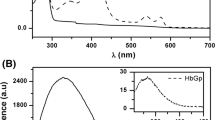
Abstract
Myoglobin was isolated from the radular muscle of the archaeogastropod mollusc Turbo cornutus (Turbinidae). This myoglobin is a monomer carrying one protoheme group; the molecular mass was estimated by SDS–PAGE to be about 40 kDa, 2.5 times larger than that of usual myoglobin. The cDNA-derived amino acid sequence of 375 residues was determined, of which 327 residues were identified directly by chemical sequencing of internal peptides. The amino acid sequence of Turbo myoglobin showed no significant homology with any other usual 16-kDa globins, but showed 36% identity with the myoglobin from Sulculus diversicolor (Haliotiidae) and 27% identity with human indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase, a tryptophan-degrading enzyme containing heme. Thus, the Turbo myoglobin can be counted among the myoglobins which evolved from the same ancestor as that of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase. The absorbance ratio of γ to CT maximum (γ/CT) of Turbo metmyoglobin was 17.8, indicating that this myoglobin probably possesses a histidine residue near the sixth coordination position of heme iron. The Turbo myoglobin binds oxygen reversibly. Its oxygen equilibrium properties are similar to those of Sulculus myoglobin, giving P 50 = 3.5 mm Hg at pH 7.4 and 20°C. The pH dependence of autoxidation of Turbo oxymyoglobin was quite different from that of mammalian myoglobin, suggesting a unique protein folding around the heme cavity of Turbo myoglobin. A kinetic analysis of autoxidation indicates that the amino acid residue with pK a = 5.4 is involved in the reaction. The autoxidation reaction was enhanced markedly at pH 7.6, but not at pH 5.5 and 6.3 in the presence of tryptophan. We suggest that a noncatalytic binding site for tryptophan, in which several dissociation groups with pK a ≥ 7.6 are involved, remains in Turbo myoglobin as a relic of molecular evolution.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Dai, W., and Gupta, S. L. (1990). Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 168, 1–8.
Geraci, G., Sada, A., and Cirotto, C. (1977). Eur. J. Biochem. 77, 555–560.
Giacometti, G. M., Ascenzi, P., Brunori, M., Rigatti, G., Giacometti, G., and Bolognesi, M. (1981). J. Mol. Biol. 151, 315–319.
Habara-Ohkubo, A., Takikawa, O., and Yoshida, R. (1991). Gene 105, 221–227.
Hanania, G. I. H., Yeghiayan, A., and Cameron, B. (1966). Biochem. J. 98, 189–192.
Hayashi, A., Suzuki, T., and Shin, M. (1973). Biochim. Biophys. Acta 310, 309–316.
Hirata, F., Ohnishi, T., and Hayaishi, O. (1977). J. Biol. Chem. 252, 4637–4642.
Imai, K. (1981). Meth. Ezymol. 76, 438–449.
Kadoya, A., Tone, S., Maeda, H., Minatogawa, Y., and Kido, R. (1992). Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 189, 530–536.
Matsuoka, A., Ohie, Y., Imai, K., and Shikama, K. (1996). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 115B, 483–492.
Phillips, S. E. V., and Schoenborn, B. P. (1981). Nature 292, 81–82.
Read, K. R. H. (1966). In Physiology of Mollusca (Wilbur, K. M., and Yonge, C. M., eds.), Academic Press, New York, vol. II, pp. 209–232.
Rossi-Fanelli, A., and Antonini, E. (1957). Biochimia 22, 335–342.
Seamonds, B., Forster, R. E., and George, P. (1971). J. Biol. Chem. 246, 5391–5397.
Shikama, K. (1988). Coord. Chem. Rev. 83, 73–91.
Shikama, K., and Katagiri, T. (1984). J. Mol. Biol. 174, 697–704.
Shiro, Y., Sato, F., Suzuki, T., Iizuka, T., Matsushita, T., and Oyanagi, H. (1990). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 112, 2921–2924.
Smith, S. E., Brittain, T., and Wells, R. M. G. (1988). Biochem. J. 252, 673–678.
Suzuki, T. (1986). J. Biol. Chem. 261, 3692–3699.
Suzuki, T. (1987). Biochim. Biophys. Acta 914, 170–176.
Suzuki, T. (1994). J. Protein Chem. 13, 9–13.
Suzuki, T., and Furukohri, T. (1989). Experientia 45, 998–1002.
Suzuki, T., and Imai, K. (1997). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 117B, 599–604.
Suzuki, T., and Shikama, K. (1983). Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 224, 695–699.
Suzuki, T., and Takagi, T. (1992). J. Mol. Biol. 228, 698–700.
Suzuki, T., Muramatsu, R., Kisamori, T., and Furukohri, T. (1988). Zool. Sci. 5, 69–76.
Suzuki, T., Yuasa, H., and Imai, K. (1996). Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1308, 41–48.
Terwilliger, R. C., and Terwilliger, N. B. (1985). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 81B, 255–261.
Tone, S., Takikawa, O., Habara-Ohkubo, A., Kadoya, A., Yoshida, R., and Kido, R. (1990). Nucleic Acids Res. 18, 367.
van Holde, K. E., and Miller, K. I. (1982). Q. Rev. Biophys. 15, 1–129.
Vinogradov, S. N., Walz, D. A., Pohajdak, B., Moens, L., Kapp, O., Suzuki, T., and Trotman, C. N. A. (1993). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 106B, 1–26.
Wang, C. M., and Briniger, W. S. (1979). Biochemistry 18, 4960–4977.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Suzuki, T., Kawamichi, H. & Imai, K. Amino Acid Sequence, Spectral, Oxygen-Binding, and Autoxidation Properties of Indoleamine Dioxygenase-Like Myoglobin from the Gastropod Mollusc Turbo cornutus. J Protein Chem 17, 817–826 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1020782403070
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1020782403070