Abstract
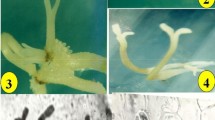
Plant regeneration through indirect somatic embryogenesis has been established on Holostemma ada-kodien Schult. Type of auxin significantly influenced somatic embryogenesis. Friable callus, developed from leaf, internode and root explants on Murashige and Skoog (MS) medium supplemented with 2,4-D (1.0 mg l−1), was most effective for the induction of somatic embryos. Subculture of the friable callus developed on 2,4-D (1.0 mg l−1) onto solid or liquid 1/2 MS medium with 0.1 or 0.5 mg l 2,4-D turned the callus embryogenic. Suspension cultures were superior to static cultures (solid medium) for the induction of somatic embryos. Transfer of embryogenic callus to liquid 1/2 or 1/4 MS medium with lower levels of 2,4-D (0.05–0.1 mg l−1) induced the highest number of somatic embryos. An average of 40 embryos were obtained from 10 mg callus. Fifty per cent embryos exhibited maturation and conversion upon transfer to 1/10 MS basal solid medium. Plantlets were established in field conditions and 90 per cent survived.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
CAMP-1 (1995) The first red list of medicinal plants of South India. Foundation for Revitalisation of Local Health Tradition (FRLHT), Anandnagar, Bangalore, India
Dan M & Shanavaskhan A (1991) A glance to one rare medicinal plant of Western Ghats. In: Karunakaran KC (ed) Proceedings of the Symposium on Rare, Endangered and Endemic Plants of the Western Ghats (pp 221-226). Kerala Forest Department, Trivandrum, India
Ishii Y, Takamura T, Goi M & Tanaka M (1998) Callus induction and somatic embryogenesis of Phalaenopsis. Plant Cell Rep. 17: 446-450
Jayanthi M & Mandal PK (2001) Plant regeneration through somatic embryogenesis and RAPD analysis of regenerated plants in Tylophora indica (Burm. f. Merrill.). In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol. Plant 37: 576-580
Kahl G (1983) Wound repair and tumor induction in higher plants. In: Akazawa T & Imasei H (eds) The New Frontiers in Plant Biochemistry (pp 193-216). Jap. Scientif. Soc. Press Tokyo and Martinus Nijhoff/Dr. Junk W Publ, The Hague
Kirtikar KR & Basu BD (1975) Indian Medicinal Plants. In: Indian Medicinal Plants Vol. III (pp 1620). M/s Bishen Sigh Mahen drapal, New Delhi, India
Kolammal M (1979) Pharmacognosy of Ayurvedic Drugs. Kerala 10. (p. 21). Univ. of Kerala, Trivandrum, India
Murashige T & Skoog F (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays for tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol. Plant. 15: 473-497
Nair KV, Nair AR & Nair CPR (1992) Technoeconomic data on cultivation, preservation of some south Indian medicinal plants. Aryavaidyan 5: 238-240
Palmgren G, Mattsson O & Okkels T (1991) Specific levels of DNA methylation in various tissues, cell lines and cell types of Daucus carota. Plant Physiol. 95: 174-178
Rao PS & Narayanaswamy S (1972) Morphogenetic investigations in callus cultures of Tylophora indica. Physiol. Plant. 27: 271-276
Sahrawat AK & Chand S (2002) Somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration from root segments of Psoralea corylifolia L., an endangered medicinally important plant. In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol. Plant 38: 33-38
Sarasan V, Soniya EV & Nair GM (1994) Regeneration of Indian Sarsaparilla, Hemidesmus indicus R. Br., through organogenesis and somatic embryogenesis. Indian J. Exp. Biol. 32: 284-287
Zimmerman JL (1993) Somatic embryogenesis: A model for early development in higher plants. Plant Cell 5: 1411-1423
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Martin, K. Plant regeneration through somatic embryogenesis on Holostemma ada-kodien, a rare medicinal plant. Plant Cell, Tissue and Organ Culture 72, 79–82 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1021229422172
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1021229422172