Abstract
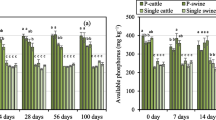
Historically, manure has been recognized as an excellent soil amendment that can improve soil quality and provide nutrients for crop production. In areas of high animal density, however, repeated high applications of manure can lead to phosphorus (P)accumulations in soils, and migration of excess manure P from soils to ground and surface waters has been linked to eutrophication of aquatic systems. The objectives of this study were to determine whether the calcareous co-amendments CaO, Ca(OH)2, cement kiln dust (CKD), and a cement kiln dust/fly ash mixture (CKD/FA) could lower the amount of extractable orthophosphate (ortho-P) in fresh and composted manure, and to monitor extractable ortho-P concentrations in cropped soils that received fresh and composted manure mixed with calcareous co-amendments. Extractable ortho-P concentrations declined by up to 37% in fresh manure and 49% in composted manure with the application of 200 g co-amendment kg-1 manure (dry weight basis), and lower extractable ortho-P levels persisted during a 6 week laboratory incubation. In a greenhouse experiment, fresh manure mixed with CaO and Ca(OH)2 co-amendments inhibited P uptake by barley and decreased extractable ortho-P concentrations in soils. Chemical and biological reactions in plant-soil systems led to the apparent dissolution or desorption of ortho-P from fresh manure mixed with CKD and CKD/FA and composted manure-co-amendment mixtures. Factors controlling the stability of newly formed Ca-P compounds in manure after they are added to plant-soil systems will require further study.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alberta Agriculture.: 1997, Phosphorus Fertilizer Application in Crop Production, Agdex 542-3, Alberta Agriculture, Edmonton, Alberta, Canada.
Chang, C., Sommerfeldt, T. G. and Entz, T.: 1991, ‘Soil chemistry after eleven annual applications of cattle feedlot manure’, J. Environ. Qual. 20, 475–480.
Dao, T. H.: 1999, ‘Coamendments to modify phosphorus extractability and nitrogen/phosphorus ratio in feedlot manure and composted manure’, J. Environ. Qual. 28, 1114–1121.
Eghball, V., Power, J. F., Gilley, J. E. and Doran, J. W.: 1997, ‘Nutrients, carbon, and mass loss during composting of beef cattle feedlot manure’, J. Environ. Qual. 26, 189–193.
Freeze, B., Heigh, J., Larney, F. J. and Olson, A. F.: 1999, ‘Economics of Windrow Composting and Land Application of Manure’, Proceedings of Manure Management’ 99, Saskatoon, Saskatchewan, Canada, pp. 311–320.
Hale, M. G. and Moore, L. D.: 1979, ‘Factors affecting root exudation. II. 1970-1978’, Adv. Agron. 31, 93–124.
Harley, J. L. and Smith, S. E.: 1983, Mycorrhizal Symbiosis, Academic Press, London.
Havlin, J. L., Beaton, J. D., Tisdale, S. L. and Nelson, W. L.: 1999, Soil Fertility and Fertilizers, 6th edn, Macmillan Publishing Co., New York.
Lennox, S. D., Foy, R. H., Smith, R. V. and Jordan, C.: 1997, ‘Estimating the Contribution from Agriculture to the Phosphorus Load in Surface Water’, in H. Tunney, O. T. Carton, P. C. Brookes and A. E. Johnston (eds), Phosphorus Loss from Soil to Water, CAB International, New York, U.S.A., pp. 55–75.
Lindsay, W. L.: 1979, Chemical Equilibria in Soils, John Wiley and Sons, New York.
Liu, F., Mitchell, C. C., Hill, D. T., Odom, J. W. and Rochester, E. W.: 1997, ‘Phosphorus recovery in surface runoff from swine lagoon effluent by overland flow’, J. Environ. Qual. 26, 995–1001.
McKenzie, R. H., Olson, B. M., Larney, F. J. and Davis, J. G.: 2000, ‘Applying Manure Based on Either Nitrogen or Phosphorus Content’, Proceedings of the 37th Annual Alberta Soil Science Workshop, Medicine Hat, Alberta, Canada, pp. 270–275.
Moore, P. A., Jr., Daniel, T. C., Edwards, D. R. and Miller, D. M.: 1995, ‘Effect of chemical amendments on ammonia volatilization from poultry litter’, J. Environ. Qual 24, 293–300.
Moore, P. A., Jr. and Miller, D. M.: 1994, ‘Decreasing phosphorus solubility in poultry litter with aluminum, calcium and iron amendments’, J. Environ. Qual. 23, 325–330.
Mozaffari, M. and Sims, J. T.: 1994, ‘Phosphorus availability and sorption in an Atlantic coastal plain watershed dominated by animal-based agriculture’, Soil Sci. 157, 97–107.
Oguntoyinbo, F. I., Aduayi, E. A. and Sobulo, R. A.: 1996, ‘Effectiveness of some local liming materials in Nigeria as ameliorants of soil acidity’, J. Plant Nutr. 19, 999–1016.
Paik, I. K., Blair, R. and Jacob, J.: 1996, ‘Strategies to reduce environmental pollution from animal manure: principles and nutritional management, a review’, Am. J. Anim. Sci. 9, 615–635.
Parfitt, R. L.: 1978, ‘Anion adsorption by soils and soil materials’, Adv. Agron. 30, 1–50.
Parkinson, J. A. and Allen, S. E.: 1975, ‘A wet oxidation procedure suitable for the determination of nitrogen and mineral nutrients in biological material’, Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 6, 1–11.
Peters, J. M. and Basta, N. T.: 1996, ‘Reduction of excessive bioavailable phosphorus in soils by using municipal and industrial wastes’, J. Environ. Qual. 25, 1236–1241.
Robertson, W. J., Jeffery, R. C. and McPharlin, I. R.: 1997, ‘Residues from bauxite-mining (Red Mud) increase phosphorus retention of a Joel sand without reducing yield of carrots’, Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 28, 1059–1079.
SAS Institute: 1990, SAS Procedures Guide, Version 6, 3rd edn, SAS Institute, Cary NC.
Sharpley, A. N.: 1995, ‘Dependence of runoff phosphorus on extractable soil phosphorus’, J. Environ. Qual. 24, 920–926.
Sharpley, A. N., Daniel, T. C. and Edwards, D. R.: 1993, ‘Phosphorus movement in the landscape’, J. Prod. Agric. 6, 492–500.
Sharpley, A. N. and Tunney, H.: 2000, ‘Phosphorus research strategies to meet agricultural and environmental challenges of the 21st century’, J. Environ. Qual. 29, 176–181.
Shreve, B. R., Moore, P. A., Jr., Daniel, T. C., Edwards, D. R. and Miller, D. M.: 1995, ‘Reduction of phosphorus in runoff from field-applied poultry litter using chemical amendments’, J. Environ. Qual. 24, 106–111.
Sims, J. T., Simard, R. R. and Joern, B. C.: 1998, ‘Phosphorus loss in agricultural drainage: historical perspective and current research’, J. Environ. Qual. 27, 277–293.
Sims, J. T., Vasilas, B. L. and Ghodrati, M.: 1995, ‘Evaluation of fly ash as a soil amendment for the Atlantic coastal plain: II. Soil chemical properties and crop growth’, Water, Air, Soil Poll. 81, 363–372.
Speir, T. W. and Ross, D. J.: 1978, ‘Soil phosphatase and sulfatase’, in R. G. Burns (ed), Soil enzymes, Academic Press, London, pp. 198–250.
Thomas, R. L., Sheard, R. W. and Moyer, J. R.: 1967, ‘Comparison of conventional and automated procedures for nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium analysis of plant material using a single digestion’, Agron. J. 59, 240–243.
Whalen, J. K. and Chang, C.: 2001, ‘Phosphorus accumulation in cultivated soils from long-term annual applications of cattle feedlot manure’, J. Environ. Qual. 30, 229–237.
Zucconi, F., Pera, A, Forte, M. and DeBertoldi, M.: 1981, ‘Evaluating toxicity of immature compost’, Biocycle 22, 54–57.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Whalen, J.K. Calcium CO-Amendments Modify Extractable Orthophosphate Levels in Fresh and Composted Cattle Manure. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution 141, 105–124 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1021398529398
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1021398529398