Abstract
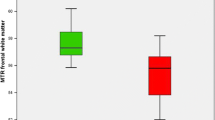
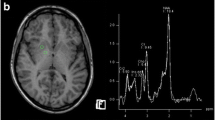
Bilateral, symmetrical hyperintensity of the globus pallidus is observed in T1-weighted cerebral magnetic resonance images in from 52 to 100% of patients with chronic liver disease. No significant relationship exists between the presence of these cerebral changes in image signal intensity and the patients' neuropsychiatric status. However, their presence significantly relates to both the severity of the liver disease and the presence and degree of portal-systemic shunting of blood. This shortening of the T1-relaxation time is associated with pallidal deposition of manganese most likely reflecting the presence of an adaptive process designed to improve the efficacy of ammonia detoxification by astrocytes. Future studies employing magnetic resonance imaging techniques to obtain information on cerebral function or combined with magnetic resonance spectroscopy to obtain localized biochemical information might further our understanding of the pathogenesis of hepatic encephalopathy in cirrhotic patients.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Adams, R.D. and Foley, J.M. (1953). The neurological disorder associated with liver disease. Assoc. Res. Nerv. Ment. Dis. Proc. 32:198–237.
Balaban, R.S. and Ceckler, P.L. (1992). Magnetisation transfer contrast imaging. Magn. Reson. Quart. 8:116–137.
Barbeau, A. (1984). Manganese and extrapyramidal disorders. Neurotoxicology 5:13–35.
Belliveau, J.W., Kennedy, D.N., McKinstry, R.C., Buchbinder, B.R., Weisskoff, R.M., Cohen, M.S. et al. (1991). Functional mapping of the human visual cortex by magnetic resonance imaging. Science 254:716–719.
Bernthal, P., Hays, A., Tarter, R.E., Van Thiel, D., Lecky, J. and Hegedus, A. (1987). Cerebral CT scan abnormalities in cholestatic and hepatocellular disease and their relationship to neuropsychologic test performance. Hepatology 7:107–114.
Bird, E.D., Anton, A.H. and Bullock, B. (1984). The effect of manganese inhalation on basal ganglia dopamine concentrations in rhesus monkey. Neurotoxicology 5:59–66.
Bokemeyer, M., Burchert, W., Ehrenheim, C., Tietge, U., Kolbe, H., Dengler, R. et al. (1997). Correlation between cerebral MRI findings and 18FDG-PET findings in patients with liver cirrhosis. In (C. Record, and H. Al-Mardini, eds.) Advances in Hepatic Encephalopathy and Metabolism in Liver Disease, 1996. University of Newcastle upon Tyne, U.K. pp 509–514.
Bosman, D.K., Chamuleau, R.A.F.M., Bovée, W.M.M.J., Barkhof, F., Luyten, P.R. et al. (1991). Chronic hepatic encephalopathy studied by 31P and 1H NMR spectroscopy and magnetic resonance imaging in man. In (D.K. Bosman) Pathophysiology and Therapy of Hepatic Encephalopathy: an Experimental and Clinical Study. PhD Thesis. Amsterdam, University of Amsterdam. pp 123–135.
Brunberg, J.A., Kanal, E., Hirsch, W. and Van Thiel, D.H. (1991). Chronic acquired hepatic failure: MR imaging of the brain at 1.5T. Am. J. Neuro. Radiol. 12:909–914.
Dell, L.A., Brown, M.S., Orrison, W.W., Eckel, C.G. and Matwiyoff, N.A. (1988). Physiologic intracranial calcification with hyperintensity on MR imaging: case report and experimental model. Am. J. Neuro. Radiol. 9:1145–1148.
Devenyi, A.G., Barron, R.F. and Mamourian, A.C. (1994). Dystonia, hyperintense basal ganglia and high whole blood manganese levels in Alagille's syndrome. Gastroenterology 106:1068–1071.
Drayer, B.P., Fram, E.K., Bird, C.R., Williams, K.D. and Keller, P.J. (1989). Systemic metabolic disease and the globus pallidus: an MRI approach. Am. J. Neuro. Radiol. 10:902 (abstract).
Farmer, P.M. and Mullakkan, T. (1990). The pathogenesis of hepatic encephalopathy. Ann. Clin. Lab. Sci. 20:91–97.
Finlayson, M.H. and Superville, B. (1981). Distribution of cerebral lesions in acquired hepatocerebral degeneration. Brain 104:79–95.
Gomori, J.M., Grossman, R.I., Goldberg, H.I., Zimmerman, R.Z. and Bilaniuk, L.T. (1985). High field magnetic resonance imaging of intracranial hematomas. Radiology 157:87–93.
Gomori, J.M., Grossman, R.I., Shields, J.A., Augsburger, J.J., Joseph, P.M. and DeSimeone, D. (1986). Choroidal melanomas: correlation of NMR spectroscopy and MR imaging. Radiology 158:443–445.
Gupta, R.K., Saraswat, V.A., Poptani, H., Dhiman, R.K., Kohli, A., Gujral, R.B. and Naik, S.R. (1993). Magnetic resonance imaging and localised in vivo proton spectroscopy in patients with fulminant hepatic failure. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 88:670–674.
Hanner, J.S., Li, K.C.P. and Davis G.L. (1988). Acquired hepatocerebral degeneration: MR similarity with Wilson's disease. J. Comp. Ass. Tomograph. 12:1076–1077.
Inoue, E., Hori, S., Narumi, Y., Fujita, M., Kuriyama, K., Kadota, T. and Kuroda, C. (1991). Portal-systemic encephalopathy: presence of basal ganglia lesions with high signal intensity on MR images. Radiology 179:551–555.
Jenner, P. (1994). Oxidative damage in neurodegenerative disease. Lancet 344:796–798.
Krieger, D., Krieger, S., Jansen, O., Gass, P., Theilmann, L. and Lichtuecker, H. (1995). Manganese and chronic hepatic encephalopathy. Lancet 346:270–274.
Kulisevsky, J., Pujol, J., Balanzó, J., Junqué, C., Deus, J., Capdevilla, A. and Villanueva, C. (1992). Pallidal hyperintensity on magnetic resonance imaging in cirrhotic patients: clinical correlations. Hepatology 16:1382–1388.
Laursen, H. (1982). Cerebral vessels and glial cells in liver disease. A morphometric and electron microscopic investigation. Acta. Neurol. Scand. 65:381–412.
Levy, L.M., Yang, A., Kumar, A.J., Hennigar, R., Rothstein, J. and Bryan, R.N. (1989). The brain and hepatic failure: MR abnormalities. Am. J. Neuro. Radiol. 10:904 (abstract).
McCarthy, G., Blamire, A.M., Rothman, D.L., Gruetter, R. and Shulman, R.G. (1993). Echo-planar magnetic resonance imaging studies of frontal cortex activation during word generation in humans. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 90:4952–4956.
Markesbery, W.R., Ehmann, W.D., Hossain, T.I. and Alauddin, M. (1984). Brain manganese concentrations in human ageing and Alzheimer's disease. Neurotoxicology 5:49–57.
Mirowitz, S.A., Sartor, K. and Gado, M. (1989). High-intensity basal ganglia lesions on T1-weighted MR images in neurofibromatosis. Am. J. Neuro. Radiol. 10:1159–1163.
Mirowitz, S.A., Westrich, T.J. and Hirsch, H.D. (1991). Hyperintense basal ganglia on T1-weighted MR images in patients receiving parenteral nutrition. Radiology 181:117–120.
Moore, J.W., Dunk, A.A., Crawford, J.R., Deans, H., Besson, J.A.O., De Lacey, G. et al. (1989). Neuropsychological deficits and morphological MRI brain scan abnormalities in apparently healthy nonencephalopathic patients with cirrhosis. A controlled study. J. Hepatol. 9:319–325.
Nelson, K., Golnick, J., Korn, T. and Angle, C. (1993). Manganese encephalopathy: utility of early magnetic resonance imaging. Br. J. Ind. Med. 40:510–513.
Norenberg, M.D. (1977). A light and electron microscopic study of experimental portal-systemic (ammonia) encephalopathy. Lab. Invest. 36:618–627.
Norenberg, M.D. (1981). The astrocyte in liver disease. Adv. Cell Neurobiol. 2:303–352.
Norenberg, M.D. (1987). The role of astrocytes in hepatic encephalopathy. Neurochem. Pathol. 6:13–33.
Norton, N.S., McConnell, J.R., Zetterman, R.K. and Rodriguez-Sierra, J.F. (1994). A quantitative evaluation of magnetic resonance image signal changes of the brain in chronic hepatic encephalopathy. J. Hepatol. 21:764–770.
Pentschew, A., Ebner, F.F. and Kovatch, R.M. (1963). Experimental manganese encephalopathy in monkeys. A preliminary report. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 22:488–499.
Pomier-Layrargues, G., Spahr, L. and Butterworth, R.F. (1995). Increased manganese concentrations in pallidum of cirrhotic patients. Lancet 345:735 (letter).
Pomier-Layrargues, G., Spahr, L., Fontaine, S. and Butterworth, R.F. (1997). T1-weighted magnetic resonance (MR) signal hyperintensity in globus palludus of cirrhotic patients results from manganese deposition. In (C. Record, and H. Al-Mardini, eds.) Advances in Hepatic Encephalopathy and Metabolism in Liver Disease, 1996. University of Newcastle-upon-Tyne, U.K. pp 251–255.
Pugh, R.N.H., Murray-Lyon, I.M., Dawson, J.L., Pietroni, M.C. and Williams, R. (1973). Transection of the oesophagus for bleeding oesophageal varices. Br. J. Surg. 60:646–649.
Pujol, A., Graus, F., Peri, J., Mercader, J.M. and Rimola, A. (1991). Hyperintensity in the globus pallidus on T1-weighted and inversion-recovery MRI: a possible marker of advanced liver disease. Neurology 41: 1526–1527.
Pujol, A., Pujol, J., Graus, F., Rimola, A., Peri, J., Mercader, J.M. et al (1993). Hyperintense globus pallidus on T1-weighted MRI in cirrhotic patients in associated with severity of liver failure. Neurology 43:65–69.
Rao, S.M., Binder, J.R., Bandettini, P.A., Hammeke, T.A., Yetkin, F.Z., Jesmanowicz, A. et al. (1993). Functional magnetic resonance imaging of complex human movements. Neurology 43:2311–2318.
Schenhammer, A.M. and Cherian, M.G. (1983). The influence of manganese on the distribution of essential trace elements. II. The tissue distribution of manganese, magnesium, zinc, iron and copper in rats after chronic manganese exposure. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health. 12:361–370.
Seth, P.K. and Chandra, A.V. (1984). Neurotransmitters and neurotransmitter receptors in developing and adult rats during manganese poisoning. Neurotoxicology 5:67–76.
Syh, H.W., Chu, W.K., Mar, N. and McConnell, J.R. (1991). An image analysis on MR imaging of the brain for hepatic encephalopathy. Biomed. Sci. Instrum. 27:29–33.
Tarter, R.E., Hays, A.L., Sandford, S.S. and Van Thiel, D.H. (1986). Cerebral morphological abnormalities associated with non-alcoholic cirrhosis. Lancet ii:893–895.
Taylor-Robinson, S.D., Oatridge, A., Hajnal, J.V., Burroughs, A.K., McIntyre, N. and de Souza, N.M. (1995). MR imaging of the basal ganglia in chronic liver disease: correlation of T1-weighted and magnetisation transfer contrast measurements with liver dysfunction and neuropsychiatric status. Metab. Brain Dis. 10:175–188.
Thuluvath, P.J., Edwin, D., Yue, N.C., de Villiers, C., Hochman, S. and Klein, A. (1995). Increased signals seen in globus pallidus in T1-weighted magnetic resonance imaging in cirrhotics are not suggestive of chronic hepatic encephalopathy. Hepatology 21:440–442.
Uchino, A., Miyoshi, T. and Ohno, M. (1989). Case report — MR imaging of chronic persistent hepatic encephalopathy. Radiat. Med. 7:257–260.
Versieck, J., Barbier, F., Speecke, A. and Hoste, J. (1974). Manganese, copper and zinc concentrations in serum and packed cells during acute hepatitis, chronic hepatitis and post-hepatitic cirrhosis. Clin. Chem. 20:1141–1145.
Victor, M., Adams, R.D. and Cole, M. (1965). The acquired (non-Wilsonian) type of chronic hepato-cerebral degeneration. Medicine (Baltimore) 44:354–396.
Wedler, F.C. and Denman, R.B. (1984). Glutamine synthetase: the major Mn(II) enzyme in mammalian brain. Curr. Top. Cell. Regul. 24:153–169.
Weissenborn, K., Ehrenheim, Ch., Hori, A., Kubicka, S. and Manns, M.P. (1995). Pallidal lesions in patients with liver cirrhosis: clinical and MRI evaluation. Metab. Brain Dis. 10:219–238.
Yamada, M., Ohno, S., Okayasu, I., Okeda, R., Hatakeyama, S., Watanabe, H. et al. (1986). Chronic manganese poisoning: a neuropathological study with determination of manganese distribution in the brain. Acta. Neuropathol. 70:273–278.
Zeneroli, M.L., Cioni, G., Vezzelli, C., Grandi, S., Crisi, G., Luzietti, R. et al. (1987). Prevalence of brain atrophy in liver cirrhosis patients with chronic persistent encephalopathy. Evaluation by computed tomography. J. Hepatol. 4:283–292.
Zeneroli, M.L., Cioni, G., Crisi, G., Vezzelli, C. and Ventura, E. (1991). Globus pallidus alterations and brain atrophy in liver cirrhosis patients with encephalopathy: an MR imaging study. Magn. Reson. Imaging 9:295–302.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Morgan, M.Y. Cerebral Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Patients with Chronic Liver Disease. Metab Brain Dis 13, 273–290 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1020680624084
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1020680624084