Abstract
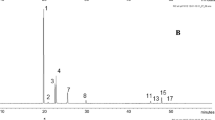
Capillary GC analysis was used to determine the proportion and quantity of terpenes in wood resin, pentane extracts from needles and liber, and headspace samples of needles and pruning wounds in 24 thirteen-year-old maritime pine. Fifteen different terpenes were identified in the samples. Germacrene D and β-pinene were the dominant terpenic compounds in the needles, while α-pinene and β-pinene were dominant in the liber and wood resin. Headspace samples of both needles and pruning wounds contained essentially monoterpenes. Only trace amounts of sesquiterpenes were found in pruning wound emissions. The presence of an oxygenated compound, linalool, in the pruning wound emissions is discussed, although this compound is not found in Maritime pine essential oil. Twelve of the 24 trees studied were infested by Dioryctria sylvestrella. Maritime pine susceptibility to this insect was related to the terpene composition of the different samples.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Baradat, P., and Marpeau-Bezard, A. 1988. Le pin maritime Pinus pinaster Ait. Biologie et génétique des terpènes pour la connaissance et l'amélioration de l'espèce. Doctoral thesis 953. Université de Bordeaux, France, 444 pp.
Baradat, P., Bernard-Dagan, C., Fillon, C., Marpeau, A., and Pauly, G. 1972. Les terpènes du pin maritime: Aspects biologiques et génétiques. II. Hérédité de la teneur en monoterpènes. Ann. Sci. For. 29(3):307–334.
Baradat, P., Marpeau, A., and Bernard-Dagan, C. 1978. Variation of Terpenes Within and Between Populations of Maritime Pine. Biochem. Gen. Forest Trees, Umea, Sweden.
Baradat, P., Marpeau, A., and Walter, J. 1991. Terpene markers, pp. 40–65, in Genetic Variation in European Populations of Forest Trees. G. Muller-Starck and M. Ziehe (eds.). Sauerlander's Verlag, Frankfurt am Main.
Baronio, P., and Buttirini, A. 1988. Gli insetti novici al bosco, Pinus spp. Pyralidae della corteccia del pino, Dioryctria sylvestrella (Lepidoptera: Phycitinae). Monti Boschi 6:3–4.
Bernard-Dagan, C. 1968. Les essences du Pin maritime: Leur répartition dans les divers organes, nature et évolution des monoterpènes. Bull. Soc. Bot. Fr., Colloq. Physiol. Arbre (Paris, November 18–19, 1966), pp. 1–14.
Bernard-Dagan, C., Fillon, C., Pauly, G., Baradat, P., and Illy, G. 1971. Les terpènes du Pin maritime: Aspect biologiques et génétiques. I. Variabilité de la composition monoterpéniques dans un individu, entre individus et entre provenances. Ann. Sci. For. 28:223–258.
Buchbauer, G., Jirovitz, L., Wasicky, M., and Nikiforov, A. 1994. Comparative investigation of Douglas fir headspace samples, essential oils, and extracts (needles and twigs) using GC-FID and GC-FTIR-MS. J. Agric. Food Chem. 42:2852–2854.
Cheniclet, C. 1987. Effects of wounding and fungus inoculation on terpene producing systems of maritime pine. J. Exp. Bot. 38(194):1557–1572.
Dagnelie, P. 1973. Théorie et Méthodes Statistiques. Presses agronomiques de Gembloux Editeur, Gembloux, Belgique. 463 pp.
Delorme, L., and Lieutier, F. 1990. Monoterpene composition of the preformed and induced resin of Scots pine, and their effect on bark beetles and associated fungi. Eur. J. For. Pathol. 20:304–316.
Evans, R., Tigey, D., and Gumpertz, M. 1985. Interspecies variation in terpenoid emissions from Engelmann and Sitka spruce seedlings. For. Sci. 31:132–142.
Fatzinger, C. W., and Merkel, E. P. 1985. Oviposition and feeding preferences of the southern pine coneworm (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae) for different host-plant materials and observations on monoterpenes as an oviposition stimulant. J. Chem. Ecol. 11:689–699.
Graedel, T. E. 1979. Terpenoïds in the atmosphere. Rev. Geophys. 17:937–947.
Hanover, J. W. 1972. Factors affecting the release of volatile chemicals by forest trees. Mitt. Forsstkichen Bundes-Versuchanst Wien 97:625–644.
Hanover, J. W. 1992. Applications of terpenes analysis in forest genetics. New For. 6:159–178.
Hanula, J. L., Berisford, C. W., and Debarr, G. L. 1985. Monoterpene oviposition stimulant of Dioryctria amatella in volatiles from fusiform rust galls and second-year loblolly pine cones. J. Chem. Ecol. 11:943–952.
Harborne, J. B. 1990. Role of secondary metabolites in chemical defence mechanisms in plants, pp. 126–134, in Bioactive Compounds from Plants. D. J. Chadwick and J. Marsh (eds.). Wiley-Interscience, Chichester, UK.
Honda, K. 1995. Chemical basis of differential oviposition by lepidopterous insects. Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 30:1–23.
Jactel, H., and Kleinhentz, M. 1997. Intensive sylvicultural practices increase the risk of infestation by Dioryctria sylvestrella Ratz (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae), the maritime pine stem borer. In Integrating Cultural Tactics into the Management of Bark Beetle and Reforestation Pests. Proceedings of a symposium held September 1–3, 1996, in Vallombrosa, Italy.
Jactel, H., Menassieu, P., and Raise, G. 1994. Infestation dynamics of Dioryctria sylvestrella (Ratz.) (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae) in pruned maritime pine (Pinus pinaster Ait). For. Ecol. Manage. 67:11–22.
Jactel, H., Menassieu, P., Raise, G., and Burban, C. 1996a. Sensitivity of pruned Maritime pine (Pinus pinaster Ait) to Dioryctria sylvestrella (Ratz.) (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae) in relation to tree vigour and date of pruning. J. Appl. Entomol. 120:153–157.
Jactel, H., Kleinhentz, M., Marpeau-Bezard, A., Marion-Poll, F., Menassieu, P., and Burban, C. 1996b. Terpene variations in maritime pine constitutive oleoresin related to host tree selection by Dioryctria sylvestrella Ratz. (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae). J. Chem. Ecol. 22(5):1037–1050.
Juuti, S., Arey, J., and Atkinson, R. 1990. Monoterpene emission rate measurements from a Monterey pine. J. Geophys. Res. 95:7515–7519.
Kleinhentz, M., Raffin, A., Jactel, H., Broquet, A., and Menassieu, P. 1998. Terpinolene as a potential marker in indirect selection for Dioryctria sylvestrella Ratz. (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae) resistance in Maritime pine. Forest genetics 5(3):147–155.
Kramer, P. J., and Kozlowski, T. T. 1979. Physiology of Woody Plants. Academic Press, New York.
Lamb, B., Westberg, H. H., Allwine, G., and Quarles, T. 1985. Biogenic hydrocarbon emissions from deciduous and coniferous trees in the United States. J. Geophys. Res. 90(D1):2380–2390.
Langenheim, J. H. 1994. Higher plants terpenoids: A phytocentric overview of their ecological roles. J. Chem. Ecol. 20:1223–1280.
Lilian, D. 1972. Photochemical smog and ozone reaction. Adv. Chem. Ser. 113:211–218.
Mathieu, F. 1995. Mécanismes de la colonisation de l'hôte chez le scolyte du café Hypothenemus hampei (Ferr.) (Coleoptera: Scolytidae). Doctoral thesis. Université de Paris VII, 133 pp.
Menassieu, P., Stockel, J., and Levieux, J. 1989. Données actuelles sur la biologie de Dioryctria sylvestrella Ratz. (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae) ravageur du Pin maritime (Pinus pinaster Ait.) dans le Sud Ouest de la France. J. Appl. Entomol. 107:238–247.
Metcalf, R. L. 1987. Plant volatiles as insect attractants. CRC Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 5:251–301.
Pauly, G. 1962. Etude de l'appareil secréteur chez le Pin maritime. Thése 3ème cycle. Univeristé de Bordeaux, 120 pp.
Pauly, G., Gleizes, M., and Bernard-Dagan, C. 1973. Identification des constituants de l'essence des aiguilles de Pinus pinaster. Phytochemistry 12:1395–1398.
Rappaport, N. G., Jenkins, M. K., and Roques, A. 1995. Cone and foliage volatiles from douglasfir and european larch: relationship to attack by cone and seed insects. In G. L. De Barr (ed.). Proceedings of the Fourth IUFRO Cone and Seed Insects Conference, Beijing, China, 1992.
Rasmussen, R. 1972. What do the hydrocarbons from trees contribute to air pollution? J. Air Pollut. Control Assoc. 22:537–543.
Rhoades, D. F. 1990. Analysis of monoterpenes emitted and absorbed by undamaged boles of lodgepole pine. Phytochemistry 29:1463–1465.
Riba, M. L. 1991. Les isoprénoîdes dans la plante et dans l'atmosphère. Etude de leur évolution en milieu forestier. Thèse de doctorat d'état de l'Institut National Polytechnique de Toulouse, 232 pp.
Sadof, C. S., and Grant, G. G. 1997. Monoterpene composition of Pinus sylvestris varieties resistant and susceptible to Dioryctria zimmermani. J. Chem. Ecol. 23:1917–1927.
SAS Institute. 1996. SAS User's Guide: Statistics, Version 5. SAS Institute, Cary, North Carolina.
Shu, S., Grant, G. G., Langevin, D., Lombardo, D. A., and MacDonald, L. 1997. Oviposition and electroantennogram responses of Dioryctria abietivorella (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae) elicited by monoterpenes and enantiomers from eastern white pine. J. Chem. Ecol. 23:35–50.
Speight, M. R., and Wainhouse, D. 1989. Ecology and Management of Forest Insects. Clarendon Press, Oxford, 374 pp.
StrÖmvall, A. M., and Petersson, G. 1992. Protection of terpenes against oxidative and acid decomposition on adsorbent cartridges. J. Chromatogr. 589:385–389.
Tingey, D. T., and Burns, W. F. 1980. Hydrocarbon emissions from vegetation, pp. 24–30, in Effects of Air Pollutants on Mediterranean and Temperate Forest Ecosystems. P. R. Miller (ed.). Pacific Southwest Forest and Range Experiment Station, Berkeley, California.
Tingey, D. T., Manning, M., Grothaus, L. C., and Burns, W. F. 1980. Influence of light and temperature on monoterpene emission rates from slash pine. Plant Physiol. 65:4013–4018.
Tucker, W. A., and Nelken, L. H. 1982. Diffusion coefficients in air and water, pp. 17-1–17-25, in W. J. Lyman, W. F. Reehl, and D. H. Rosenblatt (eds.). Handbook of Chemical Properties and Estimation Methods: Environmental Behavior of Organic Compounds. McGraw-Hill, New York.
Valterova, I., Sjodin, K., Vrkoc, J., and Nordin, T. 1995. Contents and enantiomeric composition of monoterpene hydrocarbons in xylem oleoresin from four Pinus species growing in Cuba. Comparison of trees unattacked and attacked by Dioryctria horneana. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 23:1–5.
Wright, J. W., Wilson, L. F., and Bright, J. N. 1975. Genetic variation in resistance of Scotch pine to Zimmerman pine moth. Great Lakes Entomol. 8:231–236.
Yokouchi, Y., and Ambe, Y. 1984. Factors affecting the emission of monoterpenes from red pine (Pinus densifora). Plant Physiol. 75:1009–1012.
Zimmerman, P. R. 1979. Tampa Bay area photochemical oxidant study. Determination of emission rates of hydrocarbons from indigenous species of vegetation in the Tampa/St.. Petersburg, Florida, area. EPA 904/9-77-028. US Environmental Protection Agency, Atlanta, Georgia.
Zocchi, R. 1961. Contributi alla conoscenza degli insetti delle plante forestali V il genere Dioryctria Zell (Lepi. Pyralidae) in Italia. Redia 46:9–13.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kleinhentz, M., Jactel, H. & Menassieu, P. Terpene Attractant Candidates of Dioryctria sylvestrella in Maritime Pine (Pinus pinaster) Oleoresin, Needles, Liber, and Headspace Samples. J Chem Ecol 25, 2741–2756 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1020803608406
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1020803608406