Abstract
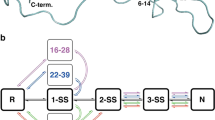
The native core structure of hirudin, a thrombin specific inhibitor, contains 24 hydrogen bonds, two stretches of β-sheet and three disulfide bonds. Hirudin unfolds in the presence of denaturant and thiol catalyst by shuffling its native disulfide bonds and converting to scrambled structures that consist of 11 identified isomers. The composition of scrambled isomers, which characterizes the structure of denatured hirudin, varies as a function of denaturing conditions. The unfolding pathway of hirudin has been constructed by quantitative analysis of scrambled isomers unfolded under increasing concentrations of various denaturants. The results demonstrate a progressive expansion of the polypeptide chain and the existence of a structurally defined stable intermediate along the pathway of unfolding.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Amir, D., and Hass, E. 1988. Biochemistry 27, 8889–8893.
Anfinsen, C. B. 1973. Science 181, 223–230.
Anfinsen, C. B., Haber, E., Sela, M., and White, F. H. Jr. 1961. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 47, 1309–1515.
Bierzynski, A., and Baldwin, R. L. 1982. J. Mol. Biol. 162, 173–186.
Chang, J. Y. 1990. J. Biol. Chem. 265, 22159–22166.
Chang, J. Y. 1991. J. Biol. Chem. 266, 10839–10843.
Chang, J. Y. 1994. Biochem. J. 300, 643–650.
Chang, J. Y. 1995. J. Biol. Chem. 270, 25661–25666.
Chang, J. Y. 1996. Biochemistry 35, 11702–11709.
Chang, J. Y. 1997. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 69–75.
Chang, J. Y. 1999. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 123–128.
Chang, J. Y, Cannals, F., Schindler, P., Querol, E., and Aviles, F. X. 1994. J. Biol. Chem. 269, 22087–22094.
Chang, J. Y., Maerki, W., and Lai, P. S. 1999. Protein Science 8, 1463–1468.
Chang, J. Y., Schindler, P., and Chatrenet, B. 1995. J. Biol. Chem. 270, 11992–11997.
Chang, J. Y., Schindler, P., Ramseier, U., and Lai, P. S. 1995. J. Biol. Chem. 270, 9207–9216.
Chatrenet, B., and Chang, J. Y. 1993. J. Biol. Chem. 268, 20988–20996.
Creighton, T. E. 1978. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 33, 231–297.
Creighton, T. E. 1979. J. Mol. Biol. 129, 411–431.
Creighton, T. E. 1986. Methods Enzymol. 131, 83–106.
Creighton, T. E. 1990. Biochem. J. 270, 1–16.
Creighton, T. E., and Goldenberg, D. P. 1984. J. Mol. Biol. 179, 497–526.
Dill, K. A., and Shortle, D. 1991. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 60, 795–825.
Dobson, C. M. 1992. Current Biology 2, 343–345.
Goto, Y., Calciano, L. J., and Fink, A. L. 1990. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 87, 573–577.
James, E. L., Whisstock, J. C., Gore, M. G., and Bottomley, S. P. 1999. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 9482–9488.
Kim, P. S., and Baldwin, R. L. 1990. Ann. Rev. Biochem. 59, 631–660.
Kuwajima, K., Ogawa, Y., and Sugai, S. 1979. Biochemistry 18, 878–882.
Li, Y. J., Rothwart, D. M., and Scheraga, H. A. 1995. Nature Struct. Biol. 2, 489–494.
Markwardt, F., and Walsmann, P. 1958. Hoppe-Seyler's Z Physiol. Chem. 312, 85–98.
Matthews, C. R. 1993. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 62, 653–683.
McWherter, C. A., Hass, E., Leed, A. R., and Scheraga, H. A. 1986. Biochemistry 25, 1951–1963.
Mendoza, J. A., Jarstfer, M. B., Goldenberg, D. P. 1994. Biochemistry 33, 1143–1148.
Pace, C. N. 1986. Methods Enzymol. 131, 226–280.
Richards, F. M. 1991. Jan Sci. Am. 34–41.
Roder, H., Eloeve, G. A., and Englander, S. W. 1988. Nature 335, 700–704.
Rosenfeld, R., Miller, J. A., Narhi, L. O., Hawkins, N., Katta, V., Weiss, M. A., and Arakawa, T. 1997. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 342, 298–305.
Scheraga, H. A., Konishi, Y., and Ooi, T. 1984. Adv. Biophys. 18, 21–41.
Shirley, B. A. 1995. Methods Mol. Biol. 40, 177–190.
Shortle, D., and Meeker, A. K. 1989. Biochemistry 28, 936–944.
Tanford, C. 1968. Adv. Protein Chem. 23, 121–282.
Tanford, C. 1970. Adv. Protein Chem. 24, 1–95.
Tanford, C., Kawahara, K., Lapanje, S., Hooker, T. M. Jr., Zarlengo, M. H., Salahuddin, A., Aune, K. C., and Takagi, T. 1967. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 89, 5023–5029.
Weissman, J. S., and Kim, P. S. 1991. Science 253, 1386–1393.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bulychev, A., Chang, JY. Unfolding of Hirudin Characterized by the Composition of Denatured Scrambled Isomers. J Protein Chem 18, 771–778 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1020681518265
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1020681518265