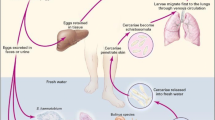
Abstract
Schistosomes are digenetic trematodes which cause schistosomiasis, also known as bilharzia, one of the main parasitic infections in man. In tropical and subtropical areas an estimated 200 million people are infected and suffer from the debilitating effects of this chronic disease. Schistosomes live in the blood vessels and strongly modulate the immune response of their host to be able to survive the hostile environment that they are exposed to. It has become increasingly clear that glycoconjugates of schistosome larvae, adult worms and eggs play an important role in the evasion mechanisms that schistosomes utilise to withstand the immunological measures of the host. Upon infection, the host mounts innate as well as adaptive immune responses to antigenic glycan elements, setting the immunological scene characteristic for schistosomiasis. In this review we summarise the structural data now available on schistosome glycans and provide data and ideas regarding the role that these glycans play in the various aspects of the glycobiology and immunology of schistosomiasis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jordan P, Webbe G, Sturrock RF, Human Schistosomiasis (Cambridge University Press, UK, 1993).
van Dam GJ, Deelder AM, Glycoproteins of parasites. In Glycoproteins and disease, edited by Montreuil J, Vliegenthart JFG, Schachter H (Elsevier Science, 1996), pp. 159–182.
Cummings RD, Nyame AK, Glycobiology of schistosomiasis, FASEB J 10, 838–48 (1996).
Cummings RD, Nyame AK, Schistosome glycoconjugates, Biochim Biophys Acta 1455, 363–74 (1999).
Haslam SM, Morris HR, Dell A, Mass spectrometric strategies: Providing structural clues for helminth glycoproteins, TrendsParasitol 17, 231–5 (2001).
Nyame K, Cummings RD, Damian RT, Characterization of the high mannose asparagine-linked oligosaccharides synthesized by Schistosoma mansoni adult male worms, Mol Biochem Parasitol 28, 265–74 (1988).
Nyame K, Smith DF, Damian RT, Cummings RD, Complex type asparagine-linked oligosaccharides in glycoproteins synthesized by Schistosoma mansoni adult males contain terminal betalinked N-acetylgalactosamine, J Biol Chem 264, 3235–43 (1989).
Srivatsan J, Smith DF, Cummings RD, Schistosoma mansoni synthesizes novel biantennary Asn-linked oligosaccharides containing terminal beta-linked N-acetylgalactosamine, Glycobiology 2, 445–52 (1992).
Srivatsan J, Smith DF, Cummings RD, The human blood fluke Schistosoma mansoni synthesizes glycoproteins containing the Lewis X antigen, J Biol Chem 267, 20196–203 (1992).
Nyame K, Cummings RD, Damian RT, Characterization of the N-and O-linked oligosaccharides in glycoproteins synthesized by Schistosoma mansoni schistosomula, J Parasitol 74, 562–72 (1988).
Khoo KH, Chatterjee D, Caulfield JP, Morris HR, Dell A, Structural mapping of the glycans from the egg glycoproteins of Schistosoma mansoni and Schistosoma japonicum: Identification of novel core structures and terminal sequences, Glycobiology 7, 663–77 (1997).
Haslam SM, Coles GC, Munn EA, Smith TS, Smith HF, Morris HR, Dell A, Haemonchus contortus glycoproteins contain Nlinked oligosaccharides with novel highly fucosylated core structures, J Biol Chem 271, 30561–70 (1996).
Lerouge P, Cabanes-Macheteau M, Rayon C, Fischette-Laine AC, Gomord V, Faye L, N-glycoprotein biosynthesis in plants: Recent developments and future trends, Plant Mol Biol 38, 31–48 (1998).
Staudacher E, Altmann F, Wilson IB, Marz L, Fucose in Nglycans: From plant to man, Biochim Biophys Acta 1473, 216–36 (1999).
Khoo KH, Huang HH, Lee KM, Characteristic structural features of schistosome cercarial N-glycans: Expression of Lewis X and core xylosylation, Glycobiology 11, 149–63 (2001).
Nyame K, Cummings RD, Damian RT, Schistosoma mansoni synthesizes glycoproteins containing terminal O-linked Nacetylglucosamine residues, J Biol Chem 262, 7990–5 (1987).
Khoo KH, Sarda S, Xu X, Caulfield JP, McNeil MR, Homans SW, Morris HR, Dell A, A unique multifucosylated-3GalNAc beta 1 → 4GlcNAc beta 1 → 3Gal alpha 1-motif constitutes the repeating unit of the complex O-glycans derived from the cercarial glycocalyx of Schistosoma mansoni, J Biol Chem 270, 17114–23 (1995).
Huang HH, Tsai PL, Khoo KH, Selective expression of different fucosylated epitopes on two distinct sets of Schistosoma mansoni cercarial O-glycans: Identification of a novel core type and Lewis X structure, Glycobiology 11, 395–406 (2001).
van Dam GJ, Bergwerff AA, Thomas-Oates JE, Rotmans JP, Kamerling JP, Vliegenthart JF, Deelder AM, The immunologically reactive O-linked polysaccharide chains derived from circulating cathodic antigen isolated from the human blood fluke Schistosoma mansoni have Lewis x as repeating unit, Eur J Biochem 225, 467–82 (1994).
Bergwerff AA, van Dam GJ, Rotmans JP, Deelder AM, Kamerling JP, Vliegenthart JF, The immunologically reactive part of immunopurified circulating anodic antigen from Schistosoma mansoni is a threonine-linked polysaccharide consisting of → 6)-(beta-D-GlcpA-(1 → 3))-beta-D-GalpNAc-(1 → repeating units, J Biol Chem 269, 31510–7 (1994).
Makaaru CK, Damian RT, Smith DF, Cummings RD, The human blood fluke Schistosoma mansoni synthesizes a novel type of glycosphingolipid, J Biol Chem 267, 2251–7 (1992).
Wuhrer M, Dennis RD, Doenhoff MJ, Lochnit G, Geyer R, Schistosoma mansoni cercarial glycolipids are dominated by Lewis X and pseudo-LewisYstructures, Glycobiology 10, 89–101 (2000).
Khoo KH, Chatterjee D, Caulfield JP, Morris HR, Dell A, Structural characterization of glycophingolipids from the eggs of Schistosoma mansoni and Schistosoma japonicum, Glycobiology 7, 653–61 (1997).
Wuhrer M, Kantelhardt SR, Dennis RD, Doenhoff MJ, Lochnit G, Geyer R, Characterization of glycosphingolipids from Schistosoma mansoni eggs carrying Fuc(α1-3)GalNAc-, GalNAc(β1-4)[Fuc(α1-3)]GlcNAc-and Gal(β1-4)[Fuc(α1-3)]-GlcNAc-(Lewis X) terminal structures, Eur J Biochem 269, 481–93 (2002).
Wuhrer M, Dennis RD, Doenhoff MJ, Geyer R, Stage-associated expression of ceramide structures in glycosphingolipids from the human trematode parasite Schistosoma mansoni, Biochim Biophys Acta 1524, 155–61 (2000).
Strand M, McMillan A, Pan X, Schistosoma mansoni: Reactivity with infected human sera and monoclonal antibody characterization of a glycoprotein in different developmental stages, Exp Parasitol 54, 145–56 (1982).
Dissous C, Capron A, Schistosoma mansoni: Antigenic community between schistosomula surface and adult worm incubation products as a support for concomitant immunity, FEBS Lett 162, 355–59 (1983).
Weiss JB, Magnani JL, Strand M, Identification of Schistosoma mansoni glycolipids that share immunogenic carbohydrate epitopes with glycoproteins, J Immunol 136, 4275–82 (1986).
Yi XY, Omer-Ali P, Kelly C, Simpson AJ, Smithers SR, IgM antibodies recognizing carbohydrate epitopes shared between schistosomula and miracidia of Schistosoma mansoni that block in vitro killing, J Immunol 137, 3946–54 (1986).
Dunne DW, Bickle QD, Identification and characterization of a polysaccharide-containing antigen from Schistosoma mansoni eggs which cross-reacts with the surface of schistosomula, Parasitology 94 (Pt 2), 255–68 (1987).
Bickle QD, Andrews BJ, Taylor MG, Schistosoma mansoni: Characterization of two protective monoclonal antibodies, Parasite Immunol 8, 95–107 (1986).
Ko AI, Dräger UC, Harn DA, A Schistosoma mansoni epitope recognized by a protective monoclonal antibody is identical to the stage-specific embryonic antigen 1, Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87, 4159–63 (1990).
Koster B, Strand M, Schistosoma mansoni: Immunolocalization of two different fucose-containing carbohydrate epitopes, Parasitology 108, 433–46 (1994).
van Dam GJ, Kornelis D, van Zeyl RJ, Rotmans JP, Deelder AM, Schistosoma mansoni: Analysis of monoclonal antibodies reactive with gut-associated antigens, Parasitol Res 79, 55–62 (1993).
Deelder AM, van Dam GJ, Kornelis D, Fillie YE, van Zeyl RJ, Schistosoma: Analysis of monoclonal antibodies reactive with the circulating antigens CAA and CCA, Parasitology 112, 21–35 (1996).
Nyame AK, Leppanen AM, DeBose-Boyd R, Cummings RD, Mice infected with Schistosoma mansoni generate antibodies to LacdiNAc (GalNAc beta 1 → 4GlcNAc) determinants, Glycobiology 9, 1029–35 (1999).
Nyame AK, Leppanen AM, Bogitsh BJ, Cummings RD, Antibody responses to the fucosylated LacdiNAc glycan antigen in Schistosoma mansoni-infected mice and expression of the glycan among schistosomes, Exp Parasitol 96, 202–12 (2000).
van Remoortere A, Hokke CH, van Dam GJ, van Die I, Deelder AM, van den Eijnden DH, Various stages of schistosoma express Lewis(x), LacdiNAc, GalNAcbeta1-4(Fucalpha1-3)GlcNAc and GalNAcbeta1-4(Fucalpha1-2Fucalpha1-3)GlcNAc carbohydrate epitopes: Detection with monoclonal antibodies that are characterized by enzymatically synthesized neoglycoproteins, Glycobiology 10, 601–9 (2000).
Deelder AM, De Jonge N, Boerman OC, Fillie YE, Hilberath GW, Rotmans JP, Gerritse MJ, Schut DW, Sensitive determination of circulating anodic antigen in Schistosoma mansoni infected individuals by an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay using monoclonal antibodies, Am J Trop Med Hyg 40, 268–72 (1989).
Nibbeling HA, Van Lieshout L, Polman K, Stelma FF, Polderman AM, Deelder AM, Serum circulating egg antigen levels in two areas endemic for Schistosoma mansoni, Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg 92, 350–4 (1998).
Polman K, Stelma FF, Gryseels B, van Dam GJ, Talla I, Niang M, Van Lieshout L, Deelder AM, Epidemiologic application of circulating antigen detection in a recent Schistosoma mansoni focus in northern Senegal, Am J Trop Med Hyg 53, 152–7 (1995).
Van Lieshout L, Polderman AM, Deelder AM, Immunodiagnosis of schistosomiasis by determination of the circulating antigens CAA and CCA, in particular in individuals with recent or light infections, Acta Trop 77, 69–80 (2000).
Nourel Din MA, Kornelis D, van Zeyl RJ, Deelder AM, Immunologic characterization of two monoclonal antibodies reactive with repetitive carbohydrate epitopes of circulating Schistosoma mansoni egg antigen, Am J Trop Med Hyg 50, 487–98 (1994).
Weiss JB, Strand M, Characterization of developmentally regulated epitopes of Schistosoma mansoni egg glycoprotein antigens, J Immunol 135, 1421–9 (1985).
Dalton JP, Lewis SA, Aronstein WS, Strand M, Schistosoma mansoni: Immunogenic glycoproteins of the cercarial glycocalyx, Exp Parasitol 63, 215–26 (1987).
Bogers JJ, Nibbeling HA, Van Marck EA, Deelder AM, Immunoelectron microscopical localization of a circulating antigen in the excretory system of Schistosoma mansoni. Ultrastructural localization studies of the excretory system of S. mansoni, Parasitol Res 81, 375–81 (1995).
Nyame AK, DeBose-Boyd R, Long TD, Tsang VC, Cummings RD, Expression of Lex antigen in Schistosoma japonicum and S. haematobium and immune responses to Lex in infected animals: Lack of Lex expression in other trematodes and nematodes, Glycobiology 8, 615–24 (1998).
Wuhrer M, Dennis RD, Doenhoff MJ, Bickle Q, Lochnit G, Geyer R, Immunochemical characterisation of Schistosoma mansoni glycolipid antigens, Mol Biochem Parasitol 103, 155–69 (1999).
van Die I, Gomord V, Kooyman FN, van den Berg TK, Cummings RD, Vervelde L, Core alpha1 → 3-fucose is a common modification of N-glycans in parasitic helminths and constitutes an important epitope for IgE from Haemonchus contortus infected sheep, FEBS Lett 463, 189–93 (1999).
Halkes KM, Lefeber DJ, Fransen CT, Kamerling JP, Vliegenthart JF, Synthesis of the spacer-containing beta-D-GalpNAc-(1 → 4)-beta-D-GlcpNAc-(1 → 3)-alpha-D-Galp moiety, representing the non-fucosylated backbone trisaccharide of the glycocalyx glycan of the parasite Schistosoma mansoni, Carbohydr Res 308, 329–38 (1998).
Ágoston K, Kerékgyártó J, Hajkó J, Batta G, Lefeber DJ, Kamerling JP, Vliegenthart JFG, Synthesis of fragments of the glycocalyx glycan of the parasite Schistosoma mansoni, Chemistry 8, 151–61 (2002).
Halkes KM, Vermeer HJ, Slaghek TM, van Hooft PA, Loof A, Kamerling JP, Vliegenthart JF, Preparation of spacer-containing di-, tri-, and tetrasaccharide fragments of the circulating anodic antigen of Schistosoma mansoni for diagnostic purposes, Carbohydr Res 309, 175–88 (1998).
Lee RT, Lee YC, Affinity enhancement by multivalent lectincarbohydrate interaction, Glycoconj J 17, 543–51 (2000).
Dell A, Haslam SM, Morris HR, Khoo KH, Immunogenic glycoconjugates implicated in parasitic nematode diseases, Biochim Biophys Acta 1455, 353–62 (1999).
Wisnewski N, McNeil M, Grieve RB, Wassom DL, Characterization of novel fucosyl-and tyvelosyl-containing glycoconjugates from Trichinella spiralis muscle stage larvae, Mol Biochem Parasitol 61, 25–35 (1993).
Reason AJ, Ellis LA, Appleton JA, Wisnewski N, Grieve RB, McNeil M, Wassom DL, Morris HR, Dell A, Novel tyvelosecontaining tri-and tetra-antennary N-glycans in the immunodominant antigens of the intracellular parasite Trichinella spiralis, Glycobiology 4, 593–603 (1994).
Morelle W, Haslam SM, Olivier V, Appleton JA, Morris HR, Dell A, Phosphorylcholine-containing N-glycans of Trichinella spiralis: Identification of multiantennary lacdiNAc structures, Glycobiology 10, 941–50 (2000).
Morelle W, Haslam SM, Morris HR, Dell A, Characterization of the N-linked glycans of adult Trichinella spiralis, Mol Biochem Parasitol 109, 171–7 (2000).
Haslam SM, Coles GC, Reason AJ, Morris HR, Dell A, The novel core fucosylation of Haemonchus contortus N-glycans is stage specific, Mol Biochem Parasitol 93, 143–7 (1998).
Maizels RM, Burke J, Denham DA, Phosphorylcholine-bearing antigens in filarial nematode parasites: Analysis of somatic extracts, in vitro secretions and infection sera from Brugia malayi and B. pahangi, Parasite Immunol 9, 49–66 (1987).
Harnett W, Houston KM, Amess R, Worms MJ, Acanthocheilonema viteae: Phosphorylcholine is attached to the major excretory-secretory product via an N-linked glycan, Exp Parasitol 77, 498–502 (1993).
Haslam SM, Houston KM, Harnett W, Reason AJ, Morris HR, Dell A, Structural studies of N-glycans of filarial parasites. Conservation of phosphorylcholine-substituted glycans among species and discovery of novel chito-oligomers, J Biol Chem 274, 20953–60 (1999).
Lochnit G, Dennis RD, Geyer R, Phosphorylcholine substituents in nematodes: Structures, occurrence and biological implications, Biol Chem 381, 839–47 (2000).
Wuhrer M, Rickhoff S, Dennis RD, Lochnit G, Soboslay PT, Baumeister S, Geyer R, Phosphocholine-containing, zwitterionic glycosphingolipids of adult Onchocerca volvulus as highly conserved antigenic structures of parasitic nematodes, Biochem J 348, 417–23 (2000).
Lochnit G, Dennis RD, Muntefehr H, Nispel S, Geyer R, Immunohistochemical localization and differentiation of phosphocholine-containing antigens of the porcine, parasitic nematode, Ascaris suum, Parasitology 122, 359–70 (2001).
Kubelka V, Altmann F, Staudacher E, Tretter V, Marz L, Hard K, Kamerling JP, Vliegenthart JF, Primary structures of the Nlinked carbohydrate chains from honeybee venom phospholipase A2, Eur J Biochem 213, 1193–204 (1993).
Faye L, Gomord V, Fitchette-Laine AC, Chrispeels MJ, Affinity purification of antibodies specific for Asn-linked glycans containing alpha 1 → 3 fucose or beta 1 → 2 xylose, Anal Biochem 209, 104–8 (1993).
van Ree R, Cabanes-Macheteau M, Akkerdaas J, Milazzo JP, Loutelier-Bourhis C, Rayon C, Villalba M, Koppelman S, Aalberse R, Rodriguez R, Faye L, Lerouge P, Beta(1,2)-xylose and alpha(1,3)-fucose residues have a strong contribution in IgE binding to plant glycoallergens, J Biol Chem 275, 11451–8 (2000).
Mansour MM, Ali PO, Farid Z, Simpson AJ, Woody JW, Serological differentiation of acute and chronic schistosomiasis mansoni by antibody responses to keyhole limpet hemocyanin, Am J Trop Med Hyg 41, 338–44 (1989).
Hamilton JV, Klinkert M, Doenhoff MJ, Diagnosis of schistosomiasis: Antibody detection, with notes on parasitological and antigen detection methods, Parasitology 117 Suppl, S41–S57 (1998).
Wuhrer M, Dennis RD, Doenhoff MJ, Geyer R, A fucosecontaining epitope is shared by keyhole limpet haemocyanin and Schistosoma mansoni glycosphingolipids, Mol Biochem Parasitol 110, 237–46 (2000).
Haslam SM, Coles GC, Morris HR, Dell A, Structural characterization of the N-glycans of Dictyocaulus viviparus: Discovery of the Lewis(x) structure in a nematode, Glycobiology 10, 223–9 (2000).
Rumjanek FD, Broomfield KE, Smithers SR, Schistosoma mansoni: Glycosyl transferase activity and the carbohydrate composition of the tegument, Exp Parasitol 47, 24–35 (1979).
Simpson AJ, Rumjanek FD, Payares G, Evans WH, Glycosyl transferase activities are associated with the surface membrane in adult Schistosoma mansoni, Mol Biochem Parasitol 4, 107–15 (1981).
Rivera-Marrero CA, Cummings RD, Schistosoma mansoni contains a galactosyltransferase activity distinct from that typically found in mammalian cells, Mol Biochem Parasitol 43, 59–67 (1990).
Srivatsan J, Smith DF, Cummings RD, Demonstration of a novel UDPGalNAc:GlcNAc beta 1-4 N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase in extracts of Schistosoma mansoni, J Parasitol 80, 884–90 (1994).
DeBose-Boyd R, Nyame AK, Cummings RD, Schistosoma mansoni: Characterization of an alpha 1-3 fucosyltransferase in adult parasites, Exp Parasitol 82, 1–10 (1996).
Marques ET Jr, Weiss JB, Strand M, Molecular characterization of a fucosyltransferase encoded by Schistosoma mansoni, Mol Biochem Parasitol 93, 237–50 (1998).
Trottein F, Mollicone R, Fontaine J, de Mendonca R, Piller F, Pierce R, Oriol R, Capron M, Molecular cloning of a putative alpha3-fucosyltransferase from Schistosoma mansoni, Mol Biochem Parasitol 107, 279–87 (2000).
Marques ET Jr, Ichikawa Y, Strand M, August JT, Hart GW, Schnaar RL, Fucosyltransferases in Schistosoma mansoni development, Glycobiology 11, 249–59 (2001).
Hokke CH, Neeleman AP, Koeleman CA, van den Eijnden DH, Identification of an alpha3-fucosyltransferase and a novel alpha2-fucosyltransferase activity in cercariae of the schistosome Trichobilharzia ocellata: Biosynthesis of the Fucalpha1 → 2Fucalpha1 → 3[Gal(NAc)beta1 → 4]GlcNAc sequence, Glycobiology 8, 393–406 (1998).
de Vries T, Knegtel RM, Holmes EH, Macher BA, Fucosyltransferases: Structure/function studies, Glycobiology 11, 119R–28R (2001).
Nash TE, Antibody response to a polysaccharide antigen present in the schistosome gut. I. Sensitivity and specificity, Am J Trop Med Hyg 27, 939–43 (1978).
Omer-Ali P, Magee AI, Kelly C, Simpson AJ, A major role for carbohydrate epitopes preferentially recognized by chronically infected mice in the determination of Schistosoma mansoni schistosomulum surface antigenicity, J Immunol 137, 3601–7 (1986).
Omer-Ali P, Smithers SR, Bickle Q, Phillips SM, Harn D, Simpson AJ, Analysis of the anti-Schistosoma mansoni surface antibody response during murine infection and its potential contribution to protective immunity, J Immunol 140, 3273–9 (1988).
Dunne DW, Schistosome carbohydrates, Parasitol Today 6, 45–8 (1990).
Nyame AK, Pilcher JB, Tsang VC, Cummings RD, Schistosoma mansoni infection in humans and primates induces cytolytic antibodies to surface Le(x) determinants on myeloid cells, Exp Parasitol 82, 191–200 (1996).
van Remoortere A, van Dam GJ, Hokke CH, van den Eijnden DH, van Die I, Deelder AM, Profiles of immunoglobulinM(IgM) and IgG antibodies against defined carbohydrate epitopes in sera of Schistosoma-infected individuals determined by surface plasmon resonance, Infect Immun 69, 2396–401 (2001).
Eberl M, Langermans JA, Vervenne RA, Nyame AK, Cummings RD, Thomas AW, Coulson PS, Wilson RA, Antibodies to glycans dominate the host response to schistosome larvae and eggs: Is their role protective or subversive? J Infect Dis 183, 1238–47 (2001).
Richter D, Incani RN, Harn DA, Lacto-N-fucopentaose III (Lewis x), a target of the antibody response in mice vaccinated with irradiated cercariae of Schistosoma mansoni, Infect Immun 64, 1826–31 (1996).
Nyame AK, Pilcher JB, Tsang VC, Cummings RD, Rodents infected with Schistosoma mansoni produce cytolytic IgG and IgM antibodies to the Lewis x antigen, Glycobiology 7, 207–15 (1997).
Deelder AM, van Zeyl RJ, Fillie YE, Rotmans JP, Duchenne W, Recognition of gut-associated antigens by immunoglobulinMin the indirect fluorescent antibody test for schistosomiasis mansoni, Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg 83, 364–7 (1989).
Deelder AM, Kornelis D, Immunodiagnosis of recently acquired Schistosoma mansoni infection, Trop Geogr Med 33, 36–41 (1981).
Qian ZL, Deelder AM, Schistosoma japonicum: Immunological responses to circulating polysaccharide antigens in rabbits with a light infection, Exp Parasitol 55, 394–403 (1983).
van Dam GJ, Qian ZL, Fillie YE, Rotmans JP, Deelder AM, Detection of IgM antibodies directed against the gut-associated circulating cathodic antigen in sera from Schistosoma mansoni infected patients. Development and comparison of three enzymelinked immunoassays, Trop Geogr Med 45, 59–65 (1993).
De Graaf TW, Van der Stelt ME, Anbergen MG, van Dijk W, Inflammation-induced expression of sialyl Lewis X-containing glycan structures on alpha 1-acid glycoprotein (orosomucoid) in human sera, J Exp Med 177, 657–66 (1993).
van Kuik JA, de Waard P, Vliegenthart JF, Klein A, Carnoy C, Lamblin G, Roussel P, Isolation and structural characterization of novel neutral oligosaccharide-alditols from respiratory-mucus glycoproteins of a patient suffering from bronchiectasis. 2. Structure of twelve hepta-to-nonasaccharides, six of which possess the GlcNAc beta(1-3)[Gal beta(1-4)GlcNAc beta(1-6)]Gal beta(1-3)GalNAc-ol common structural element, Eur J Biochem 198, 169–82 (1991).
Yan SB, Chao YB, van Halbeek H, Novel Asn-linked oligosaccharides terminating in GalNAc beta (1 → 4)[Fuc alpha (1 → 3)]GlcNAc beta (1 →.) are present in recombinant human protein C expressed in human kidney 293 cells, Glycobiology 3, 597–608 (1993).
Bergwerff AA, Thomas-Oates JE, van Oostrum J, Kamerling JP, Vliegenthart JF, Human urokinase contains GalNAc beta (1-4)[Fuc alpha (1-3)]GlcNAc beta (1-2) as a novel terminal element in N-linked carbohydrate chains, FEBS Lett 314, 389–94 (1992).
van den Eijnden DH, Bakker H, Neeleman AP, van den Nieuwenhof I, van Die I, Novel pathways in complex-type oligosaccharide synthesis: Newvistas opened by studies in invertebrates, Biochem Soc Trans 25, 887–93 (1997).
vanDam GJ, Claas FH, Yazdanbakhsh M, Kruize YC, van Keulen AC, Ferreira ST, Rotmans JP, Deelder AM, Schistosoma mansoni excretory circulating cathodic antigen shares Lewis-x epitopes with a human granulocyte surface antigen and evokes host antibodies mediating complement-dependent lysis of granulocytes, Blood 88, 4246–51 (1996).
van der Kleij D, Tielens AG, Yazdanbakhsh M, Recognition of schistosome glycolipids by immunoglobulin E: Possible role in immunity, Infect Immun 67, 5946–50 (1999).
Gregoire RJ, Shi MH, Rekosh DM, Loverde PT, Protective monoclonal antibodies from mice vaccinated or chronically infected with Schistosoma mansoni that recognize the same antigens, J Immunol 139, 3792–801 (1987).
Grzych JM, Dissous C, Capron M, Torres S, Lambert PH, Capron A, Schistosoma mansoni shares a protective carbohydrate epitope with keyhole limpet hemocyanin, J Exp Med 165, 865–78 (1987).
Jasmer DP, Perryman LE, Conder GA, Crow S, McGuire T, Protective immunity to Haemonchus contortus induced by immunoaffinity isolated antigens that share a phylogenetically conserved carbohydrate gut surface epitope, J Immunol 151, 5450–60 (1993).
Ellis LA, Reason AJ, Morris HR, Dell A, Iglesias R, Ubeira FM, Appleton JA, Glycans as targets for monoclonal antibodies that protect rats against Tirichinella spiralis, Glycobiology 4, 585–92 (1994).
Hussein AH, Kaddah MA, Hamadto HH, el Hayawan IA, Strickland PT, Abubaker S, Shiff CJ, Schistosoma mansoni: The immune response against cercarial glycocalyx, J Parasitol 83, 424–29 (1997).
Dunne DW, Bickle QD, Butterworth AE, Richardson BA, The blocking of human antibody-dependent, eosinophil-mediated killing of Schistosoma mansoni schistosomula by monoclonal antibodies which cross-react with a polysaccharide-containing egg antigen, Parasitology 94, 269–80 (1987).
Butterworth AE, Dunne DW, Fulford AJ, Thorne KJ, Gachuhi K, Ouma JH, Sturrock RF, Human immunity to Schistosoma mansoni: Observations on mechanisms, and implications for control, Immunol Invest 21, 391–407 (1992).
Hagan P, Blumenthal UJ, Dunn D, Simpson AJ, Wilkins HA, Human IgE, IgG4 and resistance to reinfection with Schistosoma haematobium, Nature 349, 243–5 (1991).
Dunne DW, Butterworth AE, Fulford AJ, Kariuki HC, Langley JG, Ouma JH, Capron A, Pierce RJ, Sturrock RF, Immunity after treatment of human schistosomiasis: Association between IgE antibodies to adult worm antigens and resistance to reinfection, Eur J Immunol 22, 1483–94 (1992).
Rihet P, Demeure CE, Dessein AJ, Bourgois A, Strong serum inhibition of specific IgE correlated to competing IgG4, revealed by a new methodology in subjects from a S. mansoni endemic area, Eur J Immunol 22, 2063–70 (1992).
Demeure CE, Rihet P, Abel L, Ouattara M, Bourgois A, Dessein AJ, Resistance to Schistosoma mansoni in humans: Influence of the IgE/IgG4 balance and IgG2 in immunity to reinfection after chemotherapy, J Infect Dis 168, 1000–8 (1993).
Grzych JM, Pearce E, Cheever A, Caulada ZA, Caspar P, Heiny S, Lewis F, Sher A, Egg deposition is the major stimulus for the production of Th2 cytokines in murine schistosomiasis mansoni, J Immunol 146, 1322–7 (1991).
Pearce EJ, Caspar P, Grzych JM, Lewis FA, Sher A, Downregulation of Th1 cytokine production accompanies induction of Th2 responses by a parasitic helminth, Schistosoma mansoni, J Exp Med 173, 159–66 (1991).
Williams ME, Montenegro S, Domingues AL, Wynn TA, Teixeira K, Mahanty S, Coutinho A, Sher A, Leukocytes of patients with Schistosoma mansoni respond with a Th2 pattern of cytokine production to mitogen or egg antigens but with a Th0 pattern to worm antigens, J Infect Dis 170, 946–54 (1994).
Okano M, Satoskar AR, Nishizaki K, Abe M, Harn DA Jr, Induction of Th2 responses and IgE is largely due to carbohydrates functioning as adjuvants on Schistosoma mansoni egg antigens, J Immunol 163, 6712–7 (1999).
Velupillai P, Secor WE, Horauf AM, Harn DA, B-1 cell (CD5+B220+) outgrowth in murine schistosomiasis is genetically restricted and is largely due to activation by polylactosamine sugars, J Immunol 158, 338–44 (1997).
Velupillai P, Harn DA, Oligosaccharide-specific induction of interleukin 10 production by B220+ cells from schistosomeinfected mice: A mechanism for regulation of CD4+ T-cell subsets, Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91, 18–22 (1994).
Hoffmann KF, Cheever AW, Wynn TA, IL-10 and the dangers of immune polarization: Excessive type 1 and type 2 cytokine responses induce distinct forms of lethal immunopathology in murine schistosomiasis, J Immunol 164, 6406–16 (2000).
van den Biggelaar AH, van Ree R, Rodrigues LC, Lell B, Deelder AM, Kremsner PG, Yazdanbakhsh M, Decreased atopy in children infected with Schistosoma haematobium: A role for parasiteinduced interleukin-10, Lancet 356, 1723–7 (2000).
Yazdanbakhsh M, van den Biggelaar AH, Maizels RM, Th2 responses without atopy: Immunoregulation in chronic helminth infections and reduced allergic disease, Trends Immunol 22, 372–7 (2001).
Velupillai P, dos Reis EA, dos Reis MG, Harn DA, Lewis(x)-containing oligosaccharide attenuates schistosome egg antigeninduced immune depression in human schistosomiasis, Hum Immunol 61, 225–32 (2000).
Okano M, Satoskar AR, Nishizaki K, Harn DA Jr, Lacto-Nfucopentaose III found on Schistosoma mansoni egg antigens functions as adjuvant for proteins by inducing Th2-type response, J Immunol 167, 442–50 (2001).
Atochina O, Daly-Engel T, Piskorska D, McGuire E, Harn DA, A schistosome-expressed immunomodulatory glycoconjugate expands peritoneal Gr1(+) macrophages that suppress naive CD4(+) T cell proliferation via an IFN-gamma and nitric oxidedependent mechanism, J Immunol 167, 4293–302 (2001).
Terrazas LI, Walsh KL, Piskorska D, McGuire E, Harn DA Jr, The schistosome oligosaccharide lacto-n-neotetraose expands gr1(+) cells that secrete anti-inflammatory cytokines and inhibit proliferation of naive cd4(+) cells: A potential mechanism for immune polarization in helminth infections, J Immunol 167, 5294–303 (2001).
van der Kleij D, van Remoortere A, Schuitemaker JHN, Deelder AM, Tielens AG, Hokke CH, Yazdanbakhsh M, Triggering of innate immune responses by schistosome egg glycolipids and their carbohydrate epitope GalNAcbeta1-4(Fucalpha1-2Fucalpha1-3)GlcNAc, J Infect Dis 185, 531–9 (2002).
Feizi T, Carbohydrate-mediated recognition systems in innate immunity, Immunol Rev 173, 79–88 (2000).
Aderem A, Ulevitch RJ, Toll-like receptors in the induction of the innate immune response, Nature 406, 782–7 (2000).
Van Marck EA, Stocker S, Grimaud JA, Kestens L, Gigase PL, Deelder AM,The implantation of sepharose beads in mouse livers as an aid in the study of hepatic schistosomal fibrosis, Experientia 36, 1116–8 (1980).
Weiss JB, Aronstein WS, Strand M, Schistosoma mansoni: Stimulation of artificial granuloma formation in vivo by carbohydrate determinants, Exp Parasitol 64, 228–36 (1987).
Boros DL, Immunopathology of Schistosoma mansoni infection, Clin Microbiol Rev 2, 250–69 (1989).
Wynn TA, Cheever AW, Cytokine regulation of granuloma formation in schistosomiasis, Curr Opin Immunol 7, 505–11 (1995).
Jacobs W, van Dam G, Bogers J, Deelder A, Van Marck E, Schistosomal granuloma modulation. I. Schistosoma mansoni worm antigens CAA and CCAprime egg-antigen-induced hepatic granuloma formation, Parasitol Res 85, 7–13 (1999).
Jacobs W, Deelder A, Van Marck E, Schistosomal granuloma modulation. II. Specific immunogenic carbohydrates can modulate schistosome-egg-antigen-induced hepatic granuloma formation, Parasitol Res 85, 14–18 (1999).
Jacobs W, Van Marck E, Adhesion and co-stimulatory molecules in the pathogenesis of hepatic and intestinal schistosomiasis mansoni, Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz 93, 523–9 (1998).
Secor WE, dos Reis MG, Ramos EA, Matos EP, Reis EA, do Carmo TM, Harn DA Jr, Soluble intercellular adhesion molecules in human schistosomiasis: Correlations with disease severity and decreased responsiveness to egg antigens, Infect Immun 62, 2695–2701 (1994).
Vestweber D, Blanks JE, Mechanisms that regulate the function of the selectins and their ligands, Physiol Rev 79, 181–213 (1999).
Grinnell BW, Hermann RB, Yan SB, Human protein C inhibits selectin-mediated cell adhesion: Role of unique fucosylated oligosaccharide, Glycobiology 4, 221–5 (1994).
El Ridi R, Velupillai P, Harn DA, Regulation of schistosome egg granuloma formation: Host-soluble L-selectin enters tissuetrapped eggs and binds to carbohydrate antigens on surface membranes of miracidia, Infect Immun 64, 4700–5 (1996).
McEver RP, Moore KL, Cummings RD, Leukocyte trafficking mediated by selectin-carbohydrate interactions, J Biol Chem 270, 11025–8 (1995).
Lejoly-Boisseau H, Appriou M, Seigneur M, Pruvost A, Tribouley-Duret J, Tribouley J, Schistosoma mansoni: In vitro adhesion of parasite eggs to the vascular endothelium. Subsequent inhibition by a monoclonal antibody directed to a carbohydrate epitope, Exp Parasitol 91, 20–9 (1999).
Trottein F, Nutten S, Papin JP, Leportier C, Poulain-Godefroy O, Capron A, Capron M, Role of adhesion molecules of the selectincarbohydrate families in antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytoxicity to schistosome targets, J Immunol 159, 804–11 (1997).
Nutten S, Papin JP, Woerly G, Dunne DW, MacGregor J, Trottein F, Capron M, Selectin and Lewis(x) are required as co-receptors in antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity of human eosinophils to Schistosoma mansoni schistosomula, Eur J Immunol 29, 799–808 (1999).
Loukas A, Maizels RM, Helminth C-type lectins and hostparasite interactions, Parasitol Today 16, 333–9 (2000).
Oliveira G, Johnston DA, Mining the schistosome DNA sequence database, Trends Parasitol 17, 501–3 (2001).
Ashton PD, Curwen RS, Wilson RA, Linking proteome and genome: How to identify parasite proteins, Trends Parasitol 17, 198–202 (2001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hokke, C.H., Deelder, A.M. Schistosome glycoconjugates in host-parasite interplay. Glycoconj J 18, 573–587 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1020634602161
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1020634602161