Abstract
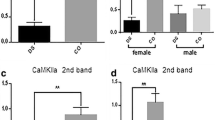
Down syndrome (DS) is characterized by abnormal brain morphology and neurological and behavioral functions. The pivotal role of helicases in brain development, growth, and differentiation made us evaluate three DEAD BOX proteins, DEAD-box protein 1 (DBP-RB), DEAD-box protein 3 (HLP2), DEAD-box protein 72 (P72), and the RuvB-like DNA helicase (TIP49b), in fetal brain of controls and DS subjects, using two-dimensional electrophoresis with subsequent mass spectroscopic (MALDI-MS) identification. HLP2 and TIP49b brain levels were comparable between DS and controls, and protein levels of p72 and DBP-RB were significantly reduced in DS fetal cortex (p72: 2.04 ± 1.90 vs. 5.57 ± 2.56 in controls, p < 0.01; DBP-RB: 0.58 ± 0.94 vs. 1.90 ± 0.97 in controls, p < 0.01). Impairment of the helicases p72 and DBP-RB may reflect or lead to deficient growth and differentiation of brain development early in life and can be considered pathogenetic factors along with the reported deficits of transcription, splicing, and elongation factors already described in fetal DS brains.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
De la Monte, S. M. 1999. Molecular abnormalities of the brain in Down syndrome: relevance to Alzheimer's neurodegeneration. Pages 161-177, in Lubec, G. (ed.), The Molecular Biology of Down Syndrome, Springer, Wien-New York.
Epstein, C. J. 1995. Down syndrome (Trisomy 21). Pages 749-794, in Scriver, C. R., Beaudet, A. L., Sly, W. S., and Valle, D. (eds.), The Metabolic and Molecular Basis of Inherited Disease, McGraw-Hill, New York.
Wisniewki, K. E. 1990. Down syndrome children often have brain with maturation delay, retardation of growth, and cortical dysgenesis. Am. J. Med. Genet. Suppl. 7:274-281.
Schmidt-Sidor, B., Wisniewski, K. E., Shepard, T. H., and Sersen, A. 1990. Brain growth in Down syndrome subjects 15 to 22 weeks of gestational age and birth to 60 months. Clin. Neuropathol. 9:181-190.
Freidl, M., Gulesserian, T., Lubec, G., Fountoulakis, M., and Lubec, B. 2001. Deterioration of the transcriptional, splicing and elongation machinery in brain of fetal Down Syndrome J. Neural. Transm. Suppl. 61:47-58.
Labudova, O., Krapfenbauer, K., Moenkemann, H., Rink, H., Kitzmüller, E., and Cairns, N. 1998. Decreased transcription factor junD in brains of patients with Down Syndrome. Neurosci. Lett. 252:159-162.
Lubec, G., Nonaka, M., Krapfenbauer, K., Gratzer, M., Cairns, N., and Fountoulakis, M. 1999. Expression of the dihydropyrimidinase related protein 2 (DRP-2) in Down syndrome and Alzheimer's disease brain is downregulated at the mRNA and dysregulated at the protein level. Pages 161-177, in Lubec, G. (ed.), The Molecular Biology of Down Syndrome, Springer, Wien-New York.
Greber-Platzer, S., Schatzmann-Turhani, D., Cairns, N., Balcz, B., and Lubec, G. 1999. Expression of the transcription factor ETS2 in brain of patients with Down syndrome·evidence against the overexpression-gene dosage hypothesis. J. Neural. Transm. Suppl. 57:269-282.
Greber-Platzer, S., Schatzmann-Turhani, D., Wollenek, G., and Lubec, G. 1999. Evidence against the current hypothesis of "gene dosage effects" of trisomy 21: ets-2, encoded on chromosome 21 is not overexpressed in hearts of patients with Down syndrome. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Comm. 254:395-399.
Linder, P., Lasko, P. F., Ashburner, M., Leroy, P., Nielsen, P. J., and Nishi, K. 1989. Birth of the D-E-A-D box. Nature 337:121-122.
Heinlein, U. A. O. 1998. DEAD box for the living. J. Pathol. 184:345-347.
De la Cruz, J., Kressler, D., and Linder, P. 1999. Unwinding RNA in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: DEAD-box proteins and related families. TIBS 24:192-198.
Sowden, J., Putt, W., Morrison, K., Beddington, R., and Edwards, Y. 1995. The embryonic RNA helicase gene (ERH): a new member of the DEAD box family of RNA helicases. Biochem. J. 308:839-846.
Lamm, G. M., Nicol, S. M., Fuller-Pace, F. V., and Lamond, A. I. 1996. P72: a human nuclear DEAD box protein highly related to p68. Nucleic Acids Res. 24:3739-3747.
Stevenson, R. J., Hamilton, S. J., MacCallum, D. E., Hall, P. A., and Fuller-Pace, F. V. 1998. Expression of the 'DEAD box' RNA helicase p68 is developmentally and growth regulated and correlates with organ differentiation/maturation in the fetus. J. Pathol. 184:351-359.
Ip, F. C. F., Chung, S. S. K., Fu, W.-Y., and Ip, N. Y. 2000. Developmental and tissue-specific expression of DEAD box protein p72. Neuroreport 11:457-462.
George, R. E., Kenyon, R. M., McGuckin, A. G., Malcolm, A. J., Pearson, A. D. J., and Lunec, J. 1996. Investigation of coamplification of the candidate genes ornithine decarboxylase, ribonucleotide reductase, syndecan-1 and a DEAD box gene, DDX1, with N-myc in neuroblastoma. Oncogene 12:1583-1587.
Kuroda, H., White, P. S., Sulman, E. P., Manohar, C. F., Reiter, J. L., and Cohn, S. L. 1996. Physical mapping of the DDX1 gene to 340 kb 59 of MYCN. Oncogene 13:1561-1565.
Manohar, C. F., Salwen, H. R., Brodeur, G. M., and Cohn, S. L. 1995. Co-amplification and concomitant high levels of expression of a DEAD box gene with MYCN in human neuroblastoma. Genes Chromosom. Cancer 14:196-203.
Godbout, R., Packer, M., and Bie, W. 1998. Overexpression of a DEAD box protein DDX1 in neuroblastoma and retinoblastoma cell lines. J. Biol. Chem. 273:21161-21168.
Chuang, R.-Y., Weaver, P. L., Liu, Z., and Chang, T.-H. 1997. Requirement of the DEAD-box protein Ded1p for messenger RNA translation. Science 275:1468-1471.
Lahn, B. T. and Page, D. C. 1997. Functional coherence of the human Y chromosome. Science 278:675-680.
Qiu, X.-B., Lin, Y.-L., Thome, K. C., Pian, P., Schlegel, B. P., and Weremowicz, S. 1998. An eukaryotic RuvB-like protein (RUVBL1) essential for growth. J. Biol. Chem. 273:27786-27793.
Kanemaki, M., Kurokawa, Y., Matsu-ura, T., Makino, Y., Masani, A., and Okazaki, K.-I. 1999. TIP49b, a new RuvB-like DNA helicase, is included in a complex together with another RuvB-like DNA helicase, TIP49a. J. Biol. Chem. 274:22437-22444.
Bradford, M. 1976. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 72:248-254.
Langen, H., Roder, D., Juranville, J., and Fountoulakis, M. 1997. Effect of protein application mode and acrylamide concentration on the resolution of protein spots separated by two dimensional gel electrophoresis. Electrophoresis 18:2085-2090.
Fountoulakis, M. and Langen, H. 1997. Identification of proteins by matrix-assisted laser desorption ionisation-mass spectroscopy following in-gel digestion in low-salt nonvolatile buffer and simplified peptide recovery. Anal. Biochem. 250:153-156.
Berndt, P., Hobolm, U., and Langen, H. 1999. Reliable automatic protein identification from matrix-assisted laser desorption/ ionisation mass spectrometric peptide fingerprints. Electrophoresis 20:3521-3526.
Wassarman, D. A. and Steitz, J. A. 1991. Alive with DEAD proteins. Nature 349:463-464.
Schwer, B. and Guthrie, C. 1991. PRP16 is an RNA-dependent ATPase that interacts transiently with the spliceosome. Nature 349:494-499.
Iost, I. and Dreyfus, M. 1994. mRNAs can be stabilized by DEAD-box proteins. Nature 372:193-196.
Burd, C. G. and Dreyfuss, G. 1994. Conserved structures and diversity of functions of RNA-binding proteins. Science 265: 615-621.
Weitzdörfer, R., Fountoulakis, M., and Lubec, G. 2001. Aberrant expression of dihydropyriminidase related proteins 2, 3 and 4 in fetal Down syndrome brain. Pages 71-82, in Lubec, G. (ed.), Protein Expression in Down Syndrome Brain, Springer, Wien-New York.
Jensen, R. D. and Miller, R. W. 1971. Retinoblastoma: epidemiologic characteristics. N. Engl. J. Med. 285:307-311.
Hasle, H. and Clemmensen, I. C. H. 2000. Incidence of cancer in individuals with Down syndrome. Tidsskr. Nor Laegeforen 120:2878-2881.
Satge, D., Sasco, A. J., Carlsen, N. L. T., Stiller, C. A., Rubie, H., and Hero, B. 1998. A lack of neuroblastoma in Down syndrome: a study from 11 European countries. Cancer Res. 58:448-452.
Barger, S. W., Van Eldik, L. J., and Mattson, M. P. 1995. S100 beta protects hippocampal neurons from damage induced by glucose deprivation. Brain Res. 677:167-170.
Satge, D., Sasco, A. J., Carlsen, N. L. T., Rubie, H., and Stiller, C. A. 1997. A negative association between Down's syndrome and neuroblastoma. Arch. Dis. Child. 76:80.
Godbout, R. and Squire, J. 1993. Amplification of a DEAD box protein gene in retinoblastoma cell lines. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U S A 90:7578-7582.
Makino, Y., Kanemaki, M., Kurokawa, Y., Koji, T. and Tamura, T.-A. 1999. A rat RuvB-like protein, TIP49a, is a germ cellenriched novel DNA helicase. J. Biol. Chem. 274:15329-15335.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kircher, S.G., Kim, S.H., Fountoulakis, M. et al. Reduced Levels of DEAD-Box Proteins DBP-RB and p72 in Fetal Down Syndrome Brains. Neurochem Res 27, 1141–1146 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1020921324871
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1020921324871