Abstract
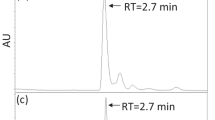
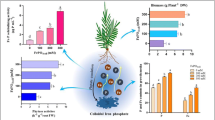
Root exudates from Tephrosia plants contained a rock-iron [Fe(OH)3] -solubilizing compound. This was purified to apparent homogeneity and appears to possess an iron-binding phenolic moiety linked to a proteinaceous component that may act as a receptor. The lyophilized purified fraction showed maximum Fe(OH)3-solubilizing activity at 50°C under acidic pH. Its activity was influenced by trace ions (Co, Cu, Zn, B, Mo, Mn) and toxic metal ions (Ni, Al, Pb, Cr, Hg), but ions such as Na, K, Mg, and Ca had no significant effects on its Fe(OH)3-solubilizing activity.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Bradford, M. M. 1976. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 72:248-254.
Briat, J. 1992. Iron assimilation storage in prokaryotes. J. Gen. Microbiol. 138:2475-2483.
Budesinsky, M., Budzikiewicz, H., Prochazka, Z., Ripperger, H., Romer, A., Scholz, G., and Schreiber, K. 1980. Nicotianamine, a possible phytosiderophore of general occurrence. Phytochemistry 19:2295-2297.
Crichton, R. R., and Charleteaux-Wauters, M. 1987. Iron transport and storage. Eur. J. Biochem. 164:485-506.
Crowley, D. E., Wang, Y. C., Reid, C. P. P., and Szaniszlo, P. J. 1991. Mechanisms of iron acquisition from siderophores by microorganisms and plants. Plant Soil 130:179-198.
Dakshini, K. M. M. 1985. Pages 69-128, in J. R. Goodin and D. K. Northington. Plant Resources of Arid and Semiarid Lands—A Global Perspective. Academic Press, Inc., London.
Date, R. A., and Halliday, J. 1979. Selecting Rhizobium for acid, infertile soils of the tropics. Nature 277:62-64.
Gries, D., and Runge, M. 1992. The ecological significance of iron mobilization in wild grasses. J. Plant Nutr. 15:1727-1737.
Guerinot, M. L. 1994. Microbial iron transport. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 48:743-772.
Guerinot, M. L., and Yi, Y. 1994. Iron: Nutritious, noxious, and not readily available. Plant Physiol. 104:815-820.
Hansen, N. C., Jolley, V. D., and Brown, J. C. 1995. Clipping foliage differentially affects phytosiderophore release by two wheat cultivars. Agron. J. 87:1060-1063.
Hansen, N. C., Jolley, V. D., Berg, W. A., Hodges, M. E., and Krenzer, E. G. 1996. Phytosiderophore release related to susceptibility of wheat to iron deficiency. Crop. Sci. 36:1473-1476.
Hopkins, B. G., Jolley, V. D., and Brown, J. C. 1992a. Plant utilization of iron solubilized by oat phytosiderophore. J. Plant Nutr. 15:1599-1612.
Hopkins, B. G., Jolley, V. D., and Brown, J. C. 1992b. Variable inhibition of iron uptake by oat phytosiderophore in five soybean cultivars. J. Plant Nutr. 15:125-135.
Jolley, V. D., Cook, K. A., Hansen, N. C., and Stevens, W. B. 1996. Plant physiological responses for genotypic evaluation of iron efficiency on strategy I and strategy II plants—A review. J. Plant Nutr. 19(8&9):1241-1255.
Lytle, C. M., and Jolley, V. D. 1991. Iron-deficiency stress to various C3 and C4 grain crop genotypes: Strategy II mechanism evaluated. J. Plant. Nutr. 14:341-362.
Marschner, H., and Romheld, V. 1994. Strategies of plants' acquisition of iron. Plant Soil 165:261-274.
Neilands, J. B. 1981. Microbial iron compounds. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 50:715-730.
Neilands, J. B., and Leong, S. A. 1986. Siderophore in relation to plant growth and disease. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. 37:187-208.
Ochsner, U. A., Vasil, A. I., and Vasil, M. L. 1995. Role of ferric uptake regulator of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in the regulation of siderophore and exotoxin A expression: Purification and activity on iron regulated promoters. J. Bacteriol. 177:7194-7201.
Porter, J. R. 1986. Production of a putative phytosiderophore by soybeans in response to iron deficiency stress. J. Plant Nutr. 9:1113-1121.
Powell, P. E., Cline, G. R., Reid, C. P. P., and Szaniszlo, P. J. 1980. Occurrence of hydroxamate siderophore iron chelators in soils. Nature 287:833-834.
Romheld, V., and Marschner, H. 1986. Evidence for a specific uptake systems for iron phytosiderophore in roots of grasses. Plant Physiol. 80:175-180.
Schwyn, B., and Neilands, J. B. 1987. Universal chemical assay for the detection and determination of siderophores. Anal. Biochem. 160:47-56.
Snowball, R., and Robson, A. D. 1985. Relationship between soil properties of the growth of legumes on acid wodjil soils in Western Australia. Aust. J. Bot. 33:299-307.
Takagi, S. 1976. Naturally occurring iron-chelating compounds in oat-and rice-root washings. I. Activity measurement and preliminary characterization. Soil. Sci. Plant Nutr. 22:423-433.
Treeby, M., Marschner, H., and Romheld, V. 1989. Mobilization of iron and other micronutrient cations from a calcareous soil by plant-borne, microbial, and synthetic metal chelators. Plant Soil 114:217-226.
von Wiren, N., Mori, S., Marschner, H., and Romheld, V. 1994. Iron inefficiency in maize mutant ysl (Zea mays L. cv Yellow Stripe) is caused by a defect in uptake of iron phytosiderophore. Plant Physiol. 106:71-77.
Young, N. R., and Mytton, L. R. 1981. The response of white clover to different strains of Rhizobium trifolii in hill land reseeding. Grass Forage Sci. 38:13-19.
Zhang, F. S., Treeby, M., Romheld, V., and Marschner, H. 1991. Mobilization of iron by phytosiderophore as affected by other micronutrients. Plant Soil 130:173-178.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aggarwal, K.K., Rajiv, J. & Babu, C.R. A Rock-Iron-Solubilizing Compound from Root Exudates of Tephrosia purpurea . J Chem Ecol 25, 2327–2336 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1020877908773
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1020877908773