Abstract
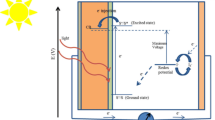
CdSe : Sb thin film electrodes with Sb3+ doping concentrations from 0 to 5 mol % were prepared in an aqueous alkaline medium (pH≈10) by a solution-growth technique. Use of these films was made as an active photoelectrode in an electrochemical photovoltaic cell comprising sulfide/polysulfide as an electrolyte redox couple and impregnated graphite as a counter electrode. The different cell characteristics such as current–voltage and capacitance–voltage in the dark, power output under 20 mW cm−2 constant illumination intensity, built-in-potential, photo and spectral responses were examined. These characteristics were evaluated through such performance parameters as open-circuit voltage (V oc), short-circuit current (I sc), shunt and series resistances (R sh and R s), fill factor (ff%), efficiency (η%), junction ideality factor (n d), lighted quality factor (n L), built-in-potential (ΦB) and the flat-band potential (V fb). Careful inspection of calculated values of these parameters revealed that the cell performance was enhanced after doping the photoelectrode by trivalent antimony. Typically, the power conversion efficiency and fill factor improved from 0.14% to 0.24% and 42% to 51%, respectively, at a doping concentration of 0.1 mol % Sb3+ in CdSe. The incremental changes in the performance parameters, and consequently enhancement in the cell performance, have been explained on the basis of alterations in the electrode properties.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
K. Tsvekova and K. Kochev, Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 31 (1993) 429.
G. S. Shahane, D. S. Sutrave and L. P. Deshmukh, Ind. J. Pure Appl. Phys. 34 (1996) 153.
L. P. Deshmukh and S. G. Holikatti, ibid. 33 (1995) 763.
L. P. Deshmukh and S. G. Holikatti, J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 27 (1994) 1786.
S. H. Pawar and L. P. Deshmukh, Ind. J. Pure Appl. Phys. 22 (1984) 315.
S. Jatar A. C. Rastogi and V. G. Bhide, Pramana 16 (1978) 477.
L. P. Deshmukh, G. S. Shahane and K. M. Garadkar, Ind. J. Pure Appl. Phys. 35 (1997) 560.
G. S. Shahane, B. M. More, C. B. Rotti and L. P. Deshmukh, Mater. Chem. Phys. 47 (1997) 266.
E. U. Masumdar, V. B. Pujari, V. B. Gaikwad, V. B. Patil and L. P. Deshmukh, ibid. (in press).
E. U. Masumdar, V. B. Pujari, V. B. Gaikwad, V. B. Patil and L. P. Deshmukh, Eleventh International Workshop on the Physics of Semiconductor Devices, New Delhi, India, Dec. 11–15, 2001.
A. Aruchamy, G. Aravamudan and G. V. Subbarao, Bull. Mater. Sci. 4 (1982) 483.
K. Rajeshwar, P. Sing and J. Dubow, J. Electrochem. Acta. 23 (1978) 1117.
R. N. Noufi, P. A. Kohl and A. J. Bard, J. Electrochem. Soc. 125 (1978) 375.
L. P. Deshmukh and G. S. Shahane, Int. J. Electron. 83 (1997) 341.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Masumdar, E.U., Deshmukh, L.P., Mane, S.H. et al. CdSe : Sb electrode for photoelectrochemical applications. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Electronics 14, 43–48 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1021579632499
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1021579632499