Abstract
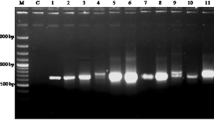
We analyzed the ITS-1 spacer region of the rDNA in Drosophila mulleri and D. arizonae, two sibling species belonging to the mulleri complex (repleta group) and in hybrids obtained in both cross directions. In spite of several previous studies showing the incompatibility of crosses involving D. arizonae females and D. mulleri males, we were able to obtain hybrids in this direction. Complete ITS-1 region was amplified using primers with homology at the 3′-end of the 18S rDNA and the 5′-end of the 5.8S rDNA genes. Our data demonstrated that D. mulleri and D. arizonae can be differentiated as they present a difference in length for the ITS-1 region. The amplified fragment for this region in D. mulleri has a length of 600 bp, whereas in D. arizonae this fragment is about 500 bp. It was also observed that male and female hybrids obtained in both cross directions present two amplified fragments, confirming the location of the ribosomal cistrons in the X chromosomes and microchromosomes of both parental species.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Amarger, V., and Mercier, L. (1996). Nuclear ribosomal DNA unit length variation: A putative marker of genetic diversity in Jojoba. Int. J. Plant Sci. 157(3):296.
Bicudo, H. E. M. C. (1981a). Nucleolar organizer activity and its regulatory mechanisms in Drosophila species of the “mulleri” complex and their hybrids. Caryologia 34(2):231.
Bicudo, H. E. M. C. (1981b). Further observations on the nucleolar organizing activity in salivary gland cells of Drosophila mulleri, D. arizonensis and their hybrids. Biol. Zbl. 100:597.
Bicudo, H. E. M. C. (1982). Estudo citogen´etico de esp´ecies de Drosophila do complexo mulleri (grupo repleta). A regula¸cão da atividade organizadora nucleolar. In Tese de Livre Docência, IBILCE-UNESP, São Jos´e do Rio Preto, SP, p. 209.
Bicudo, H. E. M. C., and Richardson, R. H. (1977). Gene regulation in Drosophila mulleri, D. arizonensis, and their hybrids: The nucleolar organizer. P. N. A. S. 74(8):3498.
Bicudo, H. E. M. C., and Richardson, R. H. (1978). Morphological and developmental studies of Drosophila mulleri, D. arizonensis and their hybrids. Biol. Zbl. 97:195.
Bicudo, H. E. M. C., and Richardson, R. H. (1981). Location of ribosomic cistrons in the salivary gland cells of Drosophila mulleri, D. arizonensis and their hybrids. Rev. Brasil Genet. 4(3):477.
Birch, A. N. E., Fenton, B., Malloch, G., Jones, A. T., Phillips, M. S., Harrower, B. E., Woodford, J. A. T., and Catley, M. A. (1994). Ribosomal spacer length variability in the large raspberry aphid, Amphorophora idaei (Aphidinae: Macrosiphini). Insect Mol. Biol. 3(4):239.
Bowen, T., and Dover, G. A. (1995). PCR amplification of intergenic spacers in the ribosomal DNA of Drosophila melanogaster reveals high levels of turnover in length and copy-number of spacers in geographically separated populations. Mol. Ecol. 4(4):419.
Brown, B., Emberson, R., and Paterson, A. (2000). Phylogenetic relationships within the genusWiseana (Lepidoptera: Hepialidae). New Zeal. J. Zool. 27(1):1.
Cocciolone, S. M., and Cone, K. C. (1993). PI-Bb, an anthocyanin regulatory gene of maize that leads to variegated pigmentation. Genetics 135:575.
Cornel, A. J., Coetzee, M., Van Rensburg, A. J., Koekemoer, L. L., Hunt, R. H., and Collins, F. H. (1997). Ribosomal DNA-polymerase chain reaction assay discriminates between Anopheles quadriannulatus and A. merus (Diptera: Culicidae). J. Med. Entomol. 34(5):573.
Crow, J. F. (1942). Cross fertility and isolating mechanisms in the Drosophila mulleri group. University of Texas Publication NO. 4228, p. 53.
Endow, S. A., and Gall, J. C. (1975). Differential replication of satellite DNA in polyploid tissue of Drosophila virilis. Chromosoma 50:175.
Ganley, A. R. D., and Scott, B. (1998). Extraordinary ribosomal spacer length heterogeneity in a Neotyphodium endophyte hybrid: Implications for concerted evolution. Genetics 150:1625.
Gloor, G., and Engels, W. (1992). Single fly DNA preps for PCR. Dros. Inf. Serv. 71:148.
Gupta, J. P., and Kumar,A. (1987). Cytogenetics of Zaprionus indianus Gupta (Diptera: Drosophilidae): nucleolar organizer regions, mitotic and polytene chromosomes and inversion polymorphism. Genetica 74:19.
H¨agele, K., and Ranganath, H. A. (1983). The chromosomes of two Drosophila races: Drosophila nasuta nasuta and Drosophila nasuta albomicans. III. Localization of nucleolar organizer regions. Genetica 60:123.
Hennig,W., Link, B., and Leoncini, O. (1975). The location of nucleolus organizer regions in Drosophila hydei. Chromosoma 51:57.
Hillis, D. M., and Dixon, M. T. (1991). Ribosomal DNA: Molecular evolution and phylogenetic inference. Q. Rev. Biol. 66:411.
Hoy, M. A. (1994). Insect molecular systematics and evolution. In Hoy, M. A. (eds.), Insect Molecular Genetics: An Introduction to Principles and Applications, Academic Press, New York pp. 360-363.
Kumar, P. L., Fenton, B., and Jones, A. T. (1999). Identification of Cecidophyopsis mites (Acari: Eriophydae) based on variable simple sequence repeats of ribosomal DNA internal transcribed spacer-1 sequences via multiplex PCR. Insect Mol. Biol. 8(3):347.
Lapenta, A. S., Bicudo, H. E. M. C., Ceron, C. R., and Cordeiro, J. A. (1995). Esterase patterns of species in the Drosophila buzzattii cluster. Cytobios 84:13.
Leoncini, O., Tovar, F. J., and Bicudo, H. E. M. C. (1996). Molecular evidence of ribosomal DNA (rDNA) amplification of a minichromosome derived from Drosophila arizonae in D. mulleri-D. arizonae hybrid males. Braz. J. Gen. 19(1):43.
Lohe, A. R., and Roberts, P. A. (1990). An unusual Y chromosome of Drosophila simulans carrying amplified rDNA spacer without rRNA genes. Genetics 125:399.
Long, E. O., and Dawid, I. B. (1980). Repeated genes in eukaryotes. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 49:727.
Lucchini, S. D., Andronico, F., and Nardi, I. (1997). Molecular structure of the rDNA intergenic spacer (IGS) in Triturus: Implications for the hypervariability of rDNA loci. Chromosoma 106:315.
Marinucci, M., Romi, R., Mancini, P., Di Luca, M., and Severini, C. (1999). Phylogenetic relationships of seven paleartic members of the maculipennis complex inferred from ITS-2 sequence analysis. Insect Mol. Biol. 8(4):469.
Mecheva, I. S., and Semionov, E. P. (1992). Localization of ribosomal DNA insertion elements in polytene chromosomes of Drosophila simulans, Drosophila mauritiana and their interspecific hybrids. Genetica 85:223.
Mehta, A., and Rosato, Y. B. (2001). Phylogenetic relationships of Xilella fastidiosa strains from different hosts, based on 16S rDNA and 16S-23S intergenic spacer sequences. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 51(2):311.
Navajas, M., Cotton, D., Kreiter, S., and Gutierrez, J. (1992). Molecular approach in spider mites (Acari: Tetranychidae): Preliminary data on ribosomal DNA sequences. Experim. Appl. Acarol. 15: 211.
Patterson, J. T. (1947). Sexual isolation in the mulleri subgroup. In Studies in the genetics of Drosophila.V. isolating mechanisms. University of Texas Publication No. 4729, p. 32.
Pen, J., Van Beeumen, J. V., and Beintema, J. J. (1986). Structural comparison of two esterases from Drosophila mojavensis isolated by immunoaffinity chromatography. Biochem. J. 278:691.
Perez-Gonzalez, C. E., and Eickbush, T. H. (2001). Dynamics of R1 and R2 elements in the rDNA locus of Drosophila simulans. Genetics 158:1557.
Polanco, C., Gonzalez, A. I., Fuente, A., and Dover, G. A. (1998). Multigene family of ribosomal DNA in Drosophila melanogaster reveals contrasting patterns of homogenization for IGS and ITS spacer region: A possible mechanism to resolve this paradox. Genetics 149:243.
Porter, C. H., and Collins, F. H. (1991). Species-diagnostic differences in a ribosomal DNA internal transcribed spacer from the sibling species Anopheles freeborni and Anopheles hermsi (Diptera: Culicidae). Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 45(2):271.
Scott, J. A., Brogdon, W. G., and Collins, F. H. (1993). Identification of a single specimen of Anopheles gambiae complex by the polymerase chain reaction. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 49(4):520.
Sinibaldi, R. M., and Cummings, M. R. (1981). Localization and characterization of rDNA in Drosophila timiditarsus. Chromosoma 81:655.
Spear, B. (1974). The genes for ribosomal RNA in diploid and polytene chromosomes of Drosophila melanogaster. Chromosoma 48:159.
Tovar, F. J., da Silva, L. A. F., Rodarte, R. S., and Leoncini, O. (2000). Characterization of rDNA in Drosophila arizonae. Genet. Mol. Biol. 23(2):331.
Wasserman, M. (1992). Cytological evolution of the Drosophila repleta species group. In: Krimbas, C. B., and Powel, J. R. (eds). Drosophila inversion polymorphism, CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL, pp. 455-552.
Whiley, R. A., Duke, B., Hardie, J. M., and Hall, L. M. (1995). Heterogeneity among 16S-23S RNAr intergenic spacers of species within the Streptococcus milleri group. Microbiology 141(6): 1461.
White, E. E., Dubetz, C. P., Cruickshank, M. G., and Morrison, D. J. (1998). DNA diagnostic for Armillaria species in British Columbia: Within and between species variation in the IGS-1 and IGS-2 regions. Mycologia 90(1):125.
Zouros, E., van Delden, W., Odense, R., and van Dijk, H. (1982). An esterase duplication in Drosophila: Differences in expression of duplicate loci within and among related species. Biochem. Genet. 20(9/10):929.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Baffi, M.A., Ceron, C.R. Molecular Analysis of the rDNA ITS-1 Intergenic Spacer in Drosophila mulleri, D. arizonae, and Their Hybrids. Biochem Genet 40, 411–421 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1020729612672
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1020729612672