Abstract
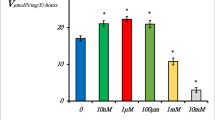
Synaptic plasma membrane (SPM)-bound, extracellular-facing (ecto) ATPases are Mg2+- or Ca2+-activated enzymes that regulate the synaptic levels of the excitatory neurotransmitter ATP and provide ADP for the further ecto-nucleotidase-mediated production of the inhibitory neuromodulator adenosine. The present results show that low concentrations (IC50 = 4 μM) of the lipid peroxidation product 4-hydroxynonenal (HNE) inhibited up to about 80% of the ecto-ATPase activity of SPM purified from rat brain cerebral cortex. In contrast, low concentrations of HNE did not inhibit the activity of the “intracellular”-facing Na+, K+, Mg2+-ATPase. In addition, the inhibition of SPM ecto-ATPase activity by HNE was largely irreversible and pH-dependent. Furthermore, structure-activity studies demonstrate that inhibition was dependent on the presence of the reactive functional groups of HNE. These findings suggest that HNE selectively inhibits SPM ecto-ATPase activity by a mechanism that may involve the covalent modification of functionally-critical nucleophilic amino acids. It is proposed that inhibition of SPM ecto-ATPase activity could contribute to the mechanisms by which lipid peroxidation and HNE formation promote excitotoxicity.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Inoue, K., Koizumi, S., and Ueno, S. 1996. Implications of ATP receptors in brain functions. Prog. Neurobiol., 50:483–492.
North, R. A., and Barnard, E. A. 1997. Nucleotide receptors. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol., 7:346–357.
Ralevic, V., and Burnstock, G. 1998. Receptors for purines and pyrimidines. Pharmacol. Rev., 50:413–492.
Zimmermann, H. 1996. Biochemistry, Localization and functional roles of ecto-nucleotidases in the central nervous system. Prog. Neurobiol., 49:589–618.
Zimmermann, H., Braun, N., Kegel, B., and Heine, P. 1998. New insights into molecular structure and function of ecto-nucleotidases in the nervous system. Neurochem. Int., 32:421–425.
Richardson, P. J., and Brown, S. J. 1987. ATP release from affinity-purified rat cholinergic nerve terminals. J. Neurochem., 48:622–630.
James, S., and Richardson, P. J. 1993. Production of adenosine from extracellular ATP at the striatal cholinergic synapse. J. Neurochem., 60:219–227.
Dunwiddie, T. V., Diao, L., and Proctor, W. R. 1997. Adenine nucleotides undergo rapid, quantitative conversion to adenosine in the extracellular space in rat hippocampus. J. Neurosci., 17:7673–7682.
Cunha, R. A., Sebastiao, A. M., and Ribeiro, J. A. 1998. Inhibition by ATP of hippocampal synaptic transmission requires localized extracellular catabolism by ecto-nucleotidases into adenosine and channeling to adenosine A1 receptors.
Esterbauer, H., Schaur, R. J., and Zollner, H. 1991. Chemistry and biochemistry of 4-hydroxynonenal, malonaldehyde and related aldehydes. Free Rad. Biol. Med., 11:81–128.
Uchida, K., and Stadtman, E. R. 1992. Modification of histidine residues in proteins by reaction with 4-hydroxynonenal. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 89:4544–4548.
Uchida, K., and Stadtman, E. R. 1992. Selective cleavage of thioether linkage in proteins modified with 4-hydroxynonenal. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 89:5611–5615.
Szweda, L. I., Uchida, K., Tsai, L., and Stadtman, E. R. 1993. Inactivation of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase by 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal. Selective modification of an active-site lysine. J. Biol. Chem., 268:3342–3347.
Kruman, I., Bruce-Keller, A. J., Bredesen, D., Waeg, G., and Mattson, M. P. 1997. Evidence that 4-hydroxynonenal mediates oxidative stress-induced neuronal apoptosis. J. Neurosci., 17:5089–5100.
Mark, R. J., Lovell, M. A., Markesbery, W. R., Uchida, K., and Mattson, M. P. 1997. A role for 4-hydroxynonenal, an aldehydic product of lipid peroxidation, in disruption of ion homeostasis and neuronal death induced by amyloid β-peptide. J. Neurochem., 68:255–264.
Mattson, M. P. 1998. Modification of ion homeostasis by lipid peroxidation: Roles in neuronal degeneration and adaptive plasticity. Trends Neurosci., 20:53–57.
Vietta, M., Frassetto, S. S., Battastini, A. M. O., Bello-Klein, A., Moreira, C., Dias, R. D., and Sarkas, J. J. F. 1996. Sensitivity of ATPase-ADPase activities from synaptic plasma membranes of rat forebrain to lipid peroxidation in vitro and the protective effect of vitamin E. Neurochem. Res., 21:299–304.
Benzi, G., Arnaboldi, G. R., Ghigini, B., and Villa, R. F. 1994. Synaptosomal Non-mitochondrial ATPase activities: Age-related alterations by chronic normobaric intermittent hypoxia. Neurochem. Int., 25:61–67.
Nagy, A. K., Walton, N. Y., and Treiman, D. M. 1997. Reduced cortical ecto-ATPase activity in rat brain during prolonged status epilepticus induced by sequential administration of lithium and pilocarpine. Mol. Chem. Neuropathol., 31:135–147.
Nagy, A. K., Shuster, T. A., and Delgado-Escueta, A. V. 1986. Ecto-ATPase of mammalian synaptosomes. Identification and enzymic characterization. J. Neurochem., 47:976–986.
Hohmann, J., Kowalewski, H., Vogel, M., and Zimmermann, H. 1993. Isolation of a Ca2+ or Mg2+-activated ATPase (ecto-ATPase) from bovine brain synaptic membranes. Biochem. Biophys. Acta, 1152:146–154.
Foley, T. D. 1997. 5-HPETE is a potent inhibitor of Neuronal Na+, K+-ATPase activity. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 235:374–376.
Booth, R. F. G., and Clark, J. B. 1978. A rapid method for the preparation of relatively pure metabolically competent synaptosomes from rat brain. Biochem. J., 176:363–370.
Kanner, B. I. 1978. Active transport of γ-aminobutyric acid by membrane vesicles isolated from rat brain. Biochemistry, 17:1207–1211.
Rhoads, D. E., Petersen, N. A., Sankaran, H., and Raghupathy, E. 1982. Inhibitory effect of scorpion venom on the uptake of amino acids by synaptosomes and synaptosomal membrane vesicles. Biochem. Pharmacol., 31:1875–1879.
Jones, D. H., and Matus, A. I. 1974. Isolation of synaptic plasma membrane from brain by combined flotation-sedimentation density gradient centrifugation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 356:276–287.
Doughty, M. J. 1978. Ciliary Ca2+-ATPase from the excitable membrane of Paramecium. Some properties and purification by affinity chromatography. Comp. Biochem. Physiol., 37:911–917.
Siems, W. G., Hapner, S. J., and Kuijk, F. J. G. M. 1996. 4-Hydroxynonenal Inhibits Na+, K+-ATPase. Free Rad. Biol., Med. 20:215–223.
Inoue, K., Koizumi, S., Nakazawa, K. 1995. Glutamate-evoked release of adenosine 5′-triphosphate causing an increase in intracellular calcium in hippocampal neurones. Neuroreport, 6:437–440.
Inoue, K., Nakazawa, K., Fugimori, W., and Takanaka, A. 1992. Extracellular adenosine 5′-triphosphate-evoked glutamate release in cultured rat hippocampal neurons. Neurosci. Lett., 134:215–218.
Jianguo, G. G., and MacDermott, A. B. 1997. Activation of ATP P2x receptors elicits glutamate release from sensory neuron synapses. Nature, 389:749–753.
Khakh, B. S., and Henderson, G. 1998. ATP receptor-mediated enhancement of fast excitatory neurotransmitter release in the brain. Mol. Pharmacol., 54:372–378.
Koles, L., Wirkner, K., Thummler, S., Furst, S., and Illes, P. 1998. Interaction between N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA)-and P2 receptors in rat prefrontal cortical slices. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol., 358(suppl. 3):R781
Daval, J.-L., Nehlig, A., and Nicolas, F. 1991. Physiological and Pharmacological properties of adenosine: Therapeutic implications. Life Sci., 49:1435–1453.
Craig, C., and White, T. D. 1993. N-Methyl-D-aspartate-and non-N-methyl-D-aspartate-evoked adenosine release from rat cortical slices: Distinct purinergic sources and mechanisms of release. J. Neurochem., 60:1073–1080.
Noremberg, W., Wirkner, K., and Illes, P. 1997. Effect of adenosine and some of its structural analogs on the conductance of NMDA receptor channels in a subset of rat neostriatal neurones. Brit. J. Pharmacol., 122:71–80.
Koles, L., Wirkner, K., Richter, M., Abmann, H., Norenberg, W., and Illes, P. 1998. Adenosine receptor-mediated inhibition of N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) and α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-isozazole-4-propionic acid (AMPA) receptor channels in rat neostriatum. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol., 358(suppl. 1):R126.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Foley, T.D. The Lipid Peroxidation Product 4-Hydroxynonenal Potently and Selectively Inhibits Synaptic Plasma Membrane Ecto-ATPase Activity, A Putative Regulator of Synaptic ATP and Adenosine. Neurochem Res 24, 1241–1248 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1020921006221
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1020921006221