Abstract
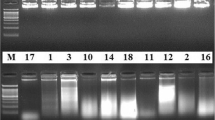
Seed protein profiles by SDS-PAGE were studied in 72 accessions ofSolanum melongena L. and its related taxa in subgenusLeptostemonum (Dunal) Bitter. Comparisons based onJaccard's similarity and UPGMA clustering revealed interrelationships broadly inconformity with the conventional taxonomic treatments. Thus,S. viarum Dunal (sectionAcanthophora Dunal), S.torvum Swartz (section Torva Nees) andS. sisymbriifolium Lam. (sectionCryptocarpum Dunal) were located on separate branches ofthe dendrogram while all taxa of section Melongena Dunal,except S. macrocarpon Dunal, wereclustered closer together. S.melongena, “incanum” and “insanum”,all members of the eggplant complex, were revealed to bear very high similaritywith each other. Most of their accessions had identical band patterns supportingthe contention that these represent an interbreeding complex with limitedgenetic differentiation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anonymous 1990. NBPGR-BARI germplasm collection of egg plant and okra in Bangladesh. IBPGR Newsl. Asia Pacific 3: 4.
Anonymous 1996. Diversity databaseTM. pdi Inc., New York.
Bhaduri P.N. 1951. Inter-relationship of the non-tuberiferous species of Solanum with some consideration on the origin of brinjal (Solanum melongena L.). Indian J. Genet. 11: 75–82.
Chen L.F.O., Cheng M.C. and Chen S.C.G. 1987. Similarity and diveristy of seed proteins in rice varieties. Bot. Bull. Acad. Sinica 28: 169–183.
Clark C.B. 1883. Solanaceae. In: Hooker J.D. (ed.), The Flora of British India. Reeves, Kent, U.K., pp. 228–246.
D'Arcy W.G. 1972. Solanaceas studies II: typification of subdivi sions of Solanum. Ann. Missouri Bot. Gard. 59: 262–278.
Deb D.B. 1989. Solanum melongena, S. incanum versus S. insanum (Solanaceae). Taxon 38: 138–139.
Duthie J.F. 1911. Flora of the Upper Gangetic Plains and of the adjacent Siwalik and sub-Himalayan tracts. Govt. Press, Calcutta. 2.
Edmonds J.W. and Glidewell S.M. 1977. Acrylamide gel electro phoresis of seed proteins from some Solanum (section Solanum) species. Plant Syst. Evol. 127: 277–291.
Hepper F.N. and Jaeger P.M.L. 1985. The typification of six Linnaean names in Solanum. Kew Bull. 40: 387–391.
Karihaloo J.L., Brauner S. and Gottlieb L.D. 1995. Random amplified polymorphic DNA variation in the eggplant Solanum melongena L. (Solanaceae). Theor. Appl. Genet. 90: 767–770.
Karihaloo J.L. and Gottlieb L.D. 1995. Allozyme variation in the eggplant, Solanum melongena L. (Solanaceae). Theor. Appl. Genet. 90: 578–583.
Karihaloo J.L. and Rai M. 1995. Significance of morphological variability in Solanum insanum L. (sensu lato). IPGRI P1. Genet. Res. Newsl. 103: 24–26.
Ladizinsky G.W. and Hymowitz T. 1979. Seed protein electro-phoresis in taxonomic and evolutionary studies. Theor. Appl. Genet. 54: 680–685.
Laemmli V.K. 1970. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227: 680–687.
Lester R.N. and Hasan S.M.Z. 1991. Origin and domestication of the brinjal egg-plant, Solanum melongena, from S. incanum, in Africa and Asia. In: Hawkes J.G., Lester R.N., Nees M. and Estrada N. (eds), Solanaceae III: taxonomy, chemistry, evolution. Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew, pp. 369–387.
Lowry O.H., Rosebrough N.J., Farr A.L. and Randall R.J. 1951. Protein measurement with the Folin-phenol reagent. J. Biol. Chem. 193: 265–275.
Mace E.S., Lester R.N. and Gebhardt C.G. 1999. AFLP analysis of genetic relationships among the cultivated eggplant, Solanum melongena L. and wild relatives (Solanaceae). Theor. Appl. Genet. 99: 626–633.
Pearce K. and Lester R.N. 1979. Chemotaxonomy of the cultivated eggplant — a new look at the taxonomic relationships of Solanum melongena L. In: Hawkes J.G., Lester R.N. and Skelding A.D. (eds), The Biology and Taxonomy of the Solanaceae. Academic Press, London, pp. 615–628.
Prain D. 1903. Bengal Plants. West, Newman & Co., Calcutta. 2.
Przybylska J., Zimniak-Przybylska Z. and Krajewski P. 1998. Diversity of seed albumins in the grass pea (Lathyrus sativus): an electrophoretic study. Genet. Res. Crop Evol. 45: 423–431.
Rohlf F.J. 1993. NTSYS-pc: numerical taxonomy and multivariate analysis system. Version 1.80. Exeter Software, New York.
Roxburgh W. 1832. Flora Indica: or description of Indian plants. Carey's Edition, London.
Sakata Y. and Lester R.N. 1997. Chloroplast DNA diversity in brinjal eggplant (Solanum melongena L.) and related species. Euphytica 97: 295–301.
Sakata Y., Nishio T. and Matthews P.T. 1991. Chloroplast DNA analysis of eggplant (Solanum melongena) and related species for their taxonomic affinity. Euphytica 55: 21–26.
Singh S.P., Nodari R. and Gepts P. 1991. Genetic diversity in cultivated common bean I. allozymes. Crop Sci. 31: 19–23.
Sneath P.H.A. and Sokal R.R. 1973. Numerical taxonomy. W. H. Freeman, California.
Vadivel E. and Bapu J.R.K. 1988. Evaluation and documentation of eggplant germplasm. Capsicum Newsl. 7: 80.
Vavilov N.I. 1951. The origin, variation, immunity and breeding of cultivated plants. Chronica Botanica 13: 1–364.
Whalen M.D. 1984. Conspectus of species groups in Solanum subgenus Leptostemonum. Gentes Herberum 12: 179–282.
Yupsanis T.M., Moustakes M. and Karakoli S. 1992. Seed protein electrophoresis for varietal identification in rice (Oryza sativa L.). J. Agron. Crop Sci. 168: 95–99.
Zeven A.C. and Zhukovsky P.M. 1975. Dictionary of cultivated plants and their centres of diveristy. Centre for Agricultural Publishing and Documentation, Wageningen, Netherlands, p. 219.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Karihaloo, J., Kaur, M. & Singh, S. Seed protein diversity in Solanum melongena L. and its wild and weedy relatives. Genetic Resources and Crop Evolution 49, 533–539 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1021288108928
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1021288108928