Abstract
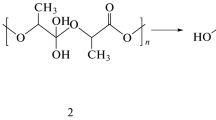
Two lactic acid–based stereocopolymers, namely 50/50 and 96/4 L/D poly(l-lactic-co-d-lactic acids) and corresponding oligomers, were allowed to age under different conditions in order to investigate their toxicity and that of some potential degradation by-products, namely lactic acid and sodium and calcium lactates, to earthworms. Degradation characteristics in various worm-free and worm-containing media were also investigated under various conditions including direct feeding using impregnated paper or coated tree-leaves, model composting, and vermi composting. Data were compared with abiotic degradation in sterile neutral phosphate buffer. Last but not least, a novel method aimed at assessing the bioassimilation of degradable polymers and oligomers was utilized, which is based on the monitoring of weight changes of a population of starved worms when the worms are given the polymeric or oligomeric compounds as potential nutrients. The work shows that high molar mass poly(lactic acids) can be ingested by earthworms provided they are disintegrated first. However, they cannot be bioassimilated before hydrolytic degradation generates oligomers. The involvement of microorganisms in the bioassimilation is discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
J. Lunt (1998) Polymer Degrad. Stab. Spec. Issue 59, 145–152.
C. David, I. Dupret, and C. Lefevre (1999) in A-C. Albertsson, E. Chiellini, J. Feijen, G. Scott and M. Vert (Eds.), Degradability, Renewability and Recycling: Key Functions for Future Materials, Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH, Weinheim, pp. 141–152.
M. Vert, S. M. Li, H. Garreau, J. Mauduit, M. Boustta, G. Schwach, R. Engel, and J. Coudane (1997) Angew. Makromol. Chem. 247, 239–253.
A. M. Abdul Rida and M. B. Bouché (1997) Soil Biol. Biochem. 29, 699–703.
S. Li and M. Vert (1999) in E. Mathiowitz (Ed.), The Encyclopedia of Controlled Drug Delivery, John Wiley & Sons, New York, pp. 71–93.
C. Braud, R. Devarieux, A. Athlan, C. Ducos, and M. Vert (1998) J. Chromatogr. Biomed. Sci. Appl. 706, 73–82.
S. Li, H. Garreau, and M. Vert (1990) J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 1, 123–130.
S. Li, H. Garreau, and M. Vert (1990) J. Mat. Sci. Mater. Med. 1, 198–206.
G. Schwach, R. Engel, J. Coudane, and M. Vert (1994) Polymer Bull. 32, 617–623.
G. Schwach, J. Coudane, R. Engel, and M. Vert (1996) Polymer Bull. 37, 771–776.
G. Schwach, J. Coudane, R. Engel, and M. Vert (1997) J. Polymer Sci. Polymer Chem. 35, 3431–3440.
G. Schwach and M.Vert (1999) Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 25, 283–291.
A. Torres, S. M. Li, S. Roussos, and M. Vert (1996) J. Environ. Polymer Degrad. 4, 213–223.
N. Alauzet, S. Roussos, H. Garreau, and M. Vert (2001) Braz. Arch. Biol. Technol. 44, 113–119.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alauzet, N., Garreau, H., Bouché, M. et al. Earthworms and the Degradation of Lactic Acid–Based Stereocopolymers. Journal of Polymers and the Environment 10, 53–58 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1021074107803
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1021074107803