Abstract
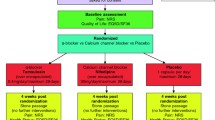
Background:Alpha – 1 blockers decrease the tension and release the spasm of smooth muscles and thus lessen the obstruction and irritation symptoms in the lower urinary tract (LUTS). They make a faster passing of calculi from the terminal part of the ureters possible.Objectives:The goal of this study was to objectively assess the improvement of difficulties caused by obstructions in ureterolithiasis localized in the lower part of the ureters of 104 randomly chosen patients (pts.) in a double-blind study.Methods:During a period of 2 and half years (June 1999–January 2002) 104 pts. suffering from ureterolithiasis of the lower urinary tract were treated and observed. Patients were divided into two groups: A (n:53; later only 51 were evaluated) which was subjected to standard treatment and group B (n:51) where the standard treatment was supplemented by the alpha – 1 blocker. As alpha – 1 blocker one capsule of Tamsulosin /OMNIC 0.4 / was administered daily.Results:With alpha – 1 blocker, we have registered a more speedy passing of calculi from the terminal parts of ureters in 17.6% of pts. Recurrence of renal colics was less frequent and occurred in one of eight pts. as compared with group A (without the alpha – 1 blocker) where a recurrence of the renal colic was observed in about every fifth pts. In group A (n:51), 62.8% of the pts. passed the calculi, whereas in group B (n:51), where standard treatment was supplemented by the administration of the alpha – 1 blocker Tamsulosin, this percentage increased to 80.4%.Conclusion:The treatment by alpha – 1 blockers considerably decreased not only LUTS but also helped to accelerate the passing of minor calculi from the terminal parts of the ureters of 80.4% of pts. It seems that alpha – 1 blockers potentiate the spasmoanalgetic action of drugs used in standard methods of treatment.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Porpiglia F, Destefanis P, Fiori C, Fontana D. Effectiveness of Nifedipine and Deflazacort in the management of distal ureter stones. Urology 2000; 56: 579–583.
Carstensen HE, Hansen JS. Stones in the ureter. Acta Chir Scand 1973; 351: 1797–1801.
Hancock AA, Meyer MD, Brune, ME et al. Fiduxosin: an alfa 1 A/D Receptor Antagonist with Enhanced in vivo uroselectivity. Relative to Terazosin and Tamsulosin. AUA Annual Meeting, Atlanta, Georgia, April 29– May 4, 2000.
Ukhal M, Malomuzh O, Strashny V. Administration of Doxazosine for speedy elimination of stones from lower section of ureter. XIV th. Congress of the EUA, Stockholm, 1999, April 7– 11.
Flam T, Saighi D, Gaél T, Denis T et al. Multiple Sessions Extracorporeal Shock Wave Lithotripsy: For Which stones is it Worth it? XIVth Congress of the EUA, Stockholm, 1999, April 7– 11.
Morse RM, Resnick M. Ureteral calculi: natural history and treatment in era of advanced technology. J Urol 1991; 145: 263–265.
Ueno A, Kawamura T, Ogawa A, Takayasu H. Relation of spontaneous passage ureteral calculi to size. Urology 1977; 10: 544–546.
Hubner WA, Irby P, Stoller ML. Natural history and current concepts for the treatment of small ureteral calculi. Eur Urol 1993; 24: 172–176.
Marenčák J, Moro R. The therapy of ureteral stones: ESWL in situ or endoscopy? Uroló gia (SK) 1997; 2: 67–73.
Cooper JT, Stack GM, Cooper TP. Intensive Medical management of Ureteral Calculi Urology 2000; 56: 575–578.
Michel MC, Bressel HU, Mehlburger L, Goepel M. Tamsulosin real life clinical experience in 19,365 patients. Eur Urol 1998; 34(2): 37–45.
Červenakov I, Fillo J. Our experience with the treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) with Tamsulosin. Bratisl Iek Listy 2001; 102(2): 138–141.
Červenakov Mardiak J, Dimov D, Mala M, Chovan D. Antimicrobial therapy of prostatitis and prostatic syndrome in a combination with alfa 1 blocker (Tamsulosin-Omnic 0,4). Uroló gia (SK) 1999; 5(1): 41–45.
Debruyne FMJ. Alpha-blockers: are all created equal? Urology 2000; 56: 20–22.
Schwinn DA. Novel role for alpha 1-adrenergic receptor subtypes in lower urinary tract symptoms. B J U International 2000; 86, Suppl. 2: 11–22.
Marks LS, Curtis SP, Narayan P et al. Effects of a Highly Selective alpha-1 A Antagonist on Urinary Flow rate in Men with symptomatic BPH. AUA Annual Meeting 2000, Atlanta, April 29– May 4.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Çervenàkov, I., Fillo, J., Mardiak, J. et al. Speedy elimination of ureterolithiasis in lower part of ureters with the alpha 1-blocker – Tamsulosin. Int Urol Nephrol 34, 25–29 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1021368325512
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1021368325512