Abstract
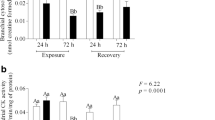
The change in the content of cyclic GMP, cyclic AMP, ATP, ADP, AMP and fructose-2,6-bisphosphate that occurred in the mantle of the mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis Lmk when specimens of this mollusk were subjected to a hypoxia/anoxia situation were assessed. After the early 24 h in anaerobiosis, a clear decrease was observed in the ATP content, which remained close to that value for the rest of the time. AMP content doubled during the early 24 h in anaerobiosis and, from that time on, it remained close to that value. Fructose-2,6-bisphoshate and cyclic GMP showed a similar behavior. The levels of these compounds rose significantly during the early hours in anaerobiosis, and then fell to values similar to those of aerobiosis, remaining constant for the rest of the time. Neither ADP nor cAMP showed significant variations.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Theede H, Ponat A, Hiroki K, Schlieper C: Studies on the resistance of marine bottom invertebrates to oxygen deficiency and hydrogen sulphide. Mar Biol 2: 325-336, 1969
de Zwaan A, Cortesi P, Van Den Thillart G, Roos J, Storey KB: Differential sensitivities to hypoxia by two anoxia-tolerant marine molluscs: A biochemical analysis. Mar Biol 111: 343-351, 1991
Atkinson DE: The energy charge of the adenylate pool as a regulatory parameter. Interaction with feedback modifiers. Biochemistry 7: 4030- 4034, 1968
Atkinson DE: Cellular energy metabolism and its regulation. Academic Press, New York, 1967
Zaroogian GE, Gentile JH, Heltshe JH, Johnson M: Application of adenine nucleotide measurements for the evaluation of stress in Mytilus edulis and Crassostrea virginica. J Exp Biochem Phys B 71: 643-649, 1982
San Juan Serrano F, Sánchez López JL, García Martín O: ATP and energy charge regulate glycogen phosphorylase from Mytilus galloprovincialis mantle. Comp Biochem Phys B 120: 483-491, 1998
Weyel W, Wegener G: Adenine nucleotide metabolism during anoxia and postanoxic recovery in insects. Experientia 52: 474-480, 1996
Ramaiah A: Pasteur effect and phosphofructokinase. Curr Top Cell Regul 8: 297-345, 1974
Depre C, Rider MH, Hue L: Mechanisms of control of heart glycolysis. Eur J Biochem 258: 277-290, 1998
Hochachka PW, Guppy M: Metabolic Arrest and the Control of Biological Time. Harvard University Press, Cambridge, 1987
De Zwaan A, Mathieu M: The mussel Mytilus: Ecology, physiology, genetics and culture. In: E. Gosling (ed). Developments in aquaculture and fisheries science, vol 25. Elsevier, Amsterdam, 1992, pp 223-307
Grieshaber MK, Hardewing I, Kreutzer U, Portner HO: Physiological and metabolic responses to hypoxia in invertebrates. Rev Physiol Biochen Physiol 125: 43-147, 1994
Schmidt H, Kamp G: The Pasteur effect in facultative anaerobic metazoa. Experientia 52: 440-448, 1996
Storey KB: Mechanisms of glycolytic control during facultative anaerobiosis in a marine mollusc: Tissue-specific analysis of glycogen phosphorylases and fructose-2,6-bisphosphate. Can J Zool 66: 1767-1771, 1988
Storey KB, Storey JM: Metabolic rate depression and biochemical adaptation in anaerobiosis, hibernation and estivation. Q Rev Biol 65: 145-174, 1990
Brooks SPJ, Storey KB: Glycolytic controls in estivation and anoxia: A comparison of metabolic arrest in land and marine molluscs. Comp Biochem Phys A 118: 1103-1114, 1997
Ibarguren I, Villamarín JA, Ramos-Martínez JI: Glucolisis en manto de Mytilus galloprovincialis Lmk: Efecto de la hipoxia provocada por el cierre de las valvas. Rev Esp Fisiol 45: 407-410, 1989
Ibarguren I, Villamarín JA, Barcia R, Ramos-Martínez JI: Efecto de la hipoxia sobre la glucolisis en mÚsculo aductor y hepatopáncreas del mejillón marino Mytilus galloprovincialis Lmk. Rev Esp Fisiol 45: 349-356, 1989
Villamarín JA: Fosfofructoquinasa en Mytilus galloprovincialis Lmk. PhD Thesis. University of Santiago de Compostela, Spain, 1989
Villamarín JA, Rodriguez-Torres AM, Ibarguren I, Ramos-Martínez JI: Phosphofructokinase in the mantle of the sea mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis Lmk. J Exp Zool 255: 272-279, 1990
Villamarín JA, Vázquez-Illanes MD, Barcia R, Ramos-Martínez JI: Effect of pH on the phosphofructokinase activity from the posterior adductor muscle of the sea mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis Lmk. Biochem Int 21: 77-84, 1990
Villamarín JA, Ramos-Martínez JI: Kinetic studies on the reaction catalysed by phosphofructokinase from Mytilus galloprovincialis (Lamark). Comp Biochem Phys B 95: 531-534, 1990
Fernández M, Cao J, Vázquez-Illanes MD, Ramos-Martínez JI, Villamarín JA: Phosphofructokinase from mantle tissue of Mytilus galloprovincialis: Purification and effects of phosphorylation on the enzymatic activity. Biochem Mol Biol Int 33: 355-364, 1994
Fernández M: 6-Fosfofructo-l-quinasa de Mytilus galloprovincialis: Regulación de la actividad enzimática por procesos de fosforilación. PhD Thesis. University of Santiago de Compostela, Spain, 1996
Cao J, Fernández M, Vázquez-Illanes MD, Ramos-Martínez JI, Villamarín JA: Purification and characterization of the catalytic subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase from the bivalve mollusc Mytilus galloprovincialis. Comp Biochem Phys B 111: 453-462, 1995
Fernández M, Cao J, Vega FV, Hellman U, Wernstedt C, Villamarín JA: cAMP-dependent phosphorylation activates phosphofructokinase from mantle tissue of the mollusc Mytilus galloprovincialis; identification of the phosphorylated site. Biochem Mol Biol Int 43: 173-181, 1997
Cao J, Ramos-Martínez JI, Villamarín JA: Characterization of a cAMP-binding protein from the bivalve mollusc Mytilus galloprovincialis. Eur J Biochem 232: 664-670, 1995
Mancebo MJ, Treviño M, Espinosa J: Adenylate cyclase activity in Mytilus galloprovincialis Lmk: Characteristics of the enzyme from mantle tissue. J Exp Zool 258: 174-180, 1991
Brooks SPJ, Storey KB: Purification and characterization of a protein phosphatase that dephosphorylates pyruvate kinase in anoxia tolerant animal. Biochem Mol Biol Int 38: 1223-1234, 1996
Rodríguez JL, Barcia R, Ramos-Martínez JI, Villamarín JA: Purification of a novel isoform of the regulatory subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase from the bivalve mollusk Mytilus galloprovincialis. Arch Biochem Biophys 359: 57-62, 1998
Díaz-Enrich MJ, Barcia R, Ramos-Martínez JI, Ibarguren I: Determination of adenine nucleotides in Mytilus galloprovincialis Lmk. by ion-pair high-performnce liquid chromatography with a diode array detector. J Liq Chrom Rel Technol 22: 1391-1402, 1999
Díaz-Enrich MJ, Villamarín JA, Ramos-Martínez JI, Ibarguren I: Measurement of adenosine 3',5'-cyclic monophosphate and guanosine 3',5'-cyclic monophosphate in mussel (Mytilus galloprovincialis Lmk.) by high-performance liquid chromatography with diode array detection. Anal Biochem 285:105-112, 2000
Van Schaftingen E: D-fructose 2,6-bisphosphate. In: H.U. Bergmeyer (ed). Methods of Enzymatic Analysis, vol 7. Verlag Chemie, Basilea, 1984, pp 335-341
Churchil TA, Storey KB: Intermediary energy metabolism during dormancy and anoxia in the land snail Otala lactea. Physiol Zool 62: 1015-1030, 1989
Storey KB, Kelly DA, Duncan JA, Storey JM: Anaerobiosis and organ-specific regulation of glycolysis in a marine whelk. Can J Zool 68: 974-980, 1990
Isani G, Cattani O, Carpené E, Racconi S, Cortesi P: Energy metabolism during anaerobiosis and recovery in the posterior adductor muscle of the bivalve Scapharca inaequivalvis (Bruguiere). Comp Biochem Phys B 93: 193-200, 1989
Van Schaftingen E: Fructosa 2,6-bisphosphate. Adv Enzymol 59: 315-395, 1987
Wegener G, Schmidt H, Leech AR, Newshoime EA: Antagonist effects of hexose-1,6-bisphosphate and fructose-2,6-bisphosphate on the activity of 6-phosphofructokinase from honey-bee flight muscle. Biochem J 236: 925-928, 1986
De Zwaan A, De Bont AMT, Verhoevell A: Anaerobic energy metabolism in isolated adductor muscle of the sea mussel Mytilus edulisEL. J Comp Physiol 149: 137-143, 1982
Hardewing I, Kreutzer U, Pörtner HO, Grieshaber MK: The role of phosphofructokinase in the glycolytic control in the facultative anaerobe Sipunculus nudus. J Comp Physiol 161: 581-589, 1991
Schmidt H, Nieczaj R: Phosphofructokinase from the body wale of the leech Hirudo medicinalis: Regulation of glycolysis during hypoxia. Verh Dtsch Zool Ges 87: 194-200, 1994
Kamp G, Juretschke HP, Thieu U, Englisch H: In vivo nuclear magnetic resonance studies on the lugworn Arenicola marina L. Free Pi and free AMP concentrations in the body wall and their dependence on hypoxia. J Comp Physiol 165: 143-152, 1995
Enomoto T, Nakao C, Ohyama H: Regulation of glycolysis during acclimation of scallops (Patinopecten yessoensis Jay) to anaerobiosis. Comp Biochem Phys B 127: 45-52, 2000
Fernández M, Cao J, Villamarín JA: In vivo phosphorylation of phosphofructokinase from the bivalve mollusk Mytilus galloprovincialis. Arch Biochem Biophys 353: 251-256, 1998
Malgorzata C, Wojda I, Frajnt M, Jakubowicz T: PKA from Saccharomyces cerevisiae can be activated by cyclic AMP and cyclic GMP. Can J Microbiol 45: 31-37, 1999
Vázquez-Illanes MD, Ramos-Martínez JI: Phosphorylation activated 6-phosphofructo 2-kinase from mantle tissue of marine mussels. FEBS Lett 295:176-178, 1991
Vázquez-Illanes MD, Barcia R, Ibarguren I, Villamarín JA, Ramos-Martínez JI: Regulation of fructose 2,6-bisphosphate content in mantle tissue of the sea mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis. I. Purification and properties of 6-phosphofructo 2-kinase. Mar Biol 112: 277-281, 1992
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Díaz Enrich, M.J., Ramos Martínez, J.I. & Ibarguren Arizeta, I. Implication of guanosine 3′,5′-cyclic monophosphate, adenosine 3′,5′-cyclic monophosphate, adenosine 5′-mono-, di- and triphosphate and fructose-2,6-bisphosphate in the regulation of the glycolytic pathway in hypoxic/anoxic mussel, Mytilus galloprovincialis . Mol Cell Biochem 240, 111–118 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1020666623094
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1020666623094