Abstract
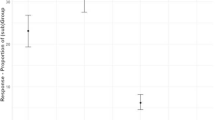
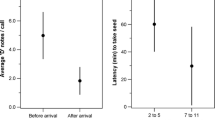
I studied antipredator behavior in two species of monkeys to elucidate the role of predation in shaping the social systems of arboreal primates. I compared the responses of monkeys to auditory and visual contact with predators to response elicited by sound playback experiments using the recorded calls of predators. Changes in vigilance and aggregation persisting up to 30 min after predator encounter occurred in both cases. Measures of vigilance shed light on individual perceptions of risk, while aggregation measures—intragroup spatial cohesion and polyspecific associations—permit direct inference about the protective benefits of grouping for the monkeys. They responded to real predator encounters and simulations in similar ways. Thus, sound playbacks of predator vocalizations are effective to simulate predator proximity. Contrary to predictions, predator encounters did not lead invariably to increased cohesion within groups or to increased time spent vigilant. Moreover, behavior in polyspecific associations was no different from that in single-species groups. Only red colobus encountering chimpanzees behaved as predicted by increasing vigilance and intragroup cohesion. The red colobus social system may have developed to protect against chimpanzee attack. In contrast, red-tailed monkey encounters with raptors and chimpanzees involved no change in time spent vigilant, coupled with decreases in intragroup cohesion. I conclude that predation is not a uniform selective pressure and patterns of social behavior within groups do not predict antipredator behavior.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Alberts, S. C. (1994). Vigilance in young baboons: Effects of habitat, age, sex and maternal rank on glance rate. Anim. Behav. 47: 749-755.
Anderson, C. M. (1986). Predation and primate evolution. Primates 27: 15-39.
Balldellou, M., and Henzi, S. P. (1992). Vigilance, predator detection and the presence of supernumerary males in vervet monkey troops. anim. Behav. 43: 451-461.
Boesch, C. (1991). The effects of leopard predation on grouping patterns in chimpanzees. Behav. 117: 220-242.
Boesch, C. (1994). Chimpanzees-red colobus monkeys: A predator-prey system. Anim. Behav. 47: 1135-1148.
Boesch, C., and Boesch, H. (1989). Hunting behavior of wild chimpanzees in the Taï National Park. Am. J. Phys. Anthropol. 78: 547-573.
Boinski, S., and Chapman, C. A. (1995). Predation on primates: Where are we and what's next? Evol. Anthropol. 4: 1-3.
Boshoff, A. F., Palmer, N. G., Avery, G., Davies, R. A. G., and Jarvis, M. J. F. (1991). Biogeographical and topographical variation in the prey of the black eagle in the Cape Province, South Africa. Ostrich 62: 59-72.
Brown, L. H. (1966). Observations on some Kenya eagles. Ibis 108: 531-572.
Brown, L. H. (1971). The relations of the crowned eagle Stephanoaetus coronatus and some of its prey animals. Ibis 113: 240-243.
Busse, C. (1980). Leopard and lion predation upon chacma baboons living in the Moremi Wildlife Reserve. Bostwana Notes Rec. 12: 15-20.
Busse, C. D. (1984). Spatial structure of chacma baboon groups. Int. J. Primatol. 5: 247-259.
Butynski, T. M. (1982a). Blue monkey (Cercopithecus mitis stuhlmanni) predation on galagos. Primates 23: 563-566.
Butynski, T. M. (1982b). Vertebrate predation by primates: A review of hunting patterns and prey. J. Hum. Evol. 11: 421-430.
Butynski, T. M. (1990). Comparative ecology of blue monkeys (Cercopithecus mitis) in high-and low-density subpopulations. Ecol. Monogr. 60: 1-26.
Caine, N. G. (1984). Visual scanning by tamarins. Folia Primatol. 43: 59-67.
Caine, N. G., and Marra, S. L. (1988). Vigilance and social organization in two species of primates. Anim. Behav. 36: 897-904.
Caro, T. M. (1987). Cheetah mothers' vigilance: Looking out for prey or for predators? Behav. Ecol. Sociobiol. 20: 351-361.
Chapman, C. A. (1986). Boa constrictor predation and group response in white-faced Cebus monkeys. Biotrop. 18: 171-172.
Chapman, C. A., and Chapman, L. J. (1996). Mixed-species primate groups in the Kibale Forest: Ecological constraints on association. Int. J. Primatol. 17: 31-50.
Cheney, D. L., and Seyfarth, R. M. (1990). How Monkeys See the World, University of Chicago Press, Chicago.
Cheney, D. L., and Wrangham, R. W. (1987). Predation. In Smuts, B. B., Cheney, D. L., Seyfarth, R., M. Wrangham, R. W., and Struhsaker, T. T. (eds.), Primate Societies, University of Chicago Press, Chicago, pp. 227-239
Cheney, D. L., Lee, P. C., and Seyfarth, R. M. (1981). Behavioral correlates of non-random mortality among free-ranging female vervet monkeys. Behav. Ecol. Sociobiol. 9: 153-161.
Clark, A. P., and Wrangham, R. W. (1993). Acoustic analysis of chimpanzee pant hoots: Do chimpanzees have an acoustically distinct food arrival pant hoot? Am. J. Primatol. 31: 99-109.
Collins, D. A. (1984). Spatial patterns in a troop of yellow baboons (Papio cynocephalus) in Tanzania. Anim. Behav. 32: 536-553.
Cords, M. (1990). Vigilance and mixed-species association of some East African forest monkeys. Behav. Ecol. Sociobiol. 26: 297-300.
Cords, M. (1995). Predator vigilance costs of allogrooming in wile blue monkeys. Behaviour 132: 559-569.
Cowlishaw, G. (1994). Vulnerability to predation in baboon populations. Behaviour 31: 293-304.
Creel, S. R. (1991). Reproductive Suppression and Cooperative Breeding in Dwarf Mongooses, Helogale parvula, Ph.D. thesis, Purdue University, Purdue, IN.
Crook, J. H., and Gartlan, J. S. (1966). Evolution of primate societies. Nature 210: 1200-1203.
Curio, E. (1976). The Ethology of Predation, Springer-Verlag, Berlin.
Daneels, A. B. C. (1979). Prey size and hunting methods of the crowned eagle. Ostrich 50: 120-121.
de Ruiter, J. R. (1986). The influence of group size on predator scanning and foraging behaviour of wedge capped capuchin monkeys (Cebus olivaceus). Behaviour 98: 240-258.
DeVore, I., and Hall, K. R. L. (1965). Baboon ecology. In DeVore, I. (ed.), Primate Behavior: Field Studies of Monkeys and Apes, Holt, Rhinehart and Winston, New York, pp. 20-52.
DeVore, I., and Washburn, S. L. (1963). Baboon ecology and human evolution. In Howell, F. C., and Bourliére, F. (eds.), African Ecology and Human Evolution, Aldine, Chicago, pp. 335-367.
Edmunds, M. (1974). Defence in Animals: A Survey of Anti-predator Defences, Longman, London.
Eisenberg, J. F., Muckenhirn, N. A., and Rudran, R. (1972). The relationship between ecology and social structure in primates. Science 176: 863-874.
Elder, W. H., and Elder, N. L. (1970). Social groupings and primate associations of the bushbuck (Tragelaphus scriptus). Mammalia 34: 356-362.
Elgar, M. A. (1989). Predator vigilance and group size in mammals and birds: A critical review of the empirical evidence. Biol. Rev. 64: 13-33.
Emmons, L. J. (1987). Comparative feeding ecology of felids in a Neotropical rainforest. Behav. Ecol. Sociobiol. 20: 271-283.
Fay, J. M., Carroll, R., Peterhans, J. C. K., and Harris, D. (1995). Leopard attack on and consumption of gorillas in the Central African Republic. J. Hum. Ecol. 29: 93-99.
Ferrari, S. F., and Lopes Ferrari, M. A. (1990). Predator avoidance behaviour in the buffy-headed marmoset, Callithrix flaviceps. Primates 31: 323-338.
Fitzgibbon, C. D. (1990). Mixed-species grouping in Thomson's gazelles: The antipredator benefits. Anim. Behav. 39: 1116-1126.
Fossey, D. (1983). Gorillas in the Mist. Houghton-Mifflin, Boston.
Freese, C. H., and Oppenheimer, J. R. (1981). The capuchin monkeys, genus Cebus. In Coimbra-Filho, A. F., and Mittermeier, R. H. (eds.), Ecology and Behavior of Neotropical Primates, Vol. 1, Academia Brasileira de Ciencias, Rio de Janeiro, pp. 331-390.
Galdikas, B. M. F., and Yeager, C. P. (1984). Crocodile predation on a crab-eating macaque in Borneo. Am. J. Primatol. 6: 49-51.
Galef, B. G., Mittermeier, R. A., and Bailey, R. C. (1976). Predation by the tayra (Eira barbara). J. Mammal. 57: 760-761.
Gautier-Hion, A. (1988). Polyspecific associations among forest guenons: Ecological behavioural, and evolutionary aspects. In Gautier-Hion, A., Bourliere, F., Gautier, M.-P., and Kingdon, J. (eds.) A Primate Radiation: Evolutionary Biology of the African Guenons, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp. 452-476.
Gautier-Hion, A., and Tutin, C. E. G. (1988). Simultaneous attack by adult males of a polyspecific troop of monkeys against a crowned hawk eagle. Folia Primatol. 51: 149-151.
Gautier-Hion, A., Quris, R., and Gautier, J.-P. (1983). Monospecific versus polyspecific life: A comparative study of foraging and antipredatory tactics in a community of Cercopithecus monkeys. Behav. Ecol. Sociobiol. 12: 325-335.
Gebo, D. L., Chapman, C. A., Chapman, L. J., and Lambert, J. (1994). Locomotor responses to predator threat in red colobus monkeys. Primates 35: 219-223.
Gerstner, G. E., and Fazio, V. A. (1995). Evidence of a universal perceptual unit in mammals. Ethology 101: 89-100.
Ghiglieri, M. P. (1988). East of the Mountains of the Moon, Free Press, New York.
Goldizen, A. W. (1987). Tamarins and marmosets: Communal care of offspring. In Smuts, B. B., Cheney, D. L., Seyfarth, R. M., Wrangham, R. W., and Struhsaker, T. T. (eds.), Primate Societies, University of Chicago Press, Chicago, pp. 34-43.
Goodman, S. M., O'Connor, S., and Langrand, O. (1993). A review of predation on lemurs: Implications for the evolution of social behavior in small, nocturnal primates. n. Kappeler, P. M., and Ganzhorn, J. U. (eds.), Lemur Social Systems and Their Ecological Basis, Plenum Press, New York, pp. 51-66.@ref alpha = Gouzoules, H., Fedigan, L. M., and Fedigan, L. (1975). Responses of a transplanted troop of Japanese macaques (Macaca fuscata) to bobcat (Lynx rufus) predation. Primates 16: 335–349.
Hauser, M. D., and Wrangham, R. W. (1990). Recognition of predator and competitor calls in nonhuman primates and birds: A preliminary report. Ethology 86: 116-130.
Hausfater, G. (1976). Predatory behavior of yellow baboons. Behaviour 56: 44-68.
Heymann, E. W. (1987). A field observation of predation on a moustached tamarin (Saguinus mystax) by an anaconda. Int. J. Primatol. 8: 193-195.
Hill, K. R., and Hurtado, A. M. (1995). Ache Life History: The Ecology and Demography of a Foraging People, Aldine-DeGruyter, New York.
Hiraiwa-Hasegawa, M., Byrne, R. W., Takasake, H., and Byrne, J. M. E. (1986). Aggression toward large carnivores by wild chimpanzees of Mahale Mountains National Park, Tanzania. Folia Primatol. 47: 8-13.
Hladik, C. M., Charles-Dominique, P., and Petter, J. J. (1980). Feeding strategies of five nocturnal prosimians in the dry forest of the west coast of Madagascar. In Charles-Dominique, P., Cooper, H. M., Hladik, A., Hladik, C. M., Pages, E., Pariente, G. F., Petter-Rousseaux, A., Schilling, A., and Petter, J. J. (eds.), Nocturnal Malagasy Primates: Ecology, Physiology and Behavior, Academic Press, New York, pp. 41-74.
Isbell, L. (1990). Sudden short-term increase in mortality of vervet monkeys (Cercopithecus aethiops) due to leopard predation in Amboseli National Park, Kenya. Am. J. Primatol. 21: 41-52.
Ivins, B. L., and Smith, A. T. (1983). Responses of pikas (Ochotona princeps, Lagomorpha) to naturally occurring terrestrial predators. Behav. Ecol. Sociobiol. 13: 277-285.
Izor, R. J. (1985). Sloths and other mammalian prey of the harpy eagle. In Montgomery, G. G. (ed.), The Evolution and Ecology of Armadillos, Sloths, and Vermilinguas, Smithsonian Institution Press, Washington, DC, pp. 85-123.
Julliot, C. (1994). Predation of a young spider monkey (Ateles paniscus) by a crested eagle (Morphnus guianensis). Folia Primatol. 63: 75-77.
Jones, W. T., and Bush, B. B. (1988). Movement and reproductive behavior of solitary male redtail guenons (Cercopithecus ascanius). Am. J. Primatol. 14: 203-222.
Kalina, J. (1988). Nest intruders, nest defence and foraging behaviour in the black-and-white casqued hornbill (Bycanistes subcylindricus). Ibis 131: 567-571.
Kruuk, H. (1972). The Spotted Hyene, University of Chicago Press, Chicago.
Landeau, L., and Terborgh, J. (1986). Oddity and the “confusion effect” in predation. Anim. Behav. 34: 1372-1388.
Leland, L., and Struhsaker, T. T. (1993). Teamwork tactics. Nat. Hist. 4: 43-48.
Lendrem, D. W. (1983). Sleeping and vigilance in birds. I. Field observations of the mallard (Anas platyrhynchos). Anim. Behav. 31: 532-538.
Lima, S. L. (1995). Back to the basics of anti-predatory vigilance: The group-size effect. Anim. Behav. 49: 11-20.
Macedonia, J. M. (1993). Adaptation and phylogenetic constraints in the antipredator behavior of ringtailed an ruffed lemurs. In Kappeler, P. M., and Ganzhorn, J. U. (eds.), Lemur Social Systems and Their Ecological Basis, Plenum Press, New York, pp. 67-84.
Macedonia, J. M., and Yount, P. L. (1991). Auditory assessment of avian predator threat in semicaptive ringtailed lemurs (Lemur catta) Primates 32: 169-182.
Maclean, G. L. (1985). Roberts' Birds of Southern Africa, New Holland, Amsterdam.
Maisels, F. G., Gautier, J.-P., Cruickshank, A., and Bosefe, J.-P. (1994). Attacks by crowned hawk eagles (Stephanoaetus coronatus) on monkeys in Zaire. Folia Primatol. 61: 157-159.
Marsh, C. E. (1979). Comparative aspects of social organization in the Tana River red colobus, Colobus badius rufomitratus. Z. Tierpsychol. 51: 337-362.
Metcalfe, N. B. (1984). The effect of habitat on the vigilance of shorebirds: Is visibility important? Anim. Behav. 32: 981-985.
Mitani, J. C., and Nishida, T. (1993). Contexts and social correlates of long-distance calling by male chimpanzees. Anim. Behav. 45: 735-746.
Marsh, C. W. (1979). Comparative aspects of social organization in the Tana River red colobus, Colobus badius rufomitratus. Z. Tierpsychol. 51: 337-362.
Metcalfe, N. B. (1984). The effect of habitat on the vigilance of shorebirds: Is visibility important? Anim. Behav. 32: 981-985.
Mitani, J. C., and Nishida, T. (1993). Contexts and social correlates of long-distance calling by male chimpanzees. Anim. Behav. 45: 735-746.
Mitchell, C., Boinski, S., van Schaik, C. P. (1991). Competitive regimes and female bonding in two species of squirrel monkey (Saimiri oerstedi and S. sciureus). Behav. Ecol. Sociobiol. 28: 55-60.
Morgan, M. J., and Godin, J. J. (1985). Antipredator benefits of schooling behaviour in a cyprinodontid fish, the banded killifish (Fundulus diaphanus). Z. Tierpsychol. 70: 236-246.
Nöe, R., and Bshary, R. (1997). The formation of red colobus-diana monkey associations under predation pressure from chimpanzees. Proc. Roy. Soc. London 264: 253-259.
Oates, J. F. (1974). The Ecology and Behaviour of the Black-and-White Colobus Monkey (Colobus guereza Rueppel) in East Africa, Ph.D. thesis, University of London, London.
Oates, J. F. (1977). The social life of black-and-white colobus monkey, Colobus guereza. Z. Tierpsychol. 45: 1-60.
O'Brien, T. G., and Robinson, J. G. (1991). Allomaternal care by female wedge-capped capuchin monkeys: Effects of age, rank and relatedness. Behaviour 119: 30-50.
Peetz, A. A., Norconk, M. A., and Kinzey, W. G. (1992). Predation by jaguar on howler monkeys (Alouatta seniculus) in Venezuela. Am. J. Primatol. 28: 223-228.
Pulliam, H. R. (1973). On the advantages of flocking. J. Theor. Biol. 38: 419-422.
Rajpurohit, L. S., and Sommer, V. (1991). Sex differences in mortality among langurs (Presbytis entellus) of Jodhpur, Rajasthan. Folia Primatol. 56: 17-27.
Rasa, O. A. E. (1983). Dwarf mongoose and hornbill mutualism in the Taru Desert, Kenya. Behav. Ecol. Sociobiol. 12: 181-190.
Rasa, O. A. E. (1986a). Coordinated vigilance in dwarf mongoose family groups: “The watchman's song” hypothesis and the costs of guarding. Ethology 71: 340-344.
Rasa, O. A. E. (1986b). Mongoose Watch: A Family Observed, Anchor Press, London.
Rijksen, H. D. (1978). A Field Study on Sumatran Orang-Utans (Pongo pygmaeus abelii Lesson 1827): Ecology, Behavior and Conservation, H. Veenman & Zonen B. V., Wageningen.
Robinson, J. G. (1988). Group size in wedge-capped capuchin monkeys, Cebus olivaceus, and the reproductive success of males and females. Behav. Ecol. Sociobiol. 23: 187-197.
Rodman, P. S. (1988). Resources and group sizes of forest primates. In Slobodchikoff, C. N. (ed.), The Ecology of Social Behavior, Academic Press, New York.
Rood, J. P. (1986). Ecology and social evolution in the mongooses. In Rubenstein, D. I., and Wrangham, R. W. (eds.), Ecological Aspects of Social Evolution: Birds and Mammals, Princeton University Press, Princeton, NJ, pp. 131-152.
Rood, J. P. (1990). Group size, survival, reproduction and routes to breeding in dwarf mongooses. Anim. Behav. 39: 566-572.
Rose, L. M., and Fedigan, L. M. (1995). Vigilance in white-faced capuchins, Cebus capucinus, in Costa Rica. Anim. Behav. 49: 63-70.
Ross, C. (1993). Predator mobbing by an all-male band of Hanuman langurs (Presbytis entellus). Primates 34: 105-107.
Schaller, G. B. (1965). The behavior of the mountain gorilla. In DeVore, I. (eds.), Primate Behavior: Field Studies of Monkeys and Apes, Holt, Rhinehart and Winston, New York.
Schaller, G. B. (1972). The Serengeti Lion: A Study of Predator-Prey Relations, University of Chicago Press, Chicago.
Schaller, G. B. (1983). Mammals and their biomass on a Brazilian Ranch. Arq. Zool. 31: 1-36.
Seidensticker, J. (1983). Predation by Panthera cats and measures of human influence in habitats of South Asian monkeys. Int. J. Primatol. 4: 323-326.
Simmons, R. (1991). Comparisons and functions of sky-dancing displays of Circus harriers: Untangling the marsh harrier complex. Ostrich 62: 45-51.
Skorupa, J. P. (1988). The Effects of Selective Timber Harvesting on Rainforest Primates in Kibale Forest Uganda, Ph.D. thesis, University of California, Davis.
Skorupa, J. P. (1989). Crowned eagles (Stephanoaetus coronatus) in rainforest: Observations on breeding chronology and diet at a nest in Uganda. Ibis 131: 294-298.
Skorupa, J. P., Kalina, T. M., Butynski, T. M., Tabor, G., and Kellogg, E. (1984). Notes on the breeding biology of Cassin's hawk eagle: Hieraaetus africanus. Ibis 127: 120-122.
Smuts, B. B. (1985). Sex and Friendship in Baboons, Aldine de Gruyter, New York.
Srivastava, A. (1991). Cultural transmission of snake-mobbing in free-ranging Hanuman langurs. Folia Primatol. 56: 117-120.
Stafford, B. J., and Ferreira, F. M. (1995). Predation attempts on Callitrichids in the Atlantic Coastal Rain Forest of Brazil. Folia Primatol 65: 229-233.
Stanford, C. B. (1989). Predation on capped langurs (Presbytis pileata) by cooperatively hunting jackals (Canis aureus). Am. J. Primatol. 19: 53-56.
Stanford, C. B. (1995). The influence of chimpanzee predation on group size and anti-predator behaviour in red colobus monkeys. Anim. Behav. 49: 577-587.
Stanford, C. B. Wallis, J., Matama, H., and Goodall, J. (1994). Patterns of predation of chimpanzees on red colobus monkeys in Gombe National Park, Tanzania 1982–1991. Am. J. Phys. Anthropol. 94: 213-228.
Steyn, P. (1982). Birds of Prey of Southern Africa, Tanager Books, Dover.
Struhsaker, T. T. (1967). Auditory communication among vervet monkeys (Cercopithecus aethiops). In Altmann, S. A. (ed.), Social Communication Among Primates, University of Chicago Press, Chicago, pp. 238-324.
Struhsaker, T. T. (1969). Correlates of ecology and social organization among African cercopithecines. Folia Primatol. 11: 80-118.
Struhsaker, T. T. (1975). The Red Colobus Monkey, University of Chicago Press, Chicago.
Struhsaker, T. T. (1977). Infanticide and social organization in the redtail monkey (Cercopithecus ascanius schmidtii) in the Kibale Forest, Uganda. Z. Tierpsychol. 45: 75-84.
Struhsaker, T. T. (1980). Comparison of the behaviour and ecology of red colobus and redtail monkeys in the Kibale Forest, Uganda. Afr. J. Ecol. 18: 33-51.
Struhsaker, T. T. (1981). Polyspecific associations among tropical rain-forest primates. Z. Tierpsychol. 57: 268-304.
Struhsaker, T. T. (1988). Male tenure, multi-male influxes, and reproductive success in redtail monkeys (Cercopithecus ascanius). In Gautier-Hion, A., Bourliere, F., Gautier, J.-P., and Kingdon, J. (eds.), A Primate Radiation: Evolutionary Biology of the African Guenons, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp. 340-363.
Struhsaker, T. T., and Leakey, M. (1990). Prey selectivity by crowned hawk-eagles on monkeys in the Kibale Forest, Uganda. Behav. Ecol. Sociobiol. 26: 435-443.
Struhsaker, T. T., and Leland, L. (1988). Group fission in redtail monkeys (Cercopithecus ascanius) in the Kibale Forest, Uganda. In Gautier-Hion, A., Bourliere, F., Gautier, J.-P., and Kingdon, J. (eds.), A Primate Radiation: Evolutionary Biology of the African Guenons, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp. 364-388.
Struhsaker, T. T., and Oates, J. F. (1975). Comparison of the behavior and ecology of red colobus and black-and-white colobus monkeys in Uganda: a summary. In Tuttle, R. H. (ed.), Socioecology and Psychology of Primates, Mouton, The Hague, pp. 103-123.
Struhsaker, T. T., and Pope, T. R. (1991). Mating system and reproductive success: A comparison of two African forest monkeys (Colobus badius and Cercopithecus ascanius) Behaviour 117: 182-205.
Sunquist, M. E. (1981). The social organization of tigers (Panthera tigris) in Royal Chitawan National Park, Nepal. Smithson. Contrib. Zool. 336: 1-92.
Tenaza, R. R., and Fuentes, A. (1995). Monandrous social organization of pigtailed langurs (Simians concolor) in the Pagai Islands, Indonesia. Int. J. Primatol. 16: 295-310.
Terborgh, J. (1983). Five New World Primates: A Study in Comparative Ecology, Princeton University Press, Princeton, NJ.
Terborgh, J., and Janson, C. H. (1986). The socioecology of primate groups. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 17: 111-135.
Treves, A. (1996). A preliminary analysis of the timing of infant exploration in relation to social structure in 17 primate species. Folia Primatol. 67: 152-156.
Treves, A. (1997a). Self-Protection in Primates, Ph.D. thesis, Harvard University, Cambridge, MA.
Treves, A. (1997b). Vigilance and use of micro-habitat in solitary rainforest mammals. Mammalia 61(4): 511-525.
Treves, A. (1998). The influence of group size and near neighbors on vigilance in two species of arboreal primates. Behaviour 135: 1-29.
Treves, A., and Chapman, C. A. (1996). Conspecific threat, predation avoidance and resource defense: Implications for grouping in langurs. Behav. Ecol. Sociobiol. 39: 43-53.
Uehara, S., Nishida, T., Hamai, M., Hasegawa, T., Hayaki, H., Huffman, M. A., Kawanaka, K., Kobayashi, S., Mitani, J. C., Takahata, Y., Takasaki, H., and Tsukahara, T. (1992). Characteristics of predation by the chimpanzees in the Mahale Mountains National Park, Tanzania. In Itoigawa, N. Sugiyama, Y., Sackett, G. P., and Thompson, R. K. R. (eds.), Topics in Primatology: Behavior, Ecology and Conservation, University of Tokyo Press, Tokyo, pp. 143-158.
Uganda News (1997). Crocodiles kill 32 on Victoria shores. Features African Network News Bulletin, Oct. 15.
Utami, S. S., and van Hooff, J. A. R. A. M. (1997). Meat-eating by adult female Sumatran orangutans (Pongo pygmaeus abelii). Am. J. Primatol. 43: 159-165.
van Schaik, C. P. (1983). Why are diurnal primates living in groups? Behaviour 87: 120-144.
van Schaik, C. P., and Mitrasetia, T. (1990). Changes in the behavior of wild long-tailed macaques (Macaca fascicularis) after encounters with a model python. Folia Primatol. 55: 104-108.
van Schaik, C. P., and van Hooff, J. A. R. A. M. (1983). On the ultimate causes of primate social systems. Behaviour 85: 91-117.
van Schaik, C. P., and van Noordwijk, M. A. (1989). The special role of male Cebus monkeys in predation avoidance and its effects on group composition. Behav. Ecol. Sociobiol. 34: 265-272.
van Schaik, C. P., van Noordwijk, M. A., Warsono, B., and Sutriono, E. (1983). Party size and early detection of predators in Sumatran forest primates. Primates 24: 211-221.
Wahome, J. M., Rowell, T. E., and Tsingalia, H. M. (1993). the natural history of de Brazza's monkeys in Kenya. Int. J. Primatol. 14: 445-466.
Waser, P. M. (1977). Sound localization by monkeys: A field experiment. Behav. Ecol. Sociobiol. 2: 427-431.
Waser, P. M., and Waser, M. S. (1977). Experimental studies of primate vocalization: Specializations for long-distance propagation. Z. Tierpsychol. 43: 239-263.
Watanabe, K. (1981). Variations in group composition and population density of two sympatric Mentawaian leaf-monkeys. Primates 22: 145-160.
Wrangham, R., and Riss, E. V. Z. B. (1990). Rates of predation on mammals by Gombe chimpanzees, 1972–1975. Primates 31: 157-170.
Wrangham, R., Conklin, N. L., Chapman, C. A., and Hunt, K. D. (1991). The significance of fibrous foods for Kibale Forest chimpanzees. Phil. Trans. Roy. Soc. Lond. B 334: 171-178.
Yaber, M. C., and Herrera, E. A. (1994). Vigilance, group size, and social status in capybaras. Anim. Behav. 48: 1301-1307.
Zuberbühler, K., Noë, R., and Seyfarth, R. M. (1997). Diana monkey long-distance calls: Messages for conspecifics and predators. Anim. Behav. 53: 589-604.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Treves, A. Has Predation Shaped the Social Systems of Arboreal Primates?. International Journal of Primatology 20, 35–67 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1020532216737
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1020532216737