiration from potential evaporation-practicality of an iconoclastic approach’ J. Hydrol. 38, 1–32.
Motovilov, Y. G., Gottschalk, L., Engeland, K. and Rodhe, A.: 1999, ‘Validation of a distributed hydrological model against spatial observations’ Agricult. Forest Meteorol. 98–99, 257–277.
Nash, J. E. and Sutcliffe, J. V.: 1970, ‘River flow forecasting through conceptual models: A discussion of principles’ J. Hydrol. 10, 282–290.
Penman, H. L.: 1948, ‘Natural Evaporation from Open Water, Bare Soil and Grass’ Proceedings of the Royal Society of London, Series A 193, pp. 120–146.
Raes, D., Van Aelst, P. and Wyseure, G.: 1986, in ETREF, ETCROP, ETSPLIT and DEFICIT, a Computer Package for Calculating Crop Water Requirements-Reference Manual, Laboratory of Soil and Water Engineering, Leuven, 66.
Refsgaard, J. C. and Storm, B.: 1995, ‘MIKE SHE’ V. P. Singh (ed.), in Computer Models of Watershed Hydrology, Water Resources Publications, U.S.A., pp. 809–846.
Refsgaard, J. C. and Knudsen, J.: 1996, ‘Operational validation and inter-comparison of different types of hydrological models’ Water Resour. Res. 32(7), 2189–2202.
Refsgaard, J. C.: 1997, ‘Parameterisation, calibration and validation of distributed hydrological models’ J. Hydrol. 198, 69–97.
Stedinger, J. R., Vogel, R. M. and Foufoula-Georgiou, E. F.: 1993, ‘Frequency Analysis of Extreme Events’ in D. R. Maidment (ed.), Handbook of Hydrology, McGraw Hill, U.S.A., pp. 18.1–18.66.
Sumner, D. M.: 1996, in Water-Resources Investigations Report (96–4244) Evapotranspiration from Successional Vegetation in a Deforested Area of Lake Wales, Florida, U.S. Geological Survey, p. 37.
Thom, A. S. and Oliver, H. R.: 1977, ‘On Penman's equation for estimating regional evaporation’ J. Royal Meteorol. Soc. 103, 345–357.
Van Genuchten, M. Th.: 1980, ‘A closed form equation for predicting the hydraulic conductivity in unsaturated soils’ Soil Sci. Soc. Amer. J. 44, 892–898.
VanOrshoven, J., Maes, J., Vereecken, H. and Feyen, J.: 1991, ‘A procedure for the statistical characterization of the units of the Belgian soil map’ Pedologie XLI(3), 193–212.
Vázquez, R. F., Feyen, L., Feyen, J. and Refsgaard, J. C.: 2002, ‘Effect of grid-size on effective parameters and model performance of the MIKE SHE code applied to a medium sized catchment’ Hydrol. Process. 16, 355–372.
Vereecken, H.: 1988, in ‘Pedotransferfunctions for the Generation of Hydraulic Properties for Belgian Soils’ Ph.D. Thesis, Laboratory of Land Management (K.U. Leuven), Leuven, p. 254.
Wilson, K. B., Hanson, P. J., Mulholland, P. J., Baldocchi, D. D. and Wullschlenger, S. D.: 2001, ‘A comparison of methods for determining forest evapotranspiration and its components: Sap-flow, soil water budget, eddy covariance and catchment water balance’ Agricult. Forest Meteorol. 106, 153–168.
Xevi, E., Christiaens, K., Espino, A., Sewnandan, W., Mallants, D., Sørensen, H. and Feyen, J.: 1997, ‘Calibration, validation and sensitivity abalysis of the MIKE-SHE model using the Neuenkirchen catchment on case study’ Water Resour. Manag. 11, 219–242.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vázquez Z, R.F., Feyen, J. Assessment of the Performance of a Distributed Code in Relation to the ETp Estimates. Water Resources Management 16, 329–350 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1021903211213
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1021903211213