Abstract
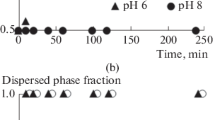
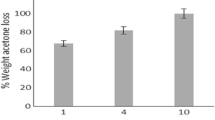
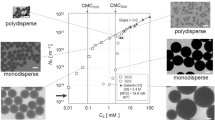
An attempt to prepare spherical particles was made using a W/O type emulsion as a reaction field. The effects of surfactant content, W/O ratio and stirring conditions for the preparation of emulsions, which determined the size of water drops in the emulsions, were investigated on the size and morphology of the obtained SnO2 particles. The size and morphology of the obtained particles were largely influenced by a water/surfactant molar ratio (R-value) for the preparation of the emulsions. Particles having relatively high sphericity were obtained at an R-value below 1500. In order to obtain mono-sized SnO2 particles with narrow distributions, R-value should be adjusted to the narrow range from 250 to 500. Spherical SnO2 particles showing narrow particle size distributions were obtained at W/O ratio of 1/1 and surfactant content of 11.2 × 10−2 mol/l or 22.4 × 10−2 mol/l. Furthermore, the particle size and morphology of SnO2 depended on the revolution rate of an emulsifier for emulsification. Mono-dispersed spherical particles having narrow size distributions formed at revolution rates of 3000 and 4000 rpm. At extremely low and high revolution rate of the emulsifier, particles showing high sphericity were not obtained, but agglomerates of un-spherical fine particles. The interfacial reaction time determined the internal structures of spherical particles. The reaction for short time yielded hollow spherical SnO2 particles, and the internal structure of the particles became denser with increasing reaction time.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. KOISHI, in“Biryu-shi sekkei” (Kogyo-chosakai, Tokyo, 1988) p. 23.
T. SUGIMOTO, Hyo-men 22 (1984) 177.
J. TAKAHASHI, J. Soc. Powder Tech. Jpn. 29 (1992) 286.
N. MIZUTANI, ibid. 26 (1989) 183.
S. HIRANO, Ceramics 22 (1987) 1052.
E. MATIJEVIC, J. Colloid Interface Sci. 58 (1976) 374.
B. J. INGEBRETHEN and E. MATIJEVIC, J. Aerosol Sci. 11 (1979) 271.
T. SUGIMOTO and E. MATIJEVIC, J. Colloid Interface Sci. 74 (1980) 227.
D. L. CATONE and E. MATIJEVIC, ibid. 48 (1974) 291.
M. D. SACKS, T. Y. TSENG and S. Y. LEE, Am. Ceram. Soc. Bull. 63 (1984) 301.
J. E. BLENDELL, H. K. BOWEN and R. L. COBLE, ibid. 63 (1984) 797.
B. FEGLEY JR, P. WHITE and H. K. BOWEN, ibid. 64 (1985) 1115.
T. OGIHARA, T. IKEMOTO, N. MIZUTANI and M. KATO, J. Mater. Sci. 21 (1986) 2771.
K. UCHYAMA, T. OGIHARA, T. IKEMOTO, N. MIZUTANI and M. KATO, ibid. 22 (1987) 4343.
T. OGIHARA and N. MIZUTANI, Inorganic Mater. 3 (1996) 194.
T. IMAI, Shikizai 71 (1998) 194.
Y. NAKAHARA, ibid. 59 (1986) 543.
S. KIDA, J. Soc. Powder Tech. Jpn. 24 (1987) 474.
M. JEFELICCI JR, M. R. DAVOLOS, F. J. D. SANTOS and S. J ANDRADE, J. Non-Cryst. Solids 247 (1999) 98.
J. F. MACALEER, P. T. MOSELEY, J. O. W. NORRIS and D. E. WILLIAMS, J. Chem. Soc., Faraday Trans. 1 83 (1987) 1323.
V. LANTTO and P. ROMPPAINEN, J. Electrochem. Soc. 135 (1988) 2550.
K. H. SONG and S. J. PARK, J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. in Electronics 4 (1993) 249.
N. L. WU, S. Y. WANG and I. A. RUSOKAVA, Science 285 (1999) 1375.
C. NAYRAL, T. O. ELY, A. MAISONNAT, B. CHAUDRET, P. FAU, L. LESCOUZERES and A. P. LAVGNE, Adv. Mater. 11 (1999) 61.
A. K. MUKHOPADHYAY, P. MITRA, A. P. CHATTERJEE and H. S. MATI, Ceram. Int. 26 (2000) 123.
E. R. LEITE, I. T. WEBER, E. LONGO and J. A. VARELA, Adv. Mater. 12 (2000) 965.
H. SHIOMI, H. KOBAYASHI, T. KIMURA and M. NAKAMURA, J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. in Electronics 7 (1996) 437.
H. SHIOMI, H. KOBAYASHI and M. NAKAMURA, J. Ceram. Soc. Jpn. 106 (1998) 213.
H. SHIOMI and H. FURUKAWA, J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. in Electronics 11 (2000) 31.
M. ABE, Shikizai 67 (1994) 263.
H. NAKAJIMA, ibid. 71 (1998) 526.
J. BOYD, C. PARKINSON and P. SHERMAN, J. Colloid Interface Sci. 41 (1972) 359.
T. KAWAI, Shikizai 71 (1998) 449.
A. KITAHARA and K. FURUSAWA, in “Saishin Koroidokagaku” (Koudan-sya, Tokyo, 1993) p. 41.
H. NAKAJIMA, Hyo-men 36 (1998) 39.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shiomi, H., Tanaka, C. Preparation of spherical SnO2 particles by W/O type emulsion method. Journal of Materials Science 37, 4683–4689 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1020625121771
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1020625121771