Abstract
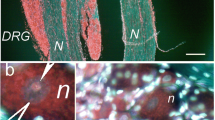
The distribution of apoptosis-inducing factor (AIF) immunoreactivity has been studied in the developing somites and nervous system of the chick embryo at embryonic day 4. AIF was found to be expressed primarily in the cytoplasm of cells of the ventral motor roots, at the points of their insertion into the neural tube. Co-localization of mitochondrial AIF immunoreactivity with the epitopes recognized by the monoclonal antibodies HNK-1 and 1E8 suggests that the AIF may be present in Schwann cell precursors as well as in nerve fibres. AIF immunoreactivity was not observed in either cell bodies in the neural tube, or in the somitic tissue surrounding the ventral roots. The results are consistent with the hypothesis that AIF may be involved in neuronal cell death during development, and that target-derived neuronal survival factors may act by controlling AIF activity.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Becker T, Becker CG, Schachner M, Bernhardt RR (2001) Antibody to the HNK-1 glycoepitope affects fasciculation and axonal path-finding in the developing posterior lateral line nerve of embryonic zebrafish. Mech Dev 109: 37–49.
Bhattacharyya A, Frank E, Ratner N, Brackenbury R(1991) P 0 is an early marker of the Schwann cell lineage in chickens. Neuron 7: 831–844.
Borner C, Monney L (1999) Apoptosis without caspases: An inefficient molecular guillotine? Cell Death Diff 6: 497–507.
Burek MJ, Oppenheim RW (1996) Programmed cell death in the developing nervous system. Brain Pathol 6: 427–446.
Christ B, Ordahl CP (1995) Early stages of chick somite development. Anat Embryol 191: 381–396.
Christ B, Schmidt C, Huang R, Wilting J, Brand-Saberi B (1998) Segmentation of the vertebrate body. Anat Embryol 197: 1–8.
Chu-Wang I-W, Oppenheim RW (1978a) Cell death of motoneurons in the chick embryo spinal cord. I. A light and electron microscopic study of naturally occurring and induced cell loss during development. J Comp Neurol 177: 33–58.
Chu-Wang I-W, Oppenheim RW (1978b) Cell death of motoneurons in the chick embryo spinal cord. II. A quantitative and qualitative analysis of degeneration in the ventral root, including evidence for axon outgrowth and limb innervation prior to cell death. J Comp Neurol 177: 59–86.
Ciutat D, Caldero J, Oppenheim RW, Esquerda JE (1996) Schwann cell apoptosis during normal development and after axonal degeneration induced by neurotoxins in the chick embryo. J Neurosci 16: 3979–3990.
Comella JX, Sanz-Rodrigues C, Aldea M, Esquerda JE (1994) Skeletal muscle-derived trophic factors prevent motoneurons from entering an active cell death program in vitro. J Neurosci 14: 2674–2686.
Cotrina ML, González-Hoyuela M, Barbas JA, Rodriguez-Tébar A (2000) Programmed cell death in the developing somites is promoted by nerve growth factor via its P75NTR receptor. Dev Biol 228: 326–336.
Daugas E, Susin SA, Zamzami N, Ferri KF, Irinopoulou T, Larochette N, Prévost M-C, Leber B, Andrews D, Penninger J, Kroemer G (2000) Mitochondrio-nuclear translocation of AIF in apoptosis and necrosis. FASEB J 14: 729–739.
D'Mello SR (1998) Molecular regulation of neuronal apoptosis. Curr Top Dev Biol 39: 187–213.
Glücksmann A (1951) Cell deaths in normal vertebrate ontogeny. Biol Rev 26: 59–86.
Gorman AM, Orrenius S, Ceccatelli S (1998) Apoptosis in neuronal cells: Role of caspases. Neuroreport 9: R49–R55.
Granville DJ, Cassidy BA, Ruehlmann DO, Choy JC, Brenner C, Kroemer G, Van Breeman C, Margaron P, Hunt DW, Mcmanus BM (2001) Mitochondrial release of apoptosis-inducing factor and cytochrome c during smooth muscle cell apoptosis. Am J Pathol 159: 305–311.
Hamburger V (1975) Cell death in the development of the lateral motor column of the chick embryo. J Comp Neurol 160: 535–546.
Hamburger V, Hamilton HL (1951) A series of normal stages in the development of the chick embryo. J Morphol 88: 59–92.
Homma S, Yaginuma H, Oppenheim RW(1994) Programmed cell death during the earliest stages of spinal cord development in the chick embryo: A possible means of early phenotypic selection. J Comp Neurol 345: 377–395.
Jacobson MD, Weil M, Raff MC (1997) Programmed cell death in animal development. Cell 88: 347–354.
Jeffs P, Osmond M (1992) A segmented pattern of cell death during development of the chick embryo. Anat Embryol 185: 589–598.
Johnson EM Jr, Deckwerth TL (1993) Molecular mechanisms of developmental neuronal death. Ann Rev Neurosci 16: 31–46.
Joza N, Susin SA, Daugas E, Stanford WL, Cho SK, Li CYJ, Saskai T, Elia AJ, Cheng H-YM, Ravgnan L, Ferri KF, Zamzami N, Wakeham A, Hakem R, Yoshida H, Kong Y-Y, Zúñuga-Pflücker JC, Kroemer G, Penninger JM (2001) Essential role of the mitochondrial apoptosis-inducing factor in programmed cell death. Nature 410: 549–554.
LaBonne C, Bronner-Fraser M (1999) Molecular mechanisms of neural crest formation. Ann Rev Cell Dev Biol 15: 81–112.
Li L, Prevette D, Oppenheim RW, Milligam CE (1998) Involvement of specific caspases in motoneuron cell death in vivo and in vitro following trophic factor deprivation. Mol Cell Neurosci 12: 157–167.
Lorenzo HK, Susin SA, Penninger J, Kroemer G(1999) Apoptosis inducing factor (AIF): A phylogenetically old, caspase-independent effector of cell death. Cell Death Diff 6: 516–524.
Martini R, Schachter M, Brushart TM (1994) The L2/HNK-1 carbohydrate is preferentially expressed by previously motor axon-associated Schwann cells in reinnervated peripheral nerves. J Neurosci 14: 7180–7191.
Marusich MF, Robinson BH, Taanman J-W, Kim SJ, Schillace R, Smith JL, Capaldi RA (1997) Expression of mtDNA and nDNA encoded respiratory chain proteins in chemically and geneticallyderived RhoO human fibroblasts: A comparison of subunit proteins in normal fibroblasts treated with ethidium bromide and fibroblasts from a patient with mtDNA depletion syndrome. Biochim Biophys Acta 1362: 145–159.
Maynard TM, Wakamatsu Y, Weston JA (2000) Cell interactions within nascent neural crest cell populations transiently promote death of neurogenic precursors. Development 127: 4561–4572.
Oppenheim RW, Haverkamp LJ, Prevette D, McManaman JL, Appel SH (1988) Reduction of naturally occurring motoneuron death in vivo by a target-derived neurotrophic factor. Science 240: 919–922.
Oppenheim RW, Flavell RA, Vinsant S, Prevette D, Kuan CY, Rakic P (2001) Programmed cell death of developing mammalian neurons after genetic deletion of caspases. J Neurosci 21: 4752–4760.
Ranganath RM, Nagashree NR (2001) Role of programmed cell death in development. Int Rev Cytol 202: 159–242.
Sanders EJ (1997) Cell death in the avian sclerotome. Dev Biol 192: 551–563.
Sanders EJ (2001) Cell death in somites. In: Sanders EJ, Lash JW, Ordahl CP, eds. The Origin and Fate of Somites. Amsterdam: IOS Press, pp. 182–194.
Sanders EJ, Parker E (2001) Ablation of axial structures activates apoptotic pathways in somite cells of the chick embryo. Anat Embryol 204: 389–398.
Sanders EJ, Wride MA (1995) Programmed cell death in development. Int Rev Cytol 163: 105–173.
Vaux DL, Korsmeyer SJ (1999) Cell death in development. Cell 96: 245–254.
Wakamatsu Y, Mochii M, Vogel KS, Weston JA (1998) Avian neural crest-derived neurogenic precursors undergo apoptosis on the lateral migration pathway. Development 125: 4205–4213.
Wride MA, Parker E, Sanders EJ (1999) Members of the bcl-2 and caspase families regulate nuclear degeneration during chick lens fibre differentiation. Dev Biol 213: 142–156.
Yaginuma H, Shiraiwa N, Shimada T, Nishiyama K, Hong J, Wang S, Momoi T, Uchiyama T, Oppenheim RW (2001) Caspase activity is involved in, but is dispensable for, early motoneuron death in the chick embryo cervical spinal cord. Mol Cell Neurosci 18: 168–182.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sanders, E.J., Parker, E. Expression of Apoptosis-inducing Factor During Early Neural Differentiation in the Chick Embryo. Histochem J 34, 161–166 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1020994515099
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1020994515099