Abstract
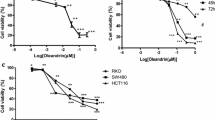
N 1,N 4-bis(2,3-butadienyl)-1,4-butanediamine (MDL 72527) was considered to be a selective inactivator of FAD-dependent tissue polyamine oxidase. Recently MDL 72527 was reported to induce apoptosis in transformed hematopoietic cells through lysosomotropic effects. Since it is the only useful inhibitor of polyamine oxidase available at present, the re-evaluation of its properties seemed important. Human colon carcinoma-derived SW480 cells and their lymph node metastatic derivatives (SW620) were chosen for our study because they differ in various aspects of polyamine metabolism but have similar polyamine oxidase activities. MDL 72527 inhibited cell growth in a concentration-dependent manner, depleted intracellular polyamine pools, and caused the accumulation of N 1-acetyl derivatives of spermidine and spermine. SW620 cells were more sensitive to the drug than were SW480 cells. At 150 μmol/L MDL 72527, SW620 cells accumulated in S-phase of the cell cycle, showed decreased polyamine transport rate, and showed no increase of polyamine N 1-acetyltransferase activity. In contrast, SW480 cells were not arrested in a particular phase of the cell cycle, showed enhanced polyamine uptake, and showed a mild induction of acetyltransferase. The results suggest that MDL 72527 retains its value as a selective tool in short-term experiments only at concentrations not exceeding those necessary for the inactivation of polyamine oxidase. At concentrations above 50 μmol/L and at exposure times longer than 24 h, it may derange cell functions nonspecifically, and thus blur the results of studies intended to elucidate polyamine oxidase functions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bey P, Bolkenius FN, Seiler N, Casara P. N-2,3-butadienyl-1,4-butanediamine derivatives: Potent irreversible inactivators of mammalian polyamine oxidase. JMed Chem. 1985;28:1-2.
Bolkenius FN, Seiler N. Polyamine oxidase inhibitors. In: Sandler M, Smith HJ, eds. Design of enzyme inhibitors as drugs. Oxford: Oxford University Press; 1989: 245-55.
Bolkenius FN, Bey P, Seiler N. Specific inhibition of polyamine oxidase in vivo is a method for the elucidation of its physiological role. Biochim Biophys Acta 1985;838:69-76
Brunton VG, Grant MH, Wallace HM. Mechanism of spermine toxicity in baby hamster kidney (BHK) cells. Biochem J. 1991;280:193-8.
Casero RA Jr, Pegg AE. Spermidine/spermine N 1-acetyltrans-ferase, the turning point in polyamine metabolism. FASEB J. 1993;7:653-61.
Cendan JC, Souba WW, Copeland EM 3rd, Lind DS. Increased l-arginine transport in a nitric oxide-producing metastatic colon cancer cell line. Ann Surg Oncol 1996;3:501-8.
Chen Y, Kramer DL, Diegelman P, Vujcic S, Porter CW. Apoptotic signalling in polyamine analogue-treated SK-MEL-28 human melanoma cells. Cancer Res. 2001;61: 6437-44.
Crissman HA, Mullner PF, Steincamp JA. Methods and applications of flow systems for analysis and sorting of mammalian cells. Methods Cell Biol. 1975;9:195-221.
Dai H, Kramer DL, Yanag C, Murti KG, Porter CW, Cleveland JL. The polyamine oxidase inhibitor MDL 72527 selectively induces apoptosis of transformed hematopoietic cells through lysosomotropic effects. Cancer Res. 1999;59:4944-54.
de Vries JE, Dinjens WN, de Bruyne G K, et al. In vivo and in vitro invasion in relation to the phenotypic characteristics of human colorectal carcinoma cells. Br J Cancer. 1995;71: 271-7.
Dogan A, Rao AM, Hatcher J, Rao VLR, Baskaya MK, Dempsey RJ. Effects of MDL 72527, a specific inhibitor of polyamine oxidase, on brain edema, ischemic injury volume, and tissue polyamine levels in rats after temporary middle cerebral artery occlusion. J Neurochem. 1999;72:765-70.
Duranton B, Holl V, Schneider Y, et al. Polyamine metabolism in primary human colon adenocarcinoma cells (SW480) and their lymph node metastatic derivatives (SW620). Amino Acids 2002 [in Press].
Firestone RA, Pisano JM, Bonney RJ. Lysosomotropic agents 1. Synthesis and cytotoxic action of lysosomotropic deter-gents. J Med Chem 1979;22:1130-3.
Fogel-Petrovic M, Shappell NW, Bergeron RJ, Porter CW. Polyamine and polyamine analog regulation of spermidine/ spermine N1-acetyltransferase in Malme-3M human mela-noma cells. J Biol Chem. 1993;268:19118-25.
Fulgosi B, Colombatto S, Grillo MA. Efflux of polyamines from human lymphocytes and from L1210 cells. Int J Biochem. 1992;24:1461-4.
Ha HC, Woster PM, Yager JD, Casero RA Jr. The role of polyamine catabolism in polyamine analogue-induced pro-grammed cell death. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1997;94: 11557-62.
Halline AG, Dudeja PK, Jacoby RF, et al. Effect of polyamine oxidase inhibition on the colonic malignant transformation process induced by 1,2-dimethylhydrazine. Carcinogenesis. 1990;11:2127-32.
Hu RH, Pegg AE. Rapid induction of apoptosis by deregulated uptake of polyamine analogues. Biochem J. 1997;328:307-16.
Huschtscha L, Rozengurt E, Bodmer WF. Growth factor requirements of human colorectal carcinomas of differing metastatic potential. Cancer Lett. 1991;60:85-92.
Hyvönen T. Excretion of acetylated and free polyamines by polyamine depleted Chinese hamster ovary cells. Int J Biochem. 1989;21: 313-16.
Igarashi K, Koga K, Shimogori T, Ekimoto H, Kashiwagi K, Shirahata, A. Inhibition of the growth of various human and mouse tumor cells by 1,15-bis(ethylamino)-4,8,12-tria-zapentadecane. Cancer Res. 1995;55:2615-19.
Leatherbarrow RJ (1992) Erithacus Software Ltd, London: Imperial College of Science, Technology Medicine.
Leibovitz A, Stinson JC, McCombs III WB, McCoy CE, Mazur KC, Mabry ND. Classification of human colorectal adeno-carcinoma cell lines. Cancer Res. 1976;36:4562-9.
Lowry OG, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ. Protein measurements with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951;193:265-75.
Maybaum J, Burton EC, Shelton DA, et al. Divergent patterns of incorporation of bromodeoxyuridine and iododeoxyur-idine in human colorectal tumor cell lines. Biochem Phar-macol. 1991;42:131-7.
Morgan DML. Measurement of polyamine transport. In: Morgan DML, ed. Polyamine protocols. Totowa, NJ: Hu-mana Press; 1998:139-47.
Nicoletti I, Migliorati G, Pagliacci MC, Grignani F, Riccardi C. A rapid and simple method for measuring thymocyte apoptosis by propidium iodide staining and flow cytometry. J Immunol Methods. 1991;139:271-6.
Porter CW, Stanek J, Black J, Vaughan M, Ganis B, Pleshke-wych A. Morphological evidence for an apparent lysosomo-tropic activity by unsaturated putrescine analogues. Cancer Res. 1990;50:1929-35.
Quemener V, Moulinoux JP, Khan N, Seiler N. Effect of a series of homologous dimethylaminoalkanes on cell proliferation: binding and uptake of putrescine by a glioblastoma cell line (U251) in culture. Biol Cell.1990;70:133-7.
Quemener V, Moulinoux JP, Lucas J, et al. The effects of structural analogs of putrescine on proliferation, morphol-ogy and karyotype of glioblastoma cells in culture. Biol Cell.1993;77:195-9.
Ray RM, McCormack SA, Johnson LR. Polyamine depletion arrests growth of IEC-6 and CaCo-2 cells by different mechanisms. Am J Physiol Liver Physiol. 2001;281:C37-G43.
Rodrigues NR, Rowan A, Smith MEF, et al. p53 mutations in colorectal cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1990;87:7555-9.
Rudkin BB, Mamont PS, Seiler N. Decreased protein synthetic activity is an early consequence of spermidine depletion in rat hepatoma tissue cell culture. Biochem J. 1984;217:731-41.
Sarhan S, Quemener V, Moulinoux JP, Knödgen B, Seiler N. On the degradation and elimination of spermine by the vertebrate organism. Int J Biochem. 1991;23:617-26.
Seiler N. Functions of polyamine acetylation. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1987;65:2024-35.
Seiler N. Polyamine oxidase, properties and functions. Prog Brain Res. 1995;106:333-44.
Seiler N, Bolkenius FN, Bey P, Mamont PS, Danzin C. Biochemical significance of inhibition of polyamine oxidase. In: Selmeci L, Brosnan ME, Seiler N, eds. Recent progress in polyamine research. Budapest: Akadémiai Kiado; 1985: 305-19.
Seiler N, Sarhan S, Grauffel C, Jones R, Knödgen B, Mouli-noux JP. Endogenous and exogenous polyamines in support of tumor growth. Cancer Res. 1990;50:5077-83.
Seiler N, Delcros JG, Moulinoux JP. Polyamine transport in mammalian cells. An update. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 1996; 28:843-61.
Seiler N, Duranton B, Gossé F, Raul F. Spermine cytotoxicity to human colon carcinoma-derived cells (CaCo-2). Cell Biol Toxicol. 2000a;16:117-30.
Seiler N, Duranton B, Vincent F, Gossé F, Renault J, Raul F. Inhibition of polyamine oxidase enhances the cytotoxicity of polyamine oxidase substrates. A model study with N 1-(n-octanesulfonyl)spermine and human colon cancer cells. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2000b;32:703-16.
Seiler N, Badolo L, Duranton B, et al. Effect of the polyamine oxidase inactivator MDL 72527 on N 1-(n-octanesulfonyl)-spermine toxicity. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2000c;32:1055-68.
Skehan P, Storeng R, Scudiero D, et al. New colorimetric cytotoxic assay for anticancer-drug screening. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1990;82:1107-12.
Trujillo JM, Yang LY. Synergism of 1-β-D-arabinofuranosylcy-tosine and cis-diamminedichloroplatinum in their lethal effcacies against seven established cancer cell lines of gastrointestinal origin. Anticancer Res. 1989;9:197-201.
Turowsky GA, Rashid Z, Hong F, Madri JA, Basson MD. Glutamine modulates phenotype and stimulates prolifera-tion in human colon cancer cell lines. Cancer Res. 1994; 54:5974-80.
Vermeulen SJ, Bruyneel EA., Bracke ME, et al. Transition from the noninvasive to the invasive phenotype and loss of b-catenin in human colon cancer cells. Cancer Res. 1995;55: 4722-8.
Wallace, HM, Coleman, C. Changes in polyamine acetylation in human cancer cells. Biochem Soc Trans. 1990;18:1091-4.
Wallace HM, Keir HM. Uptake and excretion of polyamines from baby hamster kidney cells (BHK-21/C13). The effect of serum and confluent cell cultures. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981;676:25-30.
Wallace HM, Lindsay GS. The roles of polyamine acetylation and oxidation in apoptosis. In: Bardocz, S, White, A, Hajos G, eds. Biogenically active amines in food. Vol. II. Meta-bolic effects of biologically active amines in food. Luxem-bourg: Offce for Offcial Publications of the European Community; 1998:41-7.
Warrington RC, Cheng I, Fang WD. Susceptibility of human colon carcinoma cells to anticancer drugs is enhanced by l-histidinol. Anticancer Res. 1994;14:367-72.
Zirvi KA, Keogh JP, Slomiany A, Slomiany BL. Transglutami-nase activity in human colorectal tumour cells: relations to cellular differentiation. Eur J Cancer. 1991;27:1680-4.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Duranton, B., Holl, V., Schneider, Y. et al. Cytotoxic effects of the polyamine oxidase inactivator MDL 72527 to two human colon carcinoma cell lines SW480 and SW620. Cell Biol Toxicol 18, 381–396 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1020863506170
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1020863506170