Abstract
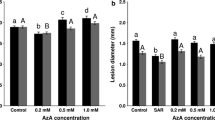
We have compared localized (LAR) and systemic (SAR) acquired resistance induced in tobacco by a hypersensitive response (HR) inducing Phytophthora megasperma glycoprotein elicitin. Three different zones were taken into account: LAR, SART and SARS. The LAR zone was 5–10 mm wide and surrounded the HR lesion. SART was the tissue of the elicitor-treated leaf immediately beyond the LAR zone. The systemic leaf was called SARS. Glycoprotein-treated plants showed enhanced resistance to challenge infection by tobacco mosaic virus (TMV). Disease resistance was similar in SART and SARS, and higher in LAR. The expression pattern, in glycoprotein-treated plants, of acidic and basic PR1, PR2, PR3 and PR5 proteins and of O-methyltransferases (OMT), enzymes of the phenylpropanoid pathway, was similar to that in TMV-infected plants. OMT was stimulated in LAR but not in SART and SARS. The four classes of acidic and basic PR proteins accumulated strongly in LAR. Reduced amounts of acidic PR1, PR2, PR3 and only minute amounts of basic PR2 and PR3 accumulated in SART and SARS. In glycoprotein-treated plants, expression of the acidic and basic PR proteins in LAR and SAR of transgenic NahG and ETR tobacco plants and in LAR of plants treated with inhibitors of salicylic acid accumulation and of ethylene biosynthesis indicated a salicylic acid-dependent signalling pathway for acidic isoform activation and an ethylene-dependent signalling pathway for basic isoform activation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baillieul, F., Fritig, B. and Kauffmann, S. 1996. Occurrence among Phytophthora species of a glycoprotein eliciting a hypersensitive response in tobacco and its relationships with elicitins. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 9: 214–216.
Baillieul, F., Genetet, I., Kopp, M., Saindrenan, P., Fritig, B. and Kauffmann, S. 1995. A new elicitor of the hypersensitive response in tobacco: a fungal glycoprotein elicits cell death, expression of defence genes, production of salicylic acid, and induction of systemic acquired resistance. Plant J. 8: 551–560.
Boller, T. 1991 Ethylene in pathogenesis and resistance. In: A.K. Mattoo and J.C. Suttle (eds), The plant hormone ethylene, CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp. 293–313.
Bonnet, P., Bourdon, E., Ponchet, M., Blein, J.-P. and Ricci, P. 1996. Acquired resistance triggered by elicitins in tobacco and other plants. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 102: 181–192.
Brederode, F.T., Linthorst, H.J.M. and Bol, J.F. 1991. Differential induction of acquired resistance and PR gene expression in tobacco by virus infection, ethephon treatment, UV light and wounding. Plant Mol. Biol. 17: 1117–1125.
Chong, C., Pierrel, M.A., Atanassova, R., Werck-Reichhart, D., Fritig, B. and Saindrenan, P. 2001. Free and conjugated benzoic acid in tobacco plants and cell cultures. Induced accumulation upon elicitation of defense responses and role as salicylic acid precursors. Plant Physiol. 125: 318–328.
Costet, L., Dorey, S., Fritig, B. and Kauffmann, S. 2002. A pharmacological approach to test the diffusible signal activity of reactive oxygen intermediates in elicitor-treated tobacco leaves. Plant Cell Physiol. 43: 91–98.
Costet, L., Fritig, B. and Kauffmann, S. 2002. Scopoletin expression in elicitor-treated and tobacco mosaic virus infected tobacco plants. Physiol. Plant. 115: 228–235.
Delaney, T.P., Ukness, S., Vernooij, B., Friedrich, L., Weymann, K., Negrotto, N., Gaffney, T., Gut-Rella, M., Kessmann, H., Ward, E. and Ryals, J. 1994. A central role of salicylic acid in plant disease resistance. Science 266: 1247–1250.
Dong, H., Delaney, T.P., Bauer, D.W. and Beer, S.V. 1999. Harpin induces disease resistance in Arabidopsis through the systemic acquired resistance pathway mediated by salicylic acid and the NIM1 gene. Plant J. 20: 207–215.
Dorey, S., Baillieul, F., Pierrel, M.A., Saindrenan, P., Fritig, B. and Kauffmann, S. 1997. Spatial and temporal induction of cell death, defense genes, and accumulation of salicylic acid in tobacco leaves reacting hypersensitively to a fungal glycoprotein elicitor. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 10: 646–655.
Dorey, S., Baillieul, F., Saindrenan, P., Fritig, B. and Kauffmann, S. 1998. Tobacco class I and II catalases are differentially expressed during elicitor-induced hypersensitive cell death and localized acquired resistance. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 11: 1102–1109.
Friedrich, L., Vernooij, B., Gaffney, T., Morse, A. and Ryals, J. 1995. Characterization of tobacco plants expressing a bacterial salicylate hydroxylase gene. Plant Mol. Biol. 29: 959–968.
Fritig, B., Heitz, T. and Legrand, M. 1998. Antimicrobial proteins in induced plant defense. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 10: 16–22.
Heath, M.C. 1998. Apoptosis, programmed cell death and the hypersensitive response. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 104: 117–124.
Kamoun, S., Huitema, E. and Vleeshouwers, V.G.A.A. 1999. Resistance to oomycetes: a general role for the hypersensitive response? Trends Plant Sci. 4: 196–200.
Kamoun, S., Lindquist, H. and Govers, F. 1997. A novel class of elicitin-like genes from Phytophthora infestans. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 10: 1028–1030.
Kamoun, S., Van West, P., Vleeshouwers, V.G.A.A., de Groot, K.E. and Govers, F. 1998. Resistance of Nicotiana benthamiana to Phytphthora infestans is mediated by the recognition of the elicitor protein INF1. Plant Cell 10: 1413–1425.
Keller, H., Blein, J.P., Bonnet, P. and Ricci, P. 1996. Physiological and molecular characteristics of elicitin-induced systemic acquired resistance in tobacco. Plant Physiol. 110: 365–376.
Knoester, M., Van Loon, L.C., Van den Heuvel, J., Hennig, J., Bol, J.F. and Linthorst, H.J.M. 1998. Ethylene-insensitive tobacco lacks nonhost resistance against soil-borne fungi. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95: 1933–1937.
Lawton, K.A., Potter, S.L., Uknes, S. and Ryals, J. 1994. Acquired resistance signal transduction in Arabidopsis is ethylene independent. Plant Cell 6: 581–588.
Legrand, M., Fritig, B. and Hirth, L. 1976. Enzymes of the phenylpropanoid pathway and the necrotic reaction of the hypersensitive tobacco to tobacco mosaic virus. Phytochem. 15: 1353–1359.
Legrand, M., Fritig, B. and Hirth, L. 1978. o-Diphenol-Omethyltransferases of healthy and tobacco mosaic virus-infected hypersensitive tobacco. Planta 144: 101–108.
Massala, R., Legrand, M. and Fritig, B. 1987. Comparative effects of two competitive inhibitors of phenylalanine ammonia-lyase on the hypersensitive resistance of tobacco to tobacco mosaic virus. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 25: 217–225.
Ohtsubo, N., Mitsuhara, I., Koga, M., Seo, S. and Ohashi, Y. 1999. Ethylene promotes the necrotic lesion formation and basic PR gene expression in TMV-infected tobacco. Plant Cell Physiol. 40: 808–817.
Pellegrini, L., Geoffroy, P., Fritig, B. and Legrand, M. 1993. Molecular cloning and expression of a new class of ortho-diphenol-O-methyltransferases induced in tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum L.) leaves by infection or elicitor treatment. Plant Physiol. 103: 509–517.
Ross, A.F. 1961a. Localized acquired resistance to plant virus infection in hypersensitive hosts. Virology 14: 329–339.
Ross, A.F. 1961b. Systemic acquired resistance induced by localized virus infections in plants. Virology 14: 340–358.
Ross, A.F. 1966 Systemic effects of local lesion formation. In: A.B.R. Beemster and J. Dijkstra (eds), Viruses of plants, North Holland Publishing Co., Amsterdam, pp. 127–150.
Ryals, J.A., Neuenschwander, U.H., Willits, G., Molina, A., Steiner, H.-Y. and Hunt, M.D. 1996. Sytemic acquired resistance. Plant Cell 8: 1809–1819.
Sticher, L., Mauch-Mani, B. and Métraux, J.-P. 1997. Systemic acquired resistance. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 35: 235–270.
Strobel, N.E., Ji, C., Gopalan, S., Kuc, J.A. and He, S.Y. 1996. Induction of systemic acquired resistance in cucumber by Pseudomonas syringae pv syringae 61 HrpZ(Pss) protein. Plant J. 9: 431–439.
Vu, H. and Gros, N. 1970. Exercices et problèmes corrigés de mathématiques. Analyse et statistique. Dunod, Paris.
Ward, E., Uknes, S., Williams, S., Dincher, S., Wiederhold, D., Alexander, D., Ahl-Goy, P., Métraux, J.P. and Ryals, J. 1991. Coordinate gene activity in response to agents that induce systemic acquired resistance. Plant Cell 3: 1085–1094.
Yalpani, N., Silvermann, P., Wilson, T.M.A., Kleier, D.A. and Raskin, I. 1991. Salicylic acid is a systemic signal and an inducer of pathogenesis-related proteins in virus-infected tobacco. Plant Cell 3: 809–818.
Zanetti, A., Beauvais, F., Huet, J.-C. and Pernollet, J.-C. 1992. Movement of elicitins, necrosis-inducing proteins secreted by Phytophthora sp., in tobacco. Planta 187: 163–170.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cordelier, S., de Ruffray, P., Fritig, B. et al. Biological and molecular comparison between localized and systemic acquired resistance induced in tobacco by a Phytophthora megasperma glycoprotein elicitin. Plant Mol Biol 51, 109–118 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1020722102871
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1020722102871