Abstract
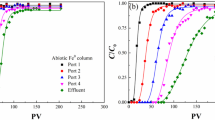
Flow-through columns were used to evaluate the efficacy of permeable reactive iron barriers to treat ground water contamination by RDX. Three columns were packed with iron filings (Fe0) between soil and sand layers, and were fed continuously with unlabeled plus 14C-labeled RDX to characterize its removal efficiency under different microbial conditions. One column was poison-sterilized to isolate chemical degradation processes, another was not poisoned to allow colonization of the Fe0 layer by indigenous microorganisms, and a third column was amended with anaerobic sludge to evaluate the benefits of enhancing biodegradation through bioaugmentation. Extensive RDX removal (>99%) occurred through the Fe0layer of all columns for more than one year, although 14C-label analysis indicated the presence of soluble byproducts such as methylenedinitramine. RDX byproducts accumulated to a lesser extent in biologically active columns, possibly due to enhanced mineralization by the cumulative action of microbial and chemical degradation processes. Denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis (DGGE) profiles and nucleotide sequencing revealed a predominance of Acetobacterium sp. in the iron layer of all columns after 95 days. Such homoacetogenic bacteria probably feed on hydrogen produced during Fe0 corrosion and participate on the RDX degradation process. This notion was supported by batch experiments with a mixed homoacetogenic culture isolated from the bioaugmented column, which degraded RDX and produced acetate when H2 was present. Overall, this work suggests that Fe0barriers can effectively intercept RDX plumes, and that treatment efficiency can be enhanced by biogeochemical interactions though bioaugmentation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adrian, N. R. and Lowder, A.: 1999, ‘Biodegradation of RDX and HMX by a methanogenic en-richment culture’, in B.C. Alleman and A. Leeson (eds.), Bioremediation of Nitroaromatic and Haloaromatic Compounds, Battelle Press, Columbus, OH, USA, pp. 1–6.
Balch, W. E. and Wolfe, R. S.: 1976, ‘A new approach to the cultivation of methanogenic bacteria: 2-mercaptoethanesulfonic acid (HS-CoM)-dependent growth of Methanobacterium ruminantium in a pressurized atmosphere’, Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 32, 781–791.
Blowes, D. W., Ptacek, C., Hanton-Fong, C. and Jambor, J.: 1995, ‘In situ remediation of chromium contaminated groundwater using zero-valent iron’, Abstracts of the 209th American Chemical Society National Meeting, 35, 780–783.
Dejournett, T. and Alvarez, P. J. J.: 2000, ‘Combined microbial-Fe(0) system to remove nitrate from contaminated groundwater’, Bioremed. J. 4, 149–154.
Domenico, P. A. and Schwartz, F. W.: 1998, Physical and Chemical Hydrogeology, Wiley, New York.
Gandhi, S., Oh, B. ‘T., Schnoor, J. L. and Alvarez, P. J.: 2002, ‘Degradation of TCE, Cr(VI), sulfate, and nitrate mixtures by granular iron in flow-through columns under different microbial conditions’, Water Res. 36(8), 1973–1982.
Garg, R., Grasso, D. and Hoag, G.: 1991, ‘Treatment of explosives contaminated lagoon sludge’, Hazard. Waste Hazard. Mater. 8, 319–340.
Helland, B. R., Alvarez, P. J. J. and Schnoor, J. L.: 1995, ‘Reductive dechlorination of carbon tetrachloride with elemental iron’, J. Hazard. Mater. 41, 205–216.
Kaplan, D. I., Cantrell, K. J., Wietsma, T. W. and Potter, M. A.: 1996, ‘Retention of zero-valent iron colloids by sand columns: application to chemical barrier formation’, J. Environ. Cont. 25, 1086–1094.
Maidak, B. L., Cole, J. R., Lilburn, T. G., Parker, Jr., C. T., Saxman, P. R., Stredwick, J. M., Bing Li, G. M., Olsen, G. J., Pramanik, S., Schmidt, T. M. and Tiedje, J. M.: 2000, ‘The RDP (Ribosomal Database Project) continues’, Nucleic Acids Res. 28(1), 173–174.
McCormick, N. G., Cornell, J. H. and Kaplan, A. M.: 1981, ‘Biodegradation of hexahydro-1,3,5-trinitro-1,3,5-triazine’, Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 42(5), 817–823.
Muyzer, G., Dewaal, E. C. and Uitterlinden, A. G.: 1993, ‘Profiling of complex microbial-populations by denaturating gradient gel electrophoresis analysis of polymerase chain reaction-amplified genes coding for 16S ribosomal RNA’, Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 59(3), 695–700.
Oh, B. -T., Just, C. L. and Alvarez, P. J.: 2001, ‘Hexahydro-1,3,5-trinitro-1,3,5-triazine min-eralization by zerovalent iron and mixed anaerobic cultures’, Environ. Sci. Technol. 35(21), 4341–4346.
O'Hannesin, S. F. and Gillham, R. W.: 1998, ‘Long-term performance of an in situ iron wall for remediation of VOCs’, Ground Water 36, 164–170.
Powell, R., Puls, R. W., Hightower, S. and Sabatini, D.: 1995, ‘Coupled iron corrosion and chromate reduction: Mechanisms for subsurface remediation’, Environ. Sci. Technol. 29, 1913–1922.
Price, C. B., Brannon, J. M., Yost, S. L. and Hayes, C. A.: 2001, ‘Relationship between redox potential and pH on RDX transformation in soil-water slurries’, J. Environ. Eng. 127, 26–31.
Rajagopal, B. S. and LeGall, J.: 1989, ‘Utilization of cathodic hydrogen by hydrogen-oxidizing bacteria’, Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 31, 406–412.
Roberts, A., Totten, L., Arnold, W., Burris, D. and Campbell, T.: 1996, ‘Reductive elimination of chlorinated ethylenes by zero-valent metals’, Environ. Sci. Technol. 30, 2654–2659.
Scherer, M. M., Richter, S., Valentine, R. L. and Alvarez, P. J. J.: 2000, ‘Chemistry and microbiology of permeable reactive barriers for in situ groundwater clean up’, Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 30, 363–411.
Sheremata, T. W. and Hawari, J.: 2000, ‘Mineralization of RDX by the white rot fungus Phan-erochaete chrysosporium to carbon dioxide and nitrous oxide’, Environ. Sci. Technol. 34, 3384–3388.
Singh, J., Comfort, S. D. and Shea, P. J.: 1998, ‘Remediating RDX-contaminated water and soil using zero-valent iron’, J. Environ. Qual. 27, 1240–1245.
Till, B. A., Weathers, L. J. and Alvarez, P. J.: 1998, ‘Fe(0)-supported autotrophic denitrification’, Environ. Sci. Technol. 32(5), 634–639.
von Gunten, U. and Zobrist, J.: 1993, ‘Biogeochemical changes in groundwater-infiltration systems: Column studies’, Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta. 57, 3895–3906.
Weathers, L. J., Parkin, G. F. and Alvarez, P. J.: 1997, ‘Utilization of cathodic hydrogen as electron donor for chloroform cometabolism by a mixed methanogenic culture’,Environ. Sci. Technol. 31(3), 880–885.
White, D. C., Pinkart, H. C. and Ringelberg, D. B.: 1997, Manual of Environmental Microbiology, American Society of Metals, Washington, D.C., pp. 91–101.
Wildman, M. J. and Alvarez, P. J.: 2001, ‘RDX degradation using an integrated Fe(0)-microbial treatment approach’, Wat. Sci. Technol. 43(2), 25–33.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Oh, BT., Alvarez, P.J.J. Hexahydro-1,3,5-Trinitro-1,3,5-Triazine (Rdx) Degradation in Biologically-Active Iron Columns. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution 141, 325–335 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1021315723654
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1021315723654