Abstract
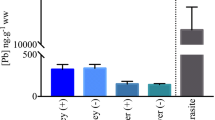
It recently became clear that acanthocephalans parasitizing mammals can bioconcentrate several heavy metals to conspicuously higher concentrations than the tissues of their definitive hosts. As cestodes are more abundant in terrestrial animals than acanthocephalans, and thus potentially more useful in attempts toward passive as well as active biomonitoring, a very common tapeworm and its synanthropic mammalian host were selected for the present study. The tapeworm Hymenolepis diminuta and experimentally infected male Wistar rats of the CD-M-strain were investigated with respect to their lead accumulation. The worms were allowed to grow up for five weeks post infection followed by a five weeks oral lead exposure of the rats. After the exposure period the rats were killed and the metal levels were determined in muscle, liver, intestine, testes and kidney of the rats as well as in the parasites. Lead concentrations were found to be 17 times higher in the cestodes than in kidney, whereas metal levels in all other host tissues were below the detection limit. Thus, this study reveals that lead accumulation also occurs in cestodes parasitizing mammals. Due to a lack of adequate sentinel species in terrestrial habitats the host-parasite-system rat-H. diminuta appears to be a useful and promising bioindication system especially in urban ecosystems.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baruš, V., Tenora, F., Kráčmar, S., Hedvábný, J., Prokeš, M. and Sitko, J. (2000). Heavy metals (Pb, Cd) concentrations in Ligula intestinalis (Cestoda) and the host Phalacocorax carbo (Aves). Helminthologia 37 , 178–79.
Greichus, A. and Greichus, Y.A. (1980). Identification and quantification of some elements in the hog roundworm, Ascaris lumbricoides suum , and certain tissues of its host. Int. J. Parasitol. 10 , 89–91.
Gunkel, G. (1994). Bioindikation in Aquatischen Ökosystemen . Jena, Stuttgart: Fischer Verlag.
Merian, E. (1991). Metals and their Compounds in the Environment Occurrence, Analysis and Biological Relevance . Weinheim, New York: Verlag Chemie.
Riggs, M.R., Lemly, A.D. and Esch, G.W. (1987). The growth, biomass and fecundity of Bothriocephalus acheilognathi in a North Carolina cooling reservoir. J. Parasitol. 73 , 893–900.
Scheef, G., Sures, B. and Taraschewski, H. (2000). Cadmium accumulation in Moniliformis moniliformis (Acanthocephala) from experimentally infected rats. Parasitol. Res. 86 , 688–91.
Schubert, R. (1991). Bioindikation in terrestrischen Ökosystemen . Jena: Fischer Verlag.
Smyth, J.D. (1994). Introduction to Animal Parasitology . Cambridge: Cambridge University press.
Sures, B. and Siddall, R. (1999). Pomphorhynchus laevis : the intestinal acanthocephalan as a lead sink for its fish host, chub (Leuciscus cephalus ). Exp. Parasitol. 93 , 66–72.
Sures, B. and Taraschewski, H. (1999). Endoparasiten einheimischer Fische als Bioindikatoren für Schwermetalle. In J. Oehlmann and B. Markert (eds) Ökotoxikologie—Ökosystemare Ansätze und Methoden , pp. 326–34. Jena: Ecomed Verlag.
Sures, B., Franken, M. and Taraschewski, H. (2000a). Element concentrations in the archiacanthocephalan Macracanthorhynchus hirudinaceus compared with those in the porcine definitive host from a slaughterhouse in La Paz, Bolivia. Int. J. Parasitol. 30 , 1071–6.
Sures, B., Jürges, G. and Taraschewski, H. (1998). Relative concentrations of heavy metals in the parasites Ascaris suum (Nematoda) and Fasciola hepatica (Digenea) and their respective porcine and bovine definitive hosts. Int. J. Parasitol. 28 , 1173–8.
Sures, B., Jürges, G. and Taraschewski, H. (2000b). Accumulation and distribution of lead in the archiacanthocephalan Moniliformis moniliformis from experimentally infected rats. Parasitology 121 , 427–33.
Sures, B., Siddall, R. and Taraschewski, H. (1999a). Parasites as accumulation indicators of heavy metal pollution. Parasitol. Today. 15 , 16–21.
Sures, B., Taraschewski, H. and Haug, C. (1995). Determination of trace metals (Cd, Pb) in fish by electrothermal absorption spectrometry after microwave digestion. Anal. Chim. Acta. 311 , 135–9.
Sures, B., Taraschewski, H. and Rokicki, J. (1997b). Lead and cadmium content of two cestodes Monobothrium wageneri and Bothriocephalus scorpii , and their fish hosts. Parasitol. Res. 83 , 618–23.
Sures, B., Taraschewski, H. and Rydlo, M. (1997a). Intestinal fish parasites as heavy metal bioindicators: a comparison between Acanthocephalus lucii (Palaeacanthocephala) and the zebra mussel, Dreissena polymorpha . Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 59 , 14–21.
Sures, B., Knopf, K., Würtz, J. and Hirt, J. (1999c). Richness and diversity of parasite communities in European eels Anguilla anguilla of the River Rhine, Germany, with special reference to helminth parasites. Parasitology 119 , 323–30.
Sures, B., Steiner, W., Rydlo, M. and Taraschewski, H. (1999b). Concentrations of 17 elements in the zebra mussel (Dreissena polymorpha ), in different tissues of perch (Perca fluviatilis ), and in perch intestinal parasites (Acanthocephalus lucii ) from the subalpin lake Mondsee (Austria). Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 18 , 2574–79.
Taraschewski, H. (2000). Host-parasite interactions in acanthocephala: A morphological approach. Adv. Parasitol. 46 , 1–179.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sures, B., Grube, K. & Taraschewski, H. Experimental Studies on the Lead Accumulation in the Cestode Hymenolepis diminuta and its Final Host, Rattus norvegicus . Ecotoxicology 11, 365–368 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1020561406624
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1020561406624