Abstract
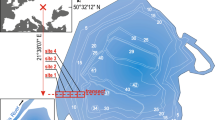
Traunsee, an oligotrophic Alpine lake, has suffered from inputsof industrial tailings (soda- and salt-mining industries) forseveral decades. The effects of the industrial sludges on thespatial distribution of the littoral and profundal invertebratefauna was investigated along three transects at five dates. Inthe littoral zone, no negative impacts were found. A distinctgradient in faunal composition and diversity was, however,observed along a profundal transect relative to the distance fromthe waste emission. Near the industrial input, the enhanced pH,the substrate instability, and the poor sediment quality forsubstrate- and deposit-feeders were the main factors that loweror prohibit colonization of the industrial sludges. Along atransitional zone between the waste emission and the deepestbasin, recolonization was delayed, but did occur as soon aslayers of a few mm natural sediment seal the sludge. Mobile,epibenthic organisms are the first to settle these areas, whereasrecolonization by tube-building oligochaetes and chironomidsrequires thicker sealings of the industrial sludges. Differencesin the abundance of benthic invertebrates at different profundalsites were not only related to the waste emission, but also tothe influence of the main tributary, the River Traun. Theenhanced availability of allochthonous organic matter wasprobably responsible for high densities of tubificids near theinlet in the South of Traunsee. Moreover, a higher proportion oftolerant oligochaete and ostracod species in the lower profundaloutside the influence of the industrial tailings was interpretedas reflecting the increased trophy of Traunsee in the 1970s,which forced sensitive species to shift to the upper profundalwhen the oxygen climate deteriorated.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bauernfeind, E.: 1990, 'Eintagsfliegen-Nachweise aus Oberösterreich (Insecta: Ephemeroptera); die Sammlung Adlmannseder am O.Ö. Landesmuseum Linz', Linz. Biol. Beitr. 22, 349–356.
Bauernfeind, E.: 1994, 'Bestimmungsschlüssel für die österreichischen Eintagsfliegen (Insecta: Ephemeroptera), part 1', Wasser und Abwasser Suppl. 4/94, 92 pp.
Bauernfeind, E.: 1995, 'Bestimmungsschlüssel für die österreichischen Eintagsfliegen (Insecta: Ephemeroptera), part 2', Wasser und Abwasser Suppl. 4/94, 96 pp.
Bayly, O. A. E.: 1972, 'Salinity tolerance and osmotic behaviour of animals in athalassic saline and marine hypersaline waters', Ann. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 3, 233–268.
Brehm, V. and Zederbauer, E.: 1906, 'Beobachtungen über das Plankton in den Seen der Ostalpen', Arch. Hydrobiol. 1, 469.
Brinkhurst, R. O. and Jamieson, B. G. M.: 1971, Aquatic Oligochaeta of the World, Oliver & Boyd, Edinburgh, 860 pp.
Brinkhurst, R. O., Chua, K. E. and Kaushik, N. K.: 1972, 'Interspecific interactions and selective feeding by tubificid oligochaetes', Limnol. Oceanogr. 17, 122–133.
Burd, B. J.: 2002, 'Evaluation of mine tailings effects on a benthic marine infaunal community over 29 years', Mar. Envir. Res. 53, 481–519.
Claus, C.: 1877, 'Zur Kenntnis des Baues und der Organisation der Polyphemiden', Denkschrift der Akademie der Wissenschaften 37.
Cori, C. J.: 1898, 'Beitrag zur Fauna des Traunsees und seiner Umgebung', in F. Krackowitzer (ed.), Geschichte der Stadt Gmunden, Gmunden.
Cranston, P. S.: 1982, 'A key to the larvae of the British Orthocladiinae (Chironomidae)', Scient. Publ. Freshw. Biol. Ass. 45, 152.
Danecker, E.: 1970, 'Gutachten über die durch die Einleitung von gelösten und festen Abfallstoffen der Ebensee Solvay-Werke hervorgerufenen chemischen und biologischen Zustände im Traunsee und deren Auswirkung auf die Fischerei', Unpublished Report, 13 pp.
Danielopol, D. L. and Niederreiter, R.: 1990, 'New sampling equipment and extraction methods for meiobenthic organisms', Bull. Inst. Géol. Bassin d'Aquitaine 47, 277–286.
Danielopol, D. L., Geiger, W., Tölderer-Farmer, M., Orellana, C. P. and Terrat, M. N.: 1985, 'The Ostracoda of Mondsee: Spatial and Temporal Changes during the Last Fifty Years', in D. Danielopol, R. Schmidt and E. Schultze (eds), Contributions to the Paleolimnology of the Trumer Lakes (Salzburg), and the Lakes Mondsee, Attersee and Traunsee (Upper Austria), Limnol. Inst. Austrian Acad. Sci., Mondsee, pp. 99–121.
Danielopol, D. L., Geiger, W., Tölderer-Farmer, M., Orellana, C. P. and Terrat, M. N.: 1988, 'In Search of Cypris and Cythere - A Report of the Evolutionary Ecological Project on Limnic Ostracoda from the Mondsee (Austria)', in T. Hanai, N. Ikeya and K. Ishizaki (eds), Evolutionary Biology of Ostracoda, its Fundamental Applications, Proc. 9th Int. Symp. on Ostracoda, Kodahsa, Tokyo and Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp. 485–499.
Danielopol, D. L., Handl, M. and Yin, Y.: 1993, 'Benthic Ostracods in the Pre-alpine Deep Lake Mondsee: Notes on the Origin and Distribution', in K. G. McKenzie and P. J. Jones (eds), Ostracoda in the Earth and Life Sciences, Proc. 11th Int. Symp. on Ostracoda, Warnambool, Victoria, A. A. Balkema, Rotterdam, pp. 465–480.
Dolezal, E.: 1980, 'Ñber die Oligochaetenfauna des Attersees und ihre Rolle als Eutrophierungsanzeiger', Ph.D. Thesis, University of Vienna, 143 pp.
Einsle, D.: 1993, Copepoda, Calanoida und Cyclopoida, Süßwasserfauna von Mitteleuropa, Vol. 8/4–1, Gustav Fischer Verlag, Stuttgart, 209 pp.
Elliott, J. M.: 1977, 'Some Methods for the Statistical Analysis of Samples of Benthic Invertebrates', Scient. Publ. Freshw. Biol. Ass. 25, 156.
Fittkau, E. J. and Colling, M.: 1992, 'Biologische Trophieindikation im Litoral von Seen', Informationsber. Bayer. Landesamt f. Wasserwirtschaft 7/92, 1–184.
Flössner, D.: 1972, 'Krebstiere, Crustacea. Kiemen-und Blattfüßer, Branchiopoda. Fischläuse, Branchiura', in Die Tiere Deutschlands und der angrenzenden Meeresteile, nach ihren Merkmalen und nach ihrer Lebensweise, 60. Teil, VEB Gustav Fischer Verlag, Jena, 501 pp.
Franz, H.: 1954, Die Nordost-Alpen im Spiegel ihrer Landtierwelt. Eine Gebietsmonographie, Band I, Universitätsverlag Wagner, Innsbruck, 664 pp.
Franz, H.: 1970, Die Nordost-Alpen im Spiegel ihrer Landtierwelt. Eine Gebietsmonographie, Band III, Universitätsverlag Wagner, Innsbruck, 501 pp.
Frenzel, P.: 1979, 'Zönosen des litoralen Mikrobenthos im Bodensee', Schweiz. Z. Hydrol. 41, 383–394.
Frenzel, P.: 1982, 'Die Coenosen der litoralen Cladoceren des Bodensees', Arch. Hydrobiol./Suppl. 62, 291–331.
Frenzel, P.: 1983a, 'Die litoralen Tubificidae des Bodensees mit besonderer Berücksichtigung von Potamothrix moldaviensis', Arch. Hydrobiol. 97, 262–280.
Frenzel, P., 1983b, 'Untersuchungen zur Ökologie der Naididae des Bodensees. Die Coenosen des eutrophierten Sees. Eutrophierung und Faunenwechsel', Arch. Hydrobiol. Suppl. 65, 106–133.
Gerstmeier, R.: 1989, 'Phenology and bathymetric distribution of the profundal chironomid fauna in Starnberger See (F.R. Germany)', Hydrobiologia 184, 29–42.
Glöer, P. and Meier-Brook, C.: 1998, Süßwassermollusken, Deutscher Jugendbund für Naturbeobachtung, Hamburg, 136 pp.
Graf, H.: 1938, 'Beitrag zur Kenntnis der Muschelkrebse der Ostalpenseen', Arch. Hydrobiol. 33, 401–502.
Griebler, C., Sonntag, B., Mindl, B., Posch, T., Klammer, S. and Psenner, R.: 2002, 'Assessment of the ecological integrity of Traunsee (Austria) via analysis of sediments and benthic microbial communities', Water, Air, and Soil Pollut.: Focus 2(4), 33–62.
Gusenleitner, J.: 1953, 'Beitrag zur Kenntnis der Litoralfauna des Traunsees und ihrer Ökologie', Ph.D. Thesis, University of Graz, 123 pp.
Haempel, O.: 1926, 'Zur Kenntnis einiger Alpenseen. IV. Der Attersee', Int. Rev. ges. Hydrobiol. 15, 273–322.
Hamann, H.: 1954, Beiträge zur Biologie und Ermittlung zu den Fischereiverhältnissen des Traunsees (1952–1953), Biol. Stat. Fischereiwesen, Linz, 246 pp.
Hydrographischer Dienst: 1989–2001, Hydrographisches Jahrbuch von Österreich 1986–1998, Federal Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry, Environment and Water Management, Hydrographisches Zentralbüro, 94.-106. Bd.
Imhof, O.: 1885, 'Faunistische Studien in 18 kleineren und größeren österreichischen Süßwasserbecken', Sitzungsber. österr. Akad. Wiss. Math.-Nat.wiss. Kl. Abt. I, 91, 203 pp.
Jagsch, A. and Schwarz, K.: 1997, 'Gutachten über den Traunsee im Rahmen der wasserrechtlichen Bewilligungsbescheide für die salzverarbeitende Industrie in Ebensee', Amt der O.Ö. Landesregierung, Linz, 1–19.
Jagsch, A., Gassner, H. and Dokulil, M. T.: 2002, 'Long-term changes in environmental variables of Traunsee, an oligotrophic Austrian lake impacted by the salt industry, and two reference sites, Hallstättersee and Attersee', Water, Air, and Soil Pollut.: Focus 2(4), 9–20.
Janecek, B. F. R.: 1998, 'Diptera: Chironomidae (Zuckmücken). Bestimmung von 4. Larvenstadien mitteleuropäischer Gattungen und österreichischer Arten', University of Agriculture, Institute of Hydrobiology, Vienna, 117 pp.
Janetzky, W., Enderle, R. and Noodt, W.: 1996, Crustacea: Gelyelloida und Harpacticoida.Süßwasserfauna von Mitteleuropa, Vol. 8/4–2, Gustav Fischer Verlag, Stuttgart, 228 pp.
Kajak, Z. and Kajak, A.: 1975, 'Some trophic relations in the benthos of shallow parts of Marion Lake', Ekol. Pol. 23, 573–586.
Keissler, K.: 1907, 'Ñber das Phytoplankton des Traunsees', Österr. bot. Z. 4, 146 pp.
Kolodziejczyk, A.: 1976, 'Ecological characteristics of the eulittoral of four water bodies in Warsaw', Ekol. Pol. 24, 431–446.
Lang, C. and Lods-Crozet, B.: 1997, 'Oligochaetes versus chironomids as indicators of trophic state in two Swiss lakes recovering from eutrophication', Arch. Hydrobiol. 139, 187–195.
Lang, C. and Reymond, O.: 1992, 'Reversal of eutrophication in Lake Geneva: Evidence from the oligochaete communities', Freshw. Biol. 28, 145–148.
Lang, C. and Reymond, O.: 1993, 'Recovery of Lake Neuchatel (Switzerland) from eutrophocation indicated by the oligochaete communities', Arch. Hydrobiol. 128, 65–71.
Lang, C.: 1984, 'Eutrophication of Lakes Léman and Neuchâtel (Switzerland) indicated by oligochaete communities', Hydrobiologia 115, 131–138.
Lang, C.: 1990, 'Quantitative relationships between oligochaete communities and phosphorus concentrations in lakes', Freshw. Biol. 24, 327–334.
Lang, C.: 1991, 'Decreasing phosphorus concentrations and unchanged oligochaete communities in Lake Geneva: How to monitor recovery?', Arch. Hydrobiol. 122, 305–312.
Lang, C.: 1998, 'Contrasting responses of oligochaetes (Annelida) and chironomids (Diptera) to the abatement of eutrophication in Lake Neuchatel', Aquat. Sci. 61, 206–214.
Lindegaard, C.: 1992, 'Zoobenthos ecology of Thingvallavatn: Vertical distribution, abundance, population dynamics and production', Oikos 64, 257–304.
Löffler, H.: 1972, 'The distribution of subfossil ostracods and diatoms in pre-alpine lakes', Verh. Int. Verein. Limnol. 18, 1039–1050.
Löffler, H.: 1983, 'Changes of the benthic fauna of the profundal zone of Traunsee (Austria) due to salt mining activities', Hydrobiologia 103, 135–139.
McLachlan, A. J. and Cantrell, M. A.: 1976, 'Sediment development and its influence on the distribution and tube structure of Chironomus plumosus L. (Chironomidae, Diptera) in a new impoundment', Freshw. Biol. 6, 437–443.
McLachlan, A. J.: 1969, 'Substrate preferences and invasion behaviour exhibited by larvae of Nilodorum brevibucca Freeman (Chironomidae) under experimental conditions', Hydrobiologia 33, 237–249.
McLachlan, A. J.: 1976, 'Factors restricting the range of Glyptotendipes paripes Edwards (Diptera: Chironomidae) in a bog lake', J. Animal Ecol. 45, 105–113.
Meisch, C.: 2000, Crustacea: Ostracoda, Süßwasserfauna von Mitteleuropa Bd. 8/3, Spektrum Akademischer Verlag, Heidelberg, Berlin, 522 pp.
Meisriemler, P., Hofbauer, M. and Miesbauer, H.: 1990, Nachweis von Schwermetallemissionen mittels der Wandermuschel Dreissena polymorpha PALLAS in der Traun. Österr. Fischerei 43, 219–229.
Moller Pillot, H. K. M.: 1984a, 'De larven der nederlandse Chironomidae (Diptera) (Inleiding, Tanypodinae and Chironominae)', Nederlandse Faunistische Mededelingen 1A, 277 pp.
Moller Pillot, H. K. M.: 1984b, 'De larven der nederlandse Chironomidae (Diptera) (Orthocladiinae sensu lato)', Nederlandse Faunistische Mededelingen 1B, 175 pp.
Müller J. and Schneider, J.: 1984, 'Die Industrieschlammablagerungen in der Bucht von Ebensee und im Profundal des Traunsees (Oberösterreich)', Limnologische Untersuchung Traunse-Traun, Report No. 12a, Amt der O.Ö. Landesregierung, Linz, 100 pp.
Müller, J., Wallner, J. and Kroemer, E.: 2002, 'Industrial Tailings in Traunsee (Austria) revisited - The status of 1999', Water, Air, and Soil Pollut.: 2(4), 21–32.
Neresheimer, E. and Ruttner, F.: 1926, 'Gutachten über die Einleitung der Abwässer der Ammoniaksoda-Fabrik (Solvay-Werke) in Ebensee in den Traunsee', Technical Report, 18 pp.
Pechlaner, R. and Sossau, C.: 1982, 'Die Ergebnisse der fünfjährigen Studie - Limnologische Untersuchung Traunsee, Traun', Limnologische Untersuchung Traunsee-Traun, Report No. 13, Amt der O.Ö. Landesregierung, Linz, 234 pp.
Pechlaner, R.: 1986, 'Einleitung zusätzlicher Feststoffe in den Traunsee', Technical Report, Österreichische Salinen AG, Ebensee, 26 pp.
Pesta, O.: 1923/24, 'Hydrobiologische Studien über Ostalpenseen', Arch. Hydrobiol. Suppl. 3, 385–595.
Probst, L.: 1987, 'Sublittoral and profundal Oligochaeta fauna of the Lake Constance (Bodensee-Obersee)', Hydrobiologia 155, 277–282.
Sachs, L.: 1992, Angewandte Statistik, Anwendung Statistischer Methoden, 7th ed., Springer-Verlag, Berlin, Heidelberg, New York, 848 pp.
Sæther, O. E.: 1979, 'Chironomid communities as water quality indicators', Holarc. Ecol. 2, 65–74.
Särkkä, J.: 1978, 'New records of profundal Oligochaeta from Finnish lakes, with ecological observations', Ann. Zool. Fenn. 15, 235–240.
Särkkä, J.: 1983, 'A quantitative ecological investigation of the littoral zoobenthos of an oligotrophic Finnish lake', Ann. Zool. Fenn. 20, 157–178.
Särkkä, J.: 1996, 'Meiofauna ratios as environmental indicators in the profundal depths of large lakes', Envir. Mon. Ass. 42, 229–240.
Saxl, R. and Zapf, F.: 1991, 'Studie über die limnologischen Auswirkungen einer Einleitung neutralisierter Schlämme in den Traunseee', Technical Report, Österreichische Salinen AG, Ebensee, 50 pp.
Schmid, P. E.: 1993, 'A key to the larval Chironomidae and their instars from Austrian Danube region streams and rivers. Part 1: Diamesinae, Prodiamesinae and Orthocladiinae', Wasser und Abwasser Suppl. 3/93, 514 pp.
Schmidt, R.: 1989, 'Diatomeenstratigraphische Untersuchungen zur Trophieänderung und Industrieschlammakkumulation im Traunsee/Österreich', Aquat. Sci. 51, 317–337.
Schneider, J., Müller, J. and Sturm, M.: 1986, 'Geology and sedimentary history of Traunsee (Salzkammergut, Austria)', Hydrobiologia 143, 227–232.
Schwalb, A., Burns, S. J., Griffiths, H. I. and Wessels, M.: 2000, 'Ostracode assemblages and stable isotopes from Lake Constrance: a 16 kyr record of faunal succession and climate for the central Alps', DEUQUA 2000, Eiszeitalter und Alltag, Kurzfassungen der Vorträge und Posters: 72.
Smith, E. P. and Van Belle, G.: 1984, 'Nonparametric estimation of species richness', Biometrics 40, 119–129.
Sossau, C.: 1982, 'Schichtungs-und Strömungsverhältnisse, Chlorid und Sauerstoff im Traunsee', Limnologische Untersuchung Traunsee-Traun, Report No. 8, Amt der oberösterreichischen Landesregierung, Linz, 90 pp.
Sperber, C.: 1948, 'A taxonomical study of the Naididae', Zool. Bidr. Upps. 28, 1–296.
Wagner, B.: 1975, 'Populationsdynamik der Oligochaeten im Vorderen Finstertaler See (2237 m, Kühtai, Tirol)', Ph.D. Thesis, University of Innsbruck, 102 pp.
Wanzenböck, J., Gassner, H., Lahnsteiner, B., Hassan, Y., Hauseder, G., Doblander, C. and Köck, G.: 2002, 'Ecological integrity assessment of lakes using fish communities: An example from Traunsee exposed to intensive fishing and to effluents from the soda industry', Water, Air, and Soil Pollut.: Focus 2(4), 227–248.
Waringer, J. and Graf, W.: 1997, Atlas der österreichischen Köcherfliegenlarven unter Einschluß der angrenzenden Gebiete, Facultas-Universitätsverlag, Wien, 286 pp.
Wiederholm, T.: 1983, 'Chironomidae of the Holarctic region, keys and diagnoses. Part 1. Larvae', Ent. Scand. Suppl. 19, 457 pp.
Wiederholm, T.: 1980, 'Use of benthos in lake monitoring', J. Wat. Pollut. Cont. Fed. 52, 537–547.
Wiederholm, T.: 1984, 'Responses of Aquatic Insects to Environmental Pollution', in V.H. Resh and D. M. Rosenberg (eds), The Ecology of Aquatic Insects, Praeger, New York, pp. 508–557.
Wolfram, G., Salbrechter, M., Weigand, E., Wychera, U. and Humpesch, U. H.: 2002, 'Variations in the epiphytic invertebrate community structure on Potamogeton Perfoliatus L. in Traunsee (Austria): Patchiness versus impacts by industrial tailings', Water, Air and Soil Pollut.: Focus 2(4), 117–136. (this issue).
Zahner, R.: 1964, 'Beziehungen zwischen dem Auftreten von Tubificiden und der Zufuhr organischer Stoffe im Bodensee', Int. Rev. Hydrobiol. 49, 417–454.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wolfram, G., Kowarc, V.A., Humpesch, U.H. et al. Distribution Pattern of Benthic Invertebrate Communities in Traunsee (Austria) in Relation to Industrial Tailings and Trophy. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution: Focus 2, 63–91 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1020397101171
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1020397101171