Abstract
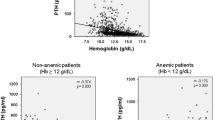
In patients on chronic hemodialysis (CHD)hyperparathyroidism (HPTH) is associated withanemia and resistance to erythropoietin (EPO). This study included 86 CHD elderly pts (meanage 74.8 y, mean time on CHD = 50.5 mos); theywere divided into two groups: I (n = 31) – PTH> 250 pg/mL and II (n = 55) – PTH < 250 pg/mL.All these patients had been on CHD for> 6 mos. No differences were found betweengroups in respect to age, sex distribution andtime on CHD. The levels of creatinine, BUN, Ca,Al, Fe, albumin and ferritin were similar.Group I had a higher P level (5.4 vs 4.3 mg/dL,p = 0.001) and Ca x P (53.5 vs 43.7, p =0.009). Also the Hct (31 vs 33.5%, p = 0.008)and the Hb (10.4 vs 11.2 g/dL, p = 0.009) values werelower in Group I. The EPO dose (88 vs 85 U/kg/week,p = ns) was similar in the two groups.Our data showed that elderly patients with HPTHhave lower Hct and Hb levels than do youngerpatients on a similar EPO dose. We believethese patients will need a more aggressivetherapy with calcitriol.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ali AA, Juhor N, Farmer B, Davenport A. Do elderly hemodialysis patients (> 70 years) respond to erythropoietin (EPO) treatment? J Am Soc Nephrol 1996; 7: 1436.
C. van Ypersele de Strihou. Nephrol Dial Transplant 1999; 14 (Suppl. 2): 37–45.
Winearls CG. Historical review on the use of recombinant human erythropoietin in chronic renal failure. Nephrol Dial Transplant 1995; 10 (Suppl. 2): 3–9.
Danielson B. R-HuEPO hyporesponsiveness – who and why? Nephrol Dial Transplant 1995; 10 (Suppl. 2): 69–73.
Druecke TB. R-HuEPO hyporesponsiveness – who and why? Nephrol Dial Transplant 1995; 10 (Suppl. 2): 62–68.
Eggers PW. Health care policies/economics of the geriatric renal population. Am J Kidney Dis 1990; 16: 384–391.
Eschbach JW, Egrie JC, Downing MR et al. Correction of the anemia of end-stage renal disease with recombinant human erythropoietin. Results of a combined I and II clinical trial. N Engl J Med 1987; 316: 73–78.
European best practice guidelines for the management of anaemia in patients with chronic renal failure. Nephrol Dial Transplant 1999; 14 (Suppl. 5).
Horl WH. Is there a role for adjuvant therapy in patients being treated with epoietin? Nephrol Dial Transplant 1999; 14 (Suppl. 2): 50–60.
Levin NW, Lazarus JM, Nissensson AR. Maximizing patients benefits with epoietin alpha therapy. National Cooperative rHu Erythropoietin Study in patients with chronic renal failure – an iterim report. Am J Kidney Dis 1993; 22 (Suppl. 1): 3–12.
Neves PL. Chronic haemodialysis in elderly patients. Nephrol Dial Transplant 1995; 10 (Suppl. 6): 69–71.
Raine AEG, Margreiter R, Brunner FP et al. Report on management of renal failure in Europe, XXII, 1991. Nephrol Dial Transplant 1992; 7 (Suppl. 2): 7–35.
Rao DS, Shih M-S, Mohini R. Effect of serum parathyroid hormone and bone marrow fibrosis on the response to erythropoietin in uremia. N Engl J Med 1993; 328: 171–175.
Valderrábano F, editor. Eritropoyetina humana recombinante. Masson SA, Barcelona 1998.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Neves, P.L., Triviño, J., Casaubon, F. et al. Elderly patients on chronic hemodialysis: Effect of the secondary hyperparathyroidism on the hemoglobin level. Int Urol Nephrol 34, 147–149 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1021380609993
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1021380609993